-
Islamist gunmen kill polio vaccinator in Pakistan
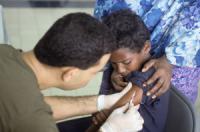
In Pakistan, a Islamist gunmen on Thursday shot dead a female polio vaccinator and wounded another. Conservative Islamic clerics – and the Taliban — have long been suspicious of the polio vaccine, claiming it is a Western plot to harm or sterilize Muslim children. The Pakistani authorities also arrested ten men in the provincial capital Peshawar for spreading unfounded rumors through fake social media videos that a polio vaccine had led to fainting and vomiting. In recent years, anti-vaccination agitators have killed dozens of people in Pakistan, one of three countries in the world — along with Afghanistan and Nigeria — where wild polio virus is still endemic.
-
-
Measles in LA County; 2 pregnant NYC women infected
In new developments in the U.S. surge of measles cases, Los Angeles County health officials announced they are investigating an outbreak, and New York City authorities said an outbreak centered in the Orthodox Jewish community under way since last fall has reached 390 cases, including infections in two pregnant women.
-
-
Decline in measles vaccination causing resurgence of preventable, nearly eradicated disease
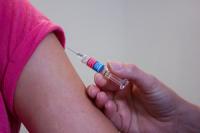
In 2000, measles was declared to be eliminated in the United States, when no sustained transmission of the virus was seen in this country for more than twelve months. Today, however, the United States and many other countries that had also eliminated the disease are experiencing concerning outbreaks of measles because of declines in measles vaccine coverage.
-
-
U.S. measles numbers continue to climb, nearing record
The U.S. measles total climbed by 71 cases last week, the U.S. Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC) said Monday in an update, putting the year’s total at 626, within striking distance of the most cases since the United States officially eliminated the disease in 2000. With weekly measles numbers continuing to grow at a steady clip, a top Food and Drug Administration (FDA) official on Monday released a statement affirming the agency’s continued confidence in the safety and effectiveness of the measles, mumps, and rubella (MMR) vaccine.
-
-
FDA confident in the safety, effectiveness of MMR vaccine
The FDA has joined other scientific and medical groups in an effort to combat the conspiracy-fueled campaign of disinformation and misrepresentation by anti-vaccine activists. “We cannot state strongly enough – the overwhelming scientific evidence shows that vaccines are among the most effective and safest interventions to both prevent individual illness and protect public health,” said Peter Marks, director of FDA’s Center for Biologics Evaluation and Research.
-
-
2019 a record year for measles infection since the disease was eradicated in 2000
The number of measles cases confirmed in the United States since the first of the year grew by 90 in the last week, raising the total to 555 cases, meaning it’s likely 2019 will see the most measles cases in the United States since the disease was eradicated in 2000. Measles is highly contagious, and can be deadly. The World Health Organization (WHO) said 110,000 deaths were attributed to the virus in 2017. “The disease is almost entirely preventable through two doses of a safe and effective vaccine. For several years, however, global coverage with the first dose of measles vaccine has stalled at 85 percent,” the WHO said. Coverage needs to reach 95 percent to prevent outbreaks.
-
-
Online anti-vax efforts prove daunting public health challenge
Earlier this week New York City Health Commissioner Oxiris Barbot blamed a small group of anti-vaccine advocates for their role in an ongoing measles outbreak among the city’s Orthodox Jewish population. In many Western countries, public health officials and scientists charge that an aggressive, conspiracy-fueled misinformation campaign by anti-vaxxers has caused the re-emergence of preventable diseases such as measles.
-
-
Anti-vaxxers are spreading a virus that just won’t die
In 1995, Andrew Wakefield began researching a possible link between autism and the measles, mumps and rubella (MMR) vaccine. Sarah Baxter notes that he was a fraudster, and that he was struck off the medical register in Britain in 2010 but, after moving to the U.S., he has become something of a celebrity, and is supported in his bogus views by Donald Trump. In the past, some religious communities rejected vaccination, but now they have been joined the hippie-dippy boho middle class and the conspiracy-minded global far right. The result: a scary rise in dangerous infectious diseases which were on the verge of eradication.
-
-
Do armed guards prevent school shootings?
The presence of guns in schools is a fact of life for millions of American children. Forty-three percent of public schools had an armed law enforcement officer during the 2015-2016 school year. Does increasing armed school security could reduce deaths from active shootings or deter the attacks in the first place? Experts say the data is not encouraging. Guns have stopped some mass shootings — but not usually in schools.
-
-
2017 DRC Ebola event tied to novel strain, as current outbreak grows
A new analysis of a 2017 Ebola outbreak in the Democratic Republic of the Congo (DRC) that occurred in a remote location and was limited to sixteen cases involved a novel variant of the virus and was probably triggered single spillover, according to a new study.
-
-
Inoculating against misinformation
In the lawless eastern provinces of sub-Saharan Africa’s biggest country, an Ebola outbreak that has quietly become history’s second-largest epidemic may wind up turning not on drugs or quarantine, but on a third, often underappreciated factor: trust.
-
-
Hackers can dupe radiologists, AI software
Hackers can access a patient’s 3-D medical scans to add or remove malignant lung cancer, and deceive both radiologists and artificial intelligence algorithms used to aid diagnosis, according to a new study.
-
-
Pox on everybody’s house
It was not so long ago that a NIH scientist stumbled across smallpox vials in a cold-storage room — and it was not during a time of increased concern for synthetic biology. Pandora Report notes that from CRISPR babies to garage DIY biohacking kits, it seems like the last few years have been inundated with synbio conversations.
-
-
Anti-vaxxers appear to be losing ground in the online vaccine debate
As measles outbreaks spread across the U.S., our new look at how information about vaccine safety and reliability spreads online suggests that the tide may be turning against the anti-vaccination movement.
-
-
Saving millions of lives by rapidly shifting to renewable energies
Reducing global air pollution can prevent millions of premature deaths according to an international team of scientists. The most significant contribution would be the rapid phasing out of fossil fuels, which is currently being discussed mainly to abate climate change.
-
More headlines
The long view
Global Anxiety and the Security Dimension: From Personal Despair to Political Violence
Uncertainty and despair—born of economic insecurity, social isolation, and widening inequality—have fueled a striking surge in anxiety across the United States. But this mental-health crisis is not confined by borders.
The Silent Epidemic: America’s Growing Anxiety Crisis
Anxiety—once dismissed as mere nerves or a passing phase—has become one of the most prevalent and debilitating public health issues facing Americans today. how did we get here—and what do we do now?
