-
Reducing U.S. firearm suicide rates

In 2014, of the more than 33,500 firearm deaths in the United States, over 21,000 were the result of suicide. Studies in the United States showed that greater firearm availability is associated with greater risk of firearm suicide. Globally, four studies in other developed countries found that per capita gun ownership correlates with national firearm suicide rates. To reduce firearm suicide rates in the United States, the authors recommended several measures, such as targeted legislation to limit firearm access to individuals at risk for suicide, using smart gun technology, offering public education on firearm suicide, and research to evaluate the effectiveness of prevention methods.
-
-
New Prize in Food and Agriculture Sciences announced
The National Academy of Sciences announced the creation of a new prize, the NAS Prize in Food and Agriculture Sciences, to be presented annually beginning in 2017 with an award of $100,000. The NAS Prize in Food and Agriculture Sciences will recognize research by a mid-career scientist at a U.S. institution who has made an extraordinary contribution to agriculture or to the understanding of the biology of a species fundamentally important to agriculture or food production.
-
-
GMOs lead the fight against Zika, Ebola and the next unknown pandemic
The shadow of the Zika virus hangs over the Rio Olympic Games, with visitors and even high-profile athletes citing worries about Zika as a reason to stay away (even if the risk is probably quite low). The public’s concerns are a striking example of the need to rapidly combat emerging infectious diseases. In the fight against Zika, public health experts have turned to what may sound like an unlikely ally: genetically modified organisms, or GMOs. To protect the public, scientists have embraced GMO technology to quickly study new health threats, manufacture enough protective vaccines, and monitor and even predict new outbreaks. With the help of GMOs, infectious disease experts have the tools to get ahead of the next outbreak, moving beyond reaction to quick detection, containment and even prevention.
-
-
Three ways synthetic biology could annihilate Zika and other mosquito-borne diseases
There are tried and tested approaches in the arsenal of weapons against the mosquito-borne disease, but to combat Zika and other mosquito-borne disease, more is needed. Gene drives, synthetic biology-based genetic engineering techniques, offer one solution by reengineering mosquitoes or obliterating them altogether. Yet we still have only the vaguest ideas of how the systems we’re hacking by using gene drives actually work. It’s as if we’ve been given free rein to play with life’s operating system code, but unlike computers, we don’t have the luxury of rebooting when things go wrong. As enthusiasm grows over the use of synthetic biology to combat diseases like Zika, greater efforts are needed to understand what could go wrong, who and what might potentially be affected, and how errors will be corrected.
-
-
Gene-drive modified organisms not yet ready to be released into environment: Scientists
The emerging science of gene drives has the potential to address environmental and public health challenges, but gene-drive modified organisms are not ready to be released into the environment and require more research in laboratories and highly controlled field trials, says a new report from the National Academies of Sciences.
-
-
Using gels for biological decontamination

Removing chemical, biological, radiological, and toxic contaminants from a range of surface types could be as easy as peeling off a sticker thanks to research conducted by scientists at the U.S. Army’s Edgewood Chemical Biological Center (ECBC) and industry partner CBI Polymer.The researchers explored how a HydroGel can be modified to decontaminate surfaces contaminated with biological agents.
-
-
UN urges heightened vigilance after H5N1 outbreaks in West and Central Africa
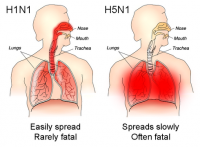
The United Nations Food and Agricultural Organization (FAO) alerted Western and Central African governments to be vigilant, and to continue their raised surveillance and prevention efforts after H5N1 avian influenza outbreaks were recently confirmed in chicken farms in Cameroon. The UN notes that the recent outbreak in Cameroon has brought the number of countries that have battled bird flu in West and Central Africa to six, also including Burkina Faso, Cote d’Ivoire, Ghana, Niger, and Nigeria.
-
-
New control strategies needed for Zika, other unexpected mosquito-borne outbreaks
A recent spate of unexpected mosquito-borne disease outbreaks — most recently the Zika virus, which has swept through parts of the Americas — have highlighted the need to better understand the development and spread of little-known diseases and for new strategies to control them, researchers say. They say that despite the discovery of Zika in Uganda in 1947 and the identification of the first confirmed human infection in Nigeria six years later, few cases were reported in humans until 2007. Even then, no one understood the grave risk the disease posed to pregnancies until the recent outbreak in Brazil, which began less than two years ago.
-
-
Zika epidemic likely to burn itself out within three years

The current Zika epidemic in Latin America is likely to burn itself out within three years, suggests new research. The findings also conclude the epidemic cannot be contained with existing control measures. The researchers predict the next large-scale epidemic is unlikely to emerge for at least another ten years — although there is a possibility of smaller outbreaks in this time.
-
-
100s of deaths in two cities in 2003 heatwave due to man-made climate change: Scientists

Scientists have specified how many deaths can be attributed to man-made climate change during an extreme heatwave in two European cities in 2003. The study says that with climate change projected to increase the frequency and severity of future heatwaves, these results highlight an emerging trend. The authors suggest that such research gives policymakers better information about the damaging effects of heatwaves to help them respond to the future challenges of climate change.
-
-
Gauging the impact of climate change on U.S. agriculture
To assess the likely impact of climate change on U.S. agriculture, researchers typically run a combination of climate and crop models that project how yields of maize, wheat, and other key crops will change over time. But the suite of models commonly used in these simulations, which account for a wide range of uncertainty, produces outcomes that can range from substantial crop losses to bountiful harvests. These mixed results often leave farmers and other agricultural stakeholders perplexed as to how best to adapt to climate change. Researchers have now devised a way to provide these stakeholders with the additional information they need to make more informed decisions. The new approach tracks key factors affecting crop yields, enabling early adaptation.
-
-
Better soil data is key for future food security

To project how much food can be produced in the future, researchers use agricultural models that estimate crop yield, or how much of a crop can be produced in a certain amount of space. These models take into account factors like climate and weather variability, irrigation, fertilizer, and soil type. A new study shows that the type of soil used in such a model can often outweigh the effects of weather variability — such as year-to-year changes in rainfall and temperature.
-
-
Influenza outbreak would cost U.S. billions of dollars in losses
An influenza pandemic would cost the nation tens of billions of dollars in economic losses — nearly double what previous estimates showed, a new study reveals. The study, which was funded by the National Biosurveillance Integration Center of the U.S. Department of Homeland Security, found that the nation would lose as much as $45 billion in gross domestic product if Americans failed to get vaccinated for the flu, compared with $34 billion if they were vaccinated.
-
-
California droughts caused mostly by changes in wind, not moisture

Droughts in California are mainly controlled by wind, not by the amount of evaporated moisture in the air, new research has found. Their analysis showed that although moisture evaporated from the Pacific Ocean is the major source for California precipitation, the amount of water evaporated did not strongly influence precipitation in California, except in the cases of very heavy flooding. The research increases the understanding of how the water cycle is related to extreme events and could eventually help in predicting droughts and floods.
-
-
The politicization of U.S. handling Ebola may carry over to Zika
If the United States responds to Zika the way it did to Ebola — and early indications are that in many ways it is — the country can expect missteps brought about by a lack of health care coordination and a lot of political finger pointing, according to a new analysis. The researchers studied the U.S. response to Ebola and found a fragmented system with no clear leadership, and considerable “strategic politicization” due to the outbreak’s arrival during a midterm election year.
-
More headlines
The long view
We Ran the C.D.C.: Kennedy Is Endangering Every American’s Health
Nine former leaders of the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC), who served as directors or acting directors under Republican and Democratic administrations, serving under presidents from Jimmy Carter to Donald Trrump, argue that HHS Secretary Roert F. Kennedy Jr. poses a clear and present danger to the health of Americans. He has placed anti-vaxxers and conspiracy theorists at top HHS positions, and he appears to be guided by a hostility to science and a belief in bizarre, unscientific approaches to public health.
