-
Smart coating could make oil-spill cleanup faster and more efficient
In the wake of recent off-shore oil spills, and with the growing popularity of “fracking” — in which water is used to release oil and gas from shale – there is a need for easy, quick ways to separate oil and water. Now, scientists have developed coatings that can do just that.
-
-
Laser weapon developed for Marine vehicles

As the U.S. Navy prepares to deploy its first laser weapon on a ship later this summer, Office of Naval Research (ONR) officials announced that they have finished awarding contracts to develop a similar weapon to be used on ground vehicles. The Ground-Based Air Defense Directed Energy On-the-Move program, commonly referred to as GBAD, aims to provide an affordable alternative to traditional firepower to keep enemy unmanned aerial vehicles (UAVs) from tracking and targeting Marines on the ground.
-
-
New material captures CO2 at natural gas wellheads
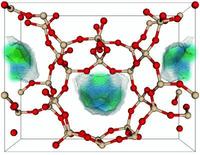
Natural gas is the cleanest fossil fuel. Development of cost-effective means to separate carbon dioxide during the production process will improve this advantage over other fossil fuels and enable the economic production of gas resources with higher carbon dioxide content that would be too costly to recover using current carbon capture technologies. Rice University chemists invented a porous material which sequesters carbon dioxide, a greenhouse gas, at ambient temperature with pressure provided by the wellhead, and lets it go once the pressure is released. The material shows promise to replace more costly and energy-intensive processes.
-
-
Nature-inspired designs for drones of the future

Based on the mechanisms adopted by birds, bats, insects, and snakes, fourteen research teams have developed solutions to some of the common problems that drones could be faced with when navigating through an urban environment and performing novel tasks for the benefit of society. Whether this is avoiding obstacles, picking up and delivering items, or improving the take-off and landing on tricky surfaces, it is hoped the solutions can lead to the deployment of drones in complex urban environments in a number of different ways, from military surveillance and search and rescue efforts to flying camera phones and reliable courier services.
-
-
DARPA Demo Day 2014: Preserving, expanding U.S. technological superiority
Information technology (IT) is a key enabler for the Defense Department (DoD) and has been a focus area for DARPA since its founding in 1958. DARPA’s contributions to modern IT are well-known — perhaps most notably, DARPA is generally credited with developing and prototyping the technology for what is now known as the Internet. While the DoD currently enjoys IT superiority, that superiority cannot be taken for granted. On Wednesday, DARPA held the largest-ever Pentagon event to showcases more than 100 projects aiming to be game-changing improvements to U.S. national security.
-
-
Floating solar power plants offer many benefits
Water-based solar plants are at least 50 percent more efficient than a land-based solar power system.The water on which the plant floats helps extending the life of the photovoltaic panels, meaning greater efficiency and performance from the solar panel system, and the plant also prevents nearly 90 percent of the evaporation for the surface area that it covers, an important benefit in dry climates.
-
-
Wireless camera network offers new possibilities for security systems
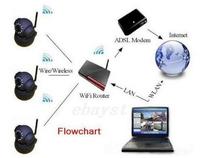
Advances in computer technology are opening up new possibilities for surveillance cameras and environmental video monitoring systems. A graduate engineering student used off-the-shelf components to build a prototype device for a solar-powered wireless network of smart cameras with potential applications in security systems and wildlife monitoring.
-
-
New technology tests ammo while saving joints
Firing and testing thousands of rounds of ammunition weekly can challenge the human body — even ones in top physical condition — causing debilitating stress injuries and chronic nerve and joint pain. DHS Science and Technology Directorate (S&T), with the help of agents from ICE Office of Firearms and Tactical Programs (OFTP) Armory Operations Branch (AOB), has taken an important step forward in reducing or eliminating these injuries by developing of the “Virtual Shooter.”
-
-
Improving gloves to enhance first responders’ safety
Firefighters wear protective gloves called “structure gloves” to keep their hands safe on the job. The structure gloves currently used by firefighters, however, are not designed for the precision movements first responders must perform. There are many different types of structure gloves available, but none fully satisfies modern firefighters’ needs. Today’s compact tools often have small buttons that require nimble movements. Bulky gloves can make it difficult for firefighters to complete simple tasks without removing their gloves and compromising their safety. As advanced textile technology and materials continue to develop, the science behind firefighter structure gloves has adapted.
-
-
Teams from U.S. service academies demonstrate potentially transformative technologies
DARPA’s mission is to ensure the technological superiority of U.S. military forces, and the agency continually seeks new sources of talent to accomplish that goal. The U.S. three military service academies are a promising source of that talent. The U.S. Air Force Academy team wins new competition — DARPA Service Academies Innovation Challenge — designed to encourage students at U.S. military academies to develop groundbreaking solutions to challenges facing the U.S. armed forces.
-
-
Teleoperated robots for smarter disaster response

Electrical engineers have developed telerobotics technology which could make disaster response faster and more efficient. The researchers aim to combine existing “smart” technologies better to serve society during disaster and crisis response. This includes using teleoperated robots for rescues and safety operations; a high-tech dispatch system that gathers information from cameras and sensors and pushes it out to first responders; drones for damage surveillance and rescues; and vests outfitted with sensors and GPS tracking to be worn by search-and-rescue dogs.
-
-
Using light to detect trace amounts of explosives

Researchers may help in the fight against terrorism with the creation of a sensor that can detect tiny quantities of explosives with the use of light and special glass fibers. The researchers describe a novel optical fiber sensor which can detect explosives in concentrations as low as 6.3 ppm (parts per million). It requires an analysis time of only a few minutes.
-
-
New scanning technique may end on-board liquid restrictions
A new machine which can identify the chemical composition of liquids sealed within non-metallic containers without opening them is one of three candidates announced Monday to be in the running to win the U.K.’s premier engineering prize, the MacRobert Award. Already being deployed in sixty-five airports across Europe, this innovation can protect travelers by screening for liquid explosives and could spell the end of the ban on liquids in hand luggage.
-
-
New bug sensor saves crops, people

For hundreds of years humans have attempted to kill unwanted insects. While some blanket methods have been successful, they can be costly and create environmental problems. A new sensor developed by UC Riverside researchers aims to change that by counting and classifying the insects so that the substance used to eradicate the harmful insects can be applied on a precision targeted level. The inexpensive wireless sensors have 99 percent accuracy, and they are expected to have applications fighting insect-borne diseases, such as malaria, and insects that damage crops.
-
-
Harder ceramic for armor windows
The Department of Defense needs materials for armor windows that provide essential protection for both personnel and equipment while still having a high degree of transparency. To meet that need, scientists have developed a method to fabricate nanocrystalline spinel that is 50 percent harder than the current spinel armor materials used in military vehicles.
-
More headlines
The long view
New Technology is Keeping the Skies Safe
DHS S&T Baggage, Cargo, and People Screening (BCP) Program develops state-of-the-art screening solutions to help secure airspace, communities, and borders
Factories First: Winning the Drone War Before It Starts
Wars are won by factories before they are won on the battlefield,Martin C. Feldmann writes, noting that the United States lacks the manufacturing depth for the coming drone age. Rectifying this situation “will take far more than procurement tweaks,” Feldmann writes. “It demands a national-level, wartime-scale industrial mobilization.”
How Artificial General Intelligence Could Affect the Rise and Fall of Nations
By Barry Pavel et al.
Visions for potential AGI futures: A new report from RAND aims to stimulate thinking among policymakers about possible impacts of the development of artificial general intelligence (AGI) on geopolitics and the world order.
Keeping the Lights on with Nuclear Waste: Radiochemistry Transforms Nuclear Waste into Strategic Materials
By John Domol
How UNLV radiochemistry is pioneering the future of energy in the Southwest by salvaging strategic materials from nuclear dumps –and making it safe.
Model Predicts Long-Term Effects of Nuclear Waste on Underground Disposal Systems
By Zach Winn
The simulations matched results from an underground lab experiment in Switzerland, suggesting modeling could be used to validate the safety of nuclear disposal sites.
