-
Compound derived from vegetables offers shield from lethal radiation doses

Researchers say a compound derived from cruciferous vegetable such as cabbage, cauliflower, and broccoli protected rats and mice from lethal doses of radiation. The compound, known as DIM could protect normal tissues in patients receiving radiation therapy for cancer, but could also protect individuals from the lethal consequences of a nuclear disaster.
-
-
Arktis closes $2 million financing round
Zürich, Switzerland-based Arktis Radiation Detectors Ltd., developer of a proprietary fast neutron detection technology which offers an innovative detection method for discovering well-shielded nuclear materials, successfully closed a round of financing worth $2 million.
-
-
$5 million NSF grant focuses on nuclear threat inspection
Penn State University has received a 5-year grant from the National Science Foundation (NSF) and DHS for nuclear threat inspection, as part of a team led by the Massachusetts Institute of Technology and including Georgia Tech. The grant will help develop new systems and sensors that will help detect nuclear weapons, special nuclear materials, radiation dispersal devices, and related threats.
-
-
Preventing nuclear terrorism

Nuclear terrorism remains a real and urgent threat. Despite an array of mechanisms established to combat this threat, several serious problems persist, requiring relentless attention and actions by the United States, Russia, and other responsible nations. These problems include continuing nuclear security vulnerabilities in a number of countries and the continued incidents of illicit trafficking in nuclear materials, radioactive sources, and the various components.
-
-
Iran indicates willingness to rethink nuclear program in exchange for sanction relief
As part of a series of steps designed to present post-election Iran as more pragmatic, President Hassan Rouhani and his advisers indicated they would be willing to consider curbs on Iran’s nuclear program in exchange for relief from the crippling economic sanctions imposed on Iran. Some Western experts say that all these steps are more than mere cosmetic changes, while skeptics note that Obama has reached out to Iran before, with no results. Veterans of past nuclear negotiations with Iran also noted that it is likely that Rouhani’s team may not yet fully understand the kinds of concessions that the Islamic republic would be required to make to have the most painful economic sanctions lifted.
-
-
Fukushima radioactive plume to reach U.S. next year
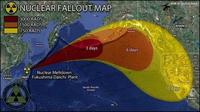
The radioactive ocean plume from the 2011 Fukushima nuclear plant disaster will reach the shores of the United States within three years from the date of the incident, but is likely to be harmless, according to a new study. While atmospheric radiation was detected on the U.S. west coast within days of the incident, the radioactive particles in the ocean plume take considerably longer to travel the same distance.
-
-
3D Earth model accurately pinpoints source of earthquakes, explosions
During the cold war, U.S. and international monitoring agencies could spot nuclear tests and focused on measuring their sizes. Today, they are looking around the globe to pinpoint much smaller explosives tests. Researchers are working on developing a 3-D model of the Earth’s mantle and crust called SALSA3D. The purpose of this model is to assist the U.S. Air Force and the international Comprehensive Nuclear-Test-Ban Treaty Organization (CTBTO) in Vienna, Austria, more accurately locate all types of explosions.
-
-
Detecting radioactive material smuggled in containers

Nearly 90 percent of imported and exported goods travel the globe in shipping containers. Roughly 500 million containers travel the sea each year. A Sandia National Laboratories team completed acceptance testing on an enormous mobile scanner — the Mobile Radiation Detection and Identification System (MRDIS) — which makes smuggling radiological materials in containers more difficult.
-
-
U.S. nuclear facilities vulnerable to terrorist attack: study

Some U.S. nuclear facilities are inadequately protected against theft of weapons-grade materials and sabotage by terrorists. Terrorist attacks on vulnerable nuclear facilities could trigger a meltdown or lead to a diversion of bomb-grade uranium. The danger is far from hypothetical since the 9/11 hijackers are known to have considered flying a passenger jet into a U.S. nuclear reactor before they settled on the World Trade Center as their main terror target.
-
-
Nuclear academics, professionals meet for 6th annual ATR NSUF Users Week
The sixth annual Advanced Test Reactor National Scientific User Facility (ATR NSUF) Users Week was held 10-14 June at University Place, the satellite campus for Idaho State University and University of Idaho in Idaho Falls. This nuclear research-themed week was the user facility’s opportunity to update the user community on nuclear energy issues and tools, conduct a research forum where users can come and present their research, run specialized workshops, and build collaboration among academic, industry and government institutions.
-
-
Top-secret super-secure vault declassified

Down a remote canyon near Los Alamos National Laboratory lies a facility known as the Tunnel Vault. Once one of the most secret and secure locations in the United States, it is the original post-Second World War nuclear stockpile storage area. Built between 1948 and 1949, the facility has a formidable security perimeter, a hardened guard tower — complete with gun ports and bulletproof glass — and a series of gates and doors that lead to a 230-foot long concrete tunnel that goes straight into the canyon wall.
-
-
Specialized gas detection helps prevent nuclear weapons proliferation
Researchers aim to design a system capable of sensing, from among the loud signals of a lot of gases, the weak signals from specific gases which are signs of nuclear weapons proliferation. The researchers believe their gas correlation technique will prove ideal for a simple, inexpensive sensor to monitor those few illusive gases. This could change how the nation thinks about monitoring the spread of nuclear weapons. Instead of single-point measurements taken with expensive sensors deployed after someone suspects a problem, 24/7 continuous monitoring could find leaks early.
-
-
Highly portable X-ray imaging system developed
Los Alamos National Laboratory and Tribogenics have developed the MiniMAX (Miniature, Mobile, Agile, X-ray) camera to provide real-time inspection of sealed containers and facilities.MiniMAX is an alternative to the large, expensive, and fixed facilities presently required for security inspections using X-ray imaging. The complete MiniMAX portable radiography system weighs less than five pounds.
-
-
Chechen Islamic terrorists threaten February 2014 Winter Olympics in Sochi, Russia

Doku Umarov, a leading Chechen Islamic rebel, on Wednesday issued a call to Islamist militants throughout the North Caucasus to begin and plan for attacks to disrupt the February 2014 Winter Olympics which will be held in the Black Sea resort of Sochi. Security experts say that securing the games would be a daunting task.
-
-
U.K. nuclear disaster exercise reveals worrisome lapses in emergency response
Up to six times a year, U.K. nuclear weapons are transported in heavily guarded convoys between production facilities in Aldermaston and Burghfield in Berkshire, where the nuclear bombs are manufactured, and the Royal Naval Armaments Depot at Coulport on Loch Long in Argyll. The trips are required because scientists must regularly examine the 200 Trident missile warheads in order to make sure they are operationally reliable and properly maintained. Every three years, the U.K. Ministry of Defense (MoD) conducts a drill aiming to test how various agencies respond to an accident involving the convoy carrying the nuclear warheads. An internal report on the last drill notes many problems in the response to the simulated accident, including five-hour wait for weapons experts, confusion over radiation monitoring, and ambulance crews refusing to take contamination victims to hospitals.
-
- All
- Regional
- Water
- Biometrics
- Borders/Immig
- Business
- Cybersecurity
- Detection
- Disasters
- Government
- Infrastructure
- International
- Public health
- Public Safety
- Communication interoperabillity
- Emergency services
- Emergency medical services
- Fire
- First response
- IEDs
- Law Enforcement
- Law Enforcement Technology
- Military technology
- Nonlethal weapons
- Nuclear weapons
- Personal protection equipment
- Police
- Notification /alert systems
- Situational awareness
- Weapons systems
- Sci-Tech
- Sector Reports
- Surveillance
- Transportation
Advertising & Marketing: advertise@newswirepubs.com
Editorial: editor@newswirepubs.com
General: info@newswirepubs.com
2010-2011 © News Wire Publications, LLC News Wire Publications, LLC
220 Old Country Road | Suite 200 | Mineola | New York | 11501
Permissions and Policies
Editorial: editor@newswirepubs.com
General: info@newswirepubs.com
2010-2011 © News Wire Publications, LLC News Wire Publications, LLC
220 Old Country Road | Suite 200 | Mineola | New York | 11501
Permissions and Policies
