-
2015 drought costs for California agriculture: Loss of $1.84 billion, 10,100 jobs

The drought is tightening its grip on California agriculture, squeezing about 30 percent more workers and cropland out of production than in 2014, according to the latest drought impact report. In 2015, the state’s agricultural economy will lose about $1.84 billion and 10,100 seasonal jobs because of the drought, the report estimated, with the Central Valley hardest hit. The heavy reliance on groundwater comes at ever-increasing energy costs as farmers pump deeper and drill more wells. Some of the heavy pumping is in basins already in severe overdraft — where groundwater use greatly exceeds replenishment of aquifers — inviting further land subsidence, water quality problems, and diminishing reserves needed for future droughts.
-
-
Cleaning explosives pollution with plants
Biologists have taken an important step in making it possible to clean millions of hectares of land contaminated by explosives. The researchers have unraveled the mechanism of TNT toxicity in plants, raising the possibility of a new approach to explosives remediation technology. TNT has become an extensive global pollutant over the last 100 years and there are mounting concerns over its toxicity to biological systems.
-
-
Radioactive contaminants found in coal ash from all three major U.S. coal-producing basins
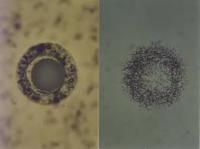
A new study has revealed the presence of radioactive contaminants in coal ash from all three major U.S. coal-producing basins. The study found that levels of radioactivity in the ash were up to five times higher than in normal soil, and up to ten times higher than in the parent coal itself because of the way combustion concentrates radioactivity. The finding raises concerns about the environmental and human health risks posed by coal ash, which is currently unregulated and is stored in coal-fired power plants’ holding ponds and landfills nationwide.
-
-
Solving the mystery of arsenic-contaminated water
Can water ever be too clean? If the intent is to store it underground, the answer, surprisingly, is yes. In a new study, scientists have shown that recycled water percolating into underground storage aquifers in Southern California picked up trace amounts of arsenic because the water was too pure. The research sheds light on a poorly understood aspect of groundwater recharge with purified recycled water, namely the potential mobilization of arsenic. Arsenic is a naturally occurring element that can cause organ failure and cancer in humans with prolonged exposure above established health thresholds. The findings pose a problem for Orange County, California, which differs from most communities in that it purifies treated wastewater instead of discharging it directly into rivers and oceans – but the problem goes beyond Orange County.
-
-
Can America cope with a resurgence of tropical disease?
Having stamped out a number of tropical diseases — including malaria — decades ago, is America today complacent about a rising wave of infectious disease? It is the nature of these diseases — neglected diseases, diseases of poverty, call them what you like — that they can go unnoticed for years, chewing away at the health of individuals and communities. As poverty, geography, climate, and social factors combine to bring tropical diseases out of hiding once again in the U.S. South, physicians, politicians, and the general public have to take the warning signs seriously and recognize that the tools available for tackling tropical diseases are sorely lacking. Despite tremendous advances in other types of illness in recent decades, tropical medicine remains stubbornly stuck in the 1950s, leaving the United States as unprepared as low-income nations to treat any significant number of cases. With diseases like Chagas now known to be prevalent and transmissible within the United States, better awareness, better tests, and better treatments are all urgently required. Otherwise, the number of people affected and infected will only continue to rise as this perfect storm grows ever stronger.
-
-
The history of biological weapons use
Few comprehensive, definitive histories of biological warfare have been written, many events reported in the literature never happened, and few details are available about some uses of biological weapons which most certainly did occur. A new review of the literature on actual and alleged instances of biological warfare finds that the incidence of illicit biological agent use has been greater than many people may realize, even as the effects have been relatively limited.
-
-
New research aims to slow the spread of infectious diseases
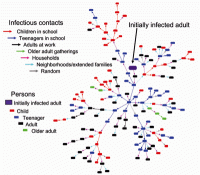
Emerging pandemic disease outbreaks such as Ebola increasingly threaten global public health and world economies, scientists say. We can expect five such new diseases to emerge each year — and spread. The tropical disease dengue fever, for example, has made its way to Florida and Texas, seemingly to stay. The NSF’s Ecology and Evolution of Infectious Diseases (EEID) program supports research aiming to help understanding of the underlying ecological and biological mechanisms behind human-induced environmental changes and the emergence and transmission of infectious diseases. This year, the program has awarded eight new grants totaling $18 million.
-
-
New book details safety, security methods for biosciences sites
Recent mishaps at laboratories which mishandled potentially dangerous biological substances and the transmission of the Ebola virus in a U.S. hospital are symptoms at bioscience facilities that two Sandia National Laboratories researchers think could be prevented by implementing the practices in a new book on biorisk management. The new book, Laboratory Biorisk Management: Biosafety and Biosecurity, is the first full-length manuscript on the detailed implementation of biorisk management.
-
-
Repurposing wasted food would feed the hungry, create jobs
Roughly one third of all global food gets wasted. In the United States, that number is even higher, with nearly 40 percent of all food going to waste, making it one of the most wasteful countries in the world. Researchers have developed a new model for recovering would-be wasted — or surplus — food and repurposing it to feed hungry people, generate revenue, and even create jobs. The model — Food System-Sensitive Methodology (FSSM) — was recently piloted in West Philadelphia. The researchers say that applying FSSM nationally would likely yield about 1.1 billion pounds of recovered wasted food annually.
-
-
EU-funded research: Climate change and food safety
The global fresh produce supply chain must take into account climate change in order to ensure food safety, warn EU-funded researchers. This was the key recommendation of the EU-funded VEG-I-TRADE project, which was launched in 2010 to assess the safety of fresh produce in a rapidly evolving context of climate change and expanding international trade.
-
-
Long-distance travelers may contribute to the spread of antibiotic resistance
Swedish exchange students who studied in India and in central Africa returned from their sojourns with an increased diversity of antibiotic resistance genes in their gut microbiomes. These resistance genes were not particularly abundant in the students prior to their travels, but the increases are nonetheless quite significant. The researchers questioned the conventional wisdom that overuse of antibiotics was entirely responsible for the surge in resistance, despite the fact that overuse is a huge problem.
-
-
New drug protects against nuclear radiation’s deadly effects 24 hours after exposure
The threat of a nuclear incident, with the potential to kill or injure thousands of people, has raised global awareness about the need for medical countermeasures that can prevent radiation-induced bodily damage and keep people alive, even if given a day or more after contact with nuclear radiation. An interdisciplinary research team reports a breakthrough in countering the deadly effects of radiation exposure. A single injection of a regenerative peptide was shown significantly to increase survival in mice when given twenty-four hours after nuclear radiation exposure.
-
-
Mobile phone data help track spread of infectious diseases
Tracking mobile phone data is often associated with privacy issues, but these vast datasets could be the key to understanding how infectious diseases are spread seasonally, according to a new study. Researchers used anonymous mobile phone records for more than fifteen million people to track the spread of rubella in Kenya and were able quantitatively to show for the first time that mobile phone data can predict seasonal disease patterns. Harnessing cellphone data in this way could help policymakers guide and evaluate health interventions like the timing of vaccinations and school closings, the researchers said. The researchers’ methodology also could apply to a number of seasonally transmitted diseases such as the flu and measles.
-
-
Toxic chemical found in fish-eating in birds outside of a Georgia’s Superfund site
Researchers have found that a contaminated mixture called Aroclor 1268 has spread beyond a former chemical plant, now a Superfund site, near Brunswick, Georgia. Aroclor 1268 is composed of a suite of toxic chemical compounds known as polychlorinated biphenyls, or PCBs. The chemical was used to produce insulation materials at the Linden Chemical Plant at the Turtle Estuary near Brunswick until 1994.
-
-
Two major U.S. aquifers contaminated with high levels of natural uranium
Nearly two million people throughout the Great Plains and California live above aquifer sites contaminated with natural uranium which is mobilized by human-contributed nitrate. Data from roughly 275,000 groundwater samples in the High Plains and Central Valley aquifers show that many Americans live less than two-thirds of a mile from wells that often far exceed the uranium guideline set by the Environmental Protection Agency. A new study reports that 78 percent of the uranium-contaminated sites were linked to the presence of nitrate, a common groundwater contaminant that originates mainly from chemical fertilizers and animal waste.
-
More headlines
The long view
We Ran the C.D.C.: Kennedy Is Endangering Every American’s Health
Nine former leaders of the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC), who served as directors or acting directors under Republican and Democratic administrations, serving under presidents from Jimmy Carter to Donald Trrump, argue that HHS Secretary Roert F. Kennedy Jr. poses a clear and present danger to the health of Americans. He has placed anti-vaxxers and conspiracy theorists at top HHS positions, and he appears to be guided by a hostility to science and a belief in bizarre, unscientific approaches to public health.
