-
Holograms to help in fighting malaria
Scientists have developed a 3D filming technique that could inform research to stem the spread of malaria. Creating moving digital holograms of malaria sperm has given researchers fresh insights into the behavior of these tiny life forms. Understanding how malaria parasites mate could pave the way for improved prevention and control of this deadly disease, which poses a threat to half of the world’s population.
-
-
Quick ID for water pathogens

New research purports to help people stay healthy by developing a real-time water bug testing that could precisely identify the culprits responsible for waterborne disease.
-
-
Zapping bugs dead

Restaurants and supermarkets could save millions of dollars by hanging on to bug zapper bulbs instead of tossing them every year as they normally do, a new study has found. What is more, the benefits could extend to the environment by keeping some of the bulbs’ mercury out of the waste stream.
-
-
DHS, FDA: Decorative contact lenses for Halloween costumes are risky
Many will celebrate Halloween today, and federal officials are warning the public about the dangers associated with counterfeit decorative contact lenses. Decorative and colored lenses are becoming increasingly popular, especially around this time of year. Several federal agencies have teamed up to launch Operation Double Vision – already underway — to seize illegal, harmful products from store shelves.
-
-
Where should U.S. radioactive waste be buried?
In the United States, about 70,000 metric tons of spent commercial nuclear fuel are located at more than seventy sites in thirty-five states. Shales and other clay-rich (argillaceous) rocks have never been seriously considered for holding America’s spent nuclear fuel, but it is different overseas. France, Switzerland, and Belgium are planning to put waste in tunnels mined out of shale formations, and Canada, Japan, and the United Kingdom are evaluating the idea.
-
-
Sharp increase in radioactive water leaks at Fukushima
Tokyo Electric Power(TEPCO) has reported a rise in groundwater radiation levels, saying a tank at the firm’s Fukushima plant leaked 300 metric tons of toxic water in August 2013. Water samples from wells, taken in mid-October, show a record-high concentration of beta-ray emitting substances, and a sharp increase in the presence of radioactive tritium. Japanese prime ministerShinzo Abe, in a tacit admission that Japan cannot effectively handle the continuing radiation leaks from the stricken plant, said Japan would be interested in receiving foreign help to contain widening radioactive water leaks at Fukushima.
-
-
New apps to keep you healthy
For those wanting to keep their distance from health threats like E. coli-contaminated lettuce or the flu, there are two upcoming apps for that. The Department of Energy’s Pacific Northwest National Laboratory (PNNL) hosted a competition this summer in which graduate students designed two mobile apps to fight the threats of food-related illnesses and the flu. The apps are called FoodFeed and FL•U (pronounced “flu you”).
-
-
1930s fight against malaria in U.S. a model for today’s global campaign

Malaria killed an estimated 1.24 million people worldwide in 2010 and has decimated economies in the heavily populated, warm climate regions. A new study about the elimination of malaria in the 1930s American South may have significant implications for solving modern day malaria outbreaks in parts of Africa, Central and Latin America, and Asia.
-
-
Iraqi war- and occupation-related death toll estimated at half a million
A scientific study calculating Iraqi deaths for almost the complete period of the U.S.-led war and subsequent occupation estimates, with 95 percent of statistical certainty, that the total excess Iraqi deaths attributable to the war through mid-2011 to be about 405,000 (“excess” death means death not related to natural causes or causes other than the war and occupation). The researchers also estimated that an additional 56,000 deaths were not counted due to migration. Including this number, their final estimate is that close to half a million people died in Iraq as a result of the war and subsequent occupation from March 2003 to June 2011.
-
-
Innovative salmonella sensing system
Foodborne illnesses making one in six Americans — or forty-eight million people — sick each year. Of these people sickened, 128,000 end up in the hospital, according to the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention, while 3,000 die. A new approach to detecting food contamination enables real-time testing of food and processing plant equipment.
-
-
One in 2,000 people in the U.K. carry mad cow disease proteins

Variant Creutzfeldt-Jakob disease (vCJD) is a degenerative brain disease — often called the human form of bovine spongiform encephalopathy (BSE) or “mad cow disease.” It emerged after widespread exposure to BSE prions in the late 1980s and early 1990s through contaminated meat products in the food chain. Around one in 2,000 people in the United Kingdom may carry variant CJD proteins, concludes a large scale survey published on BMJ.
-
-
Compound derived from vegetables offers shield from lethal radiation doses

Researchers say a compound derived from cruciferous vegetable such as cabbage, cauliflower, and broccoli protected rats and mice from lethal doses of radiation. The compound, known as DIM could protect normal tissues in patients receiving radiation therapy for cancer, but could also protect individuals from the lethal consequences of a nuclear disaster.
-
-
ASCB: U.S. scientific research will "pay dearly" for shutdown
The American Society for Cell Biology (ASCB) added its voice to those of other scientific and professional groups in warning that the federal government’s partial shutdown will hurt patients, researchers, and especially the U.S. research effort, long after an agreement to end the impasse is reached. “As America keeps hitting the brakes on scientific research, we are, in effect, accelerating the damage done to our continued leadership in global bioscience, in health outcomes and in the economic power that we have always derived from basic research,” Dr. Bertuzzi, executive director of the ASCB said. “Americans will pay dearly for these slowdowns, sequestrations, and shutdowns in finding cures and on maintaining economic competitiveness.”
-
-
Compact, high-power terahertz source at room temperature developed
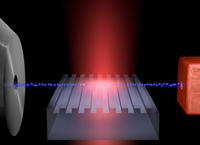
Terahertz (THz) radiation — radiation in the wavelength range of 30 to 300 microns — is gaining attention due to its applications in security screening, medical and industrial imaging, agricultural inspection, astronomical research, and other areas. Traditional methods of generating terahertz radiation usually involve large and expensive instruments, some of which also require cryogenic cooling. Researchers have developed a compact, room-temperature terahertz source with an output power of 215 microwatts.
-
-
ACS: Shutdown undermines U.S. innovation, competitiveness, critical services
American Chemical Society (ACS) president Marinda Li Wu said that the budget impasse is effectively choking America’s science innovation pipeline, strangling new discoveries, future economic growth, and job creation. “[T]o shut down a critical part of our nation’s research and innovation pipeline puts our nation at a severe competitive disadvantage globally,” said Wu. “A government shutdown that closes the world’s largest research system can lead to unintended negative consequences putting at peril America’s economic growth and long-term stability.”
-
More headlines
The long view
We Ran the C.D.C.: Kennedy Is Endangering Every American’s Health
Nine former leaders of the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC), who served as directors or acting directors under Republican and Democratic administrations, serving under presidents from Jimmy Carter to Donald Trrump, argue that HHS Secretary Roert F. Kennedy Jr. poses a clear and present danger to the health of Americans. He has placed anti-vaxxers and conspiracy theorists at top HHS positions, and he appears to be guided by a hostility to science and a belief in bizarre, unscientific approaches to public health.
