-
New virus could be the first filovirus to cause disease in bats

A team of international researchers has discovered a new Ebola-like virus — Lloviu virus — in bats from northern Spain; filoviruses, which include well-known viruses like Ebola and Marburg, are among the deadliest pathogens in humans and non-human primates, and are generally found in East Africa and the Philippines
-
-
Laser keeps an eye for spoiled food

Minced meat, bread, fruit juice, and many other foods are packaged in a protective gas which extends their shelf life; there is currently no good method to check whether the packaging has the correct gas content — and thus, whether the content is spoiled or not; researchers have developed a new laser instrument which could solve the problem
-
-
DHS funds Ricin detection
Positive ID announces the company’s immunodetection assay for the identification of Ricin toxin to meet DHS specifications; Ricin, a chemical warfare agent, is derived from the seeds of the castor oil plant Ricinus communis and has become a tool of terrorist groups across the world due to its easy production and high toxicity
-
-
A new pest threatens U.S. agriculture -- iPhone owners can help
A new meandering pest — the brown marmorated stink bug (BMSB) — is feasting on many of North America’s most important crops, posing an unprecedented threat to U.S. agriculture; the value of susceptible crops in the thirty-three states where BMSB has been established or sighted exceeds $21 billion
-
-
Google Earth typhoid maps traces disease outbreaks
Recent advances in DNA sequencing have allowed scientists accurately to track the spread of some diseases by measuring mutations in the pathogen’s DNA when the DNA replicates; tracing the spread of typhoid, however, has proved challenging because these mutations are small in number and not detectable by most techniques in use
-
-
Little progress despite $3.4 billion spent on food safety programs

In the past decade the U.S. government has gone to great lengths to secure the nation’s food supply against terrorists, but more than $3.4 billion later it has little to show for its efforts; despite all the government spending, key food safety programs and counter-terror policies have been bogged down by a murky, convoluted bureaucratic process
-
-
Argonne software help decode German E. coli strain
In the early days of annotating genomes in the mid-1990s, it took four or five scientists more than a year to analyze just one genome; now, with the help of Rapid Annotation using Subsystems Technology (RAST), which was developed by Argonne scientists, researchers needed only eight hours to sequence the genome of the rogue E. coli strain which struck Europe this summer; the next-generation RAST will cut this time to just fifteen minutes
-
-
UN warns record food prices to continue
Food prices are projected to continue skyrocketing and remain volatile leaving poor countries and consumers exposed to food insecurity, according to a recently released UN report
-
-
U.S. unprepared for large-scale bio-attack, report warns

On Wednesday, the WMD Center released its latest report that found the United States is unprepared for a large-scale biological attack, despite spending more than $65 billion on biodefense over the past decade; the report warned that the threat of biological weapons is now greater than ever as a result of technological advances; a small team of individuals with training in key disciplines can produce “the type of bioweapons created by nation-states in the 1960s”
-
-
Focus on terrorism allowed foreign pests to slip into U.S.

Following the 9/11 attacks the U.S. government assigned hundreds of agricultural scientists responsible for stopping invasive species at the border to anti-terrorism duties; the result has been that dozens of foreign insects and plant diseases managed to slip undetected into the United States
-
-
Traceability key to food safety

The produce industry looks at food safety and traceability as the key to reducing the instances of food-borne illnesses; the Food and Drug Administration (FDA) has launched its own effort to protect the integrity of the food supply with the Food Safety Modernization Act, which President Barack Obama signed into law 4 January
-
-
Former colleagues: accused anthrax killer could not have done it
Two former colleagues of Bruce Ivins, a scientist who worked at the U.S. Army Medical Research Institute of Infectious Disease (USAMRIID) in Frederick, Maryland, and who was accused by the FBI of being behind the 2001 anthrax attacks in the United States, said he could not have done it (Ivins committed suicide in July 2008)
-
-
Virus movement in Wisconsin groundwater
Drinking water taken from a deep aquifer protected by a semi-permeable layer of rock should be safe because the water is protected from many contaminants, including viruses — but is it safe? University of Wisconsin scientists find virus particles in many deep Madison, Wisconsin water wells, raising questions about how viruses, which should not survive more than two years underground, reached so deep and survive for so long
-
-
11,000 California parents refuse basic vaccinations for their children
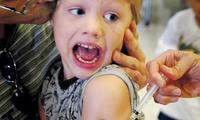
Even with the massive whooping cough outbreak last year in California that sickened more than 9,100 people and killed ten babies, over 11,000 hesitant parents chose not to vaccinate their children against the infectious disease; with record numbers of children going unvaccinated, there have been an increasing number of outbreaks of highly infectious diseases like measles and whooping cough
-
-
HHS proposes new rule regarding toxins
The U.S. Department of Health and Human Services (HHS) has issued a proposed rule regarding the biennial review of the possession, use, and transfer of select agents and toxins, according to Secretary Kathleen Sebelius
-
More headlines
The long view
We Ran the C.D.C.: Kennedy Is Endangering Every American’s Health
Nine former leaders of the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC), who served as directors or acting directors under Republican and Democratic administrations, serving under presidents from Jimmy Carter to Donald Trrump, argue that HHS Secretary Roert F. Kennedy Jr. poses a clear and present danger to the health of Americans. He has placed anti-vaxxers and conspiracy theorists at top HHS positions, and he appears to be guided by a hostility to science and a belief in bizarre, unscientific approaches to public health.
