-
Drug-resistant Salmonella outbreak in seven states
The Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC) said that seven strains of Salmonella Heidelberg bacteria have been identified as being linked to an outbreak in seven states. The outbreak, associated with Foster Farm chicken product, has so far sickened 278 people. The outbreak strains of Salmonella Heidelberg are resistant to several commonly prescribed antibiotics. The CDC unit tracking disease outbreaks has been working with less than half its personnel since the government shutdown began, and had had to call back thirty furloughed inspectors.
-
-
Dog's mood offers insight into owner’s wellbeing

Researchers are using movement sensors to track normal dog behavior while the animals are both home alone and out-and-about. Providing a unique insight into the secret life of man’s best friend, the sensors show not only when the dog is on the move, but also how much he is barking, sitting, digging, and other key canine behaviors.
-
-
New view of dengue fever

Dengue fever is a mosquito-borne illness that infects at least fifty million people worldwide each year. This infectious tropical disease is found in more than 100 countries, and it has no cure and no vaccine. One reason why it has been difficult to develop new drugs for dengue fever is that there are no good animal models of the disease, which only infects humans. Researchers have now produced a “humanized mouse” that mimics many features of the human immune system. These mice with human immune cells help researchers discover how the mosquito-borne virus depletes blood platelets.
-
-
Facebook, Twitter may yield clues on how to prevent the spread of disease
Cold and flu season prompts society to find ways to prevent the spread of disease though measures like vaccination all the way through to covering our mouths when we cough and staying in bed. These social responses are much more difficult to predict than the way biological contagion will evolve, but new methods are being developed to do just that. Facebook and Twitter could provide vital clues to control infectious diseases by using mathematical models to understand how we respond socially to biological contagions.
-
-
Predicting violence among psychopaths no more accurate than tossing a coin
Risk assessment tools used to predict prisoner re-offending are no more accurate than tossing a coin when it comes to psychopaths, according to new research. The researchers say the findings — which also show the tools perform at best moderately in those with depression, drug and alcohol dependence, and schizophrenia — have major implications for risk assessment in criminal populations.
-
-
Making clean drinking water universally available “achievable”
More than 780 million people around the world still do not have safe and reliable drinking water. The problem of providing clean water is most acute in developing countries, particularly in Africa, where creaking infrastructures struggle to keep pace with fast-growing urban populations; in rural areas, millions of water pumps stand unused waiting to be repaired.
-
-
Toxic threats: More mercury released to the environment

Mercury, especially in the form of methylmercury, is an extremely toxic chemical to all life forms. It occurs both naturally and as the result of human activities. A majority of mercury releases to the environment presently are atmosphere emissions from human activities, and reemissions of previously deposited mercury from soils and the oceans. The largest sources of man-made mercury emissions are small-scale gold mining and burning coal for electrical generation.
-
-
Universal flu vaccine within sight
Researchers asked volunteers to donate blood samples just as the swine flu pandemic was getting underway and report any symptoms they experienced over the next two flu seasons. They found that those who avoided severe illness had more CD8 T cells, a type of virus-killing immune cell, in their blood at the start of the pandemic. The researchers believe a vaccine that stimulates the body to produce more of these cells could be effective at preventing flu viruses, including new strains that cross into humans from birds and pigs, from causing serious disease.
-
-
Children living close to nuclear power plants do not have higher risk of developing leukemia

Young children who live near nuclear power plants do not have a greater risk of developing childhood leukemia or non-Hodgkin Lymphoma according to new research. Researchers conducted a study of almost 10,000 children under five years of age who were diagnosed with leukemia or similar cancers in Britain between 1962 and 2007. The scientists measured the distance from the nearest nuclear power plant both at birth and when diagnosed with childhood leukemia or non-Hodgkin lymphoma, and found that there was no apparent extra risk living near a nuclear power plant.
-
-
Sewage treatment removes widely used home and garden insecticides from wastewater
Even though sewage treatment plants are not designed to remove tiny amounts of pesticides, they do an excellent job of dealing with the most widely used family of home and garden insecticides, scientists reported. The use of pyrethrins, derived from chrysanthemum flowers, and the related synthetic pyrethroids, has been on the increase during the last decade. Researchers found that advanced sewage treatment reduced the levels of pyrethroids by more than 97 percent.
-
-
Making people invisible to mosquitoes
Mosquitoes are more deadly to humans than any other animal. Their bites transmit malaria and other diseases that kill an estimated one million people around the world each year. In the United States, mosquitoes spread rare types of encephalitis, an inflammation of the brain. They also transmit heartworms to pet dogs and cats. Scientists described discovery of substances that occur naturally on human skin and block mosquitoes’ ability to smell and target their victims – in effect, offering people, pets, and livestock with an invisibility cloak against these blood-sucking insects.
-
-
Wildfires to worsen with climate change

Air quality has vastly improved over much of the United States in the past forty years as a result of government efforts to regulate emissions. Gradual climate change may contribute in the coming years to increases in significant, disruptive events like severe storms, floods, and wildfires. A Harvard model predicts wildfire seasons by 2050 will be three weeks longer, up to twice as smoky, and will burn a wider area in the western United States. These increasing wildfires may erase some of the progress made on air quality.
-
-
Fukushima radioactive plume to reach U.S. next year
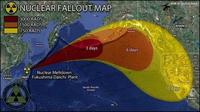
The radioactive ocean plume from the 2011 Fukushima nuclear plant disaster will reach the shores of the United States within three years from the date of the incident, but is likely to be harmless, according to a new study. While atmospheric radiation was detected on the U.S. west coast within days of the incident, the radioactive particles in the ocean plume take considerably longer to travel the same distance.
-
-
Irradiated mosquitoes provide malaria vaccine
A new malaria vaccine is derived from mosquitoes that have been irradiated but not killed. The radiation critically weakens the malaria parasite, Plasmodium falciparum, which is extracted from the insects’ salivary glands and administered intravenously to subjects.
-
-
Rapid response, imaging of injuries aided Boston Marathon bombing victims
According to the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC), bombing survivors have the highest incidence of injury to soft tissue and musculoskeletal systems with the most extreme injury being traumatic amputation, which is reported in up to 3 percent of cases. The Boston Marathon bombings resulted in three fatalities and 264 casualties, with the most severe injuries involving lower extremities of those located closest to the blasts. Blast injuries within civilian populations are rare in the United States, so when they do occur they challenge the medical community rapidly to respond to concurrent evaluation and treatment of many victims.
-
More headlines
The long view
We Ran the C.D.C.: Kennedy Is Endangering Every American’s Health
Nine former leaders of the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC), who served as directors or acting directors under Republican and Democratic administrations, serving under presidents from Jimmy Carter to Donald Trrump, argue that HHS Secretary Roert F. Kennedy Jr. poses a clear and present danger to the health of Americans. He has placed anti-vaxxers and conspiracy theorists at top HHS positions, and he appears to be guided by a hostility to science and a belief in bizarre, unscientific approaches to public health.
