-
Biometric workshop studied voice, dental, oral standards
The National Institute of Standards and Technology (NIST) hosted a workshop to discuss proposed supplements to the biometric data format standard that support voice recognition, dental and oral data, disaster victim identification, and special data needs for mobile ID applications.
-
-
Laser scanner documents crimes scenes quickly, accurately
The Carlsbad, California police is using a new laser scanner to capture what happened at crime scene. Thenew technology cuts the time it takes to document a crime scene, from the size of the room to the bullet holes in the wall, by up to 80 percent.
-
-
Developing educational materials, courses on standards
So called “documentary standards,” generally developed by industry-based committees, significantly influence industry, commerce and even daily life, but their role is often unrecognized save by those people who are immediately concerned.
-
-
Using silicon to produce hydrogen on demand
Super-small particles of silicon react with water to produce hydrogen almost instantaneously, according to researchers. In a series of experiments, the scientists created spherical silicon particles about ten nanometers in diameter. When combined with water, these particles reacted to form silicic acid (a nontoxic byproduct) and hydrogen — a potential source of energy for fuel cells.
-
-
“Rebound” effect of energy-efficient technology exaggerated
The argument that those who have fuel-efficient cars drive them more and hence use more energy is overplayed and inaccurate. Researchers find evidence that, indeed, if a technology is cheaper to run – for example, a fuel-efficient car — people may use it more, but the effects of an increased use of the technology are too small to erase energy savings from energy efficiency standards and energy-efficient technologies.
-
-
Blast-resilient carriages to reduce impact of a terrorist attack on trains, metros
Engineers have developed a blast-resilient carriages which are better able to withstand a terrorist attack and ultimately save lives. The engineers have e focused on two key areas — containing the impact of the blast and reducing debris — the main cause of death and injury in an explosion and the key obstacle for emergency services trying to gain access to injured passengers.
-
-
Thwarting facial-recognition, photo-tagging software

Information about when and where photographed subjects were when their pictures were taken is readily disclosed through photos taken, and the information is disclosed and distributed without their permission. The problem has become even worse due to the popularization of portable terminals with built-in cameras and developments in SNS and image search technologies. Japanese researchers offer a solution: goggles or glasses which, when equipped with near-infrared LED emitter. :
-
-
New approach to military manufacturing

In the past, fighter aircraft, tanks, and other complex military systems have been built in a craftsman-like process by a small number of highly specialized contractors. This is a costly approach and DARPA is attempting to replace it with a more efficient “correct by construction” process similar to that practiced by the semiconductor industry, which has an impressive track record in getting systems right in the first place.
-
-
Metamaterial sensor improves security, collision avoidance

Engineers have developed a novel sensor which is more efficient, versatile, and cheaper for potential use in such applications as airport security scanners and collision avoidance systems for aircraft, cars, or maritime vessels.
-
-
Aerial platform helps in developing lightweight sensors for UAVs

A research team at the Georgia Tech Research Institute (GTRI) is developing an airborne testing capability for sensors, communications devices, and other airborne payloads. This aerial test bed, called the GTRI Airborne Unmanned Sensor System (GAUSS), is based on an unmanned aerial vehicle (UAV) made by Griffon Aerospace and modified by GTRI.
-
-
New design for clean nuclear fusion reactor unveiled
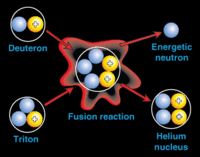
Researchers have patented a nuclear fusion reactor by inertial confinement which, in addition to being used to generate electric power in plants, could be applied to propel ships. The fusion chamber shape and size can adapt to the type of fuel being used.
-
-
Military systems hibernate on the sea floor, then woken up remotely
Almost half of the world’s oceans are more than four kilometers deep. This provides considerable opportunity for cheap stealth, but the vastness and depth make retrieval costs prohibitive. DARPA wants to developing deployable, unmanned, distributed systems which hibernate on the deep-ocean floor in special containers for years at a time. These deep-sea nodes would then be woken up remotely when needed and recalled to the surface
-
-
DARPA’s first FANG Challenge begun yesterday

More than 700 participants, organized in 150 teams, yesterday begun collaboration to design the mobility and drivetrain systems of a next-generation, amphibious infantry fighting vehicle. The goal of the competition is to compress the design-to-production time of a complex defense system by up to a factor of five.
-
-
Neutralizing the effects of lethal chemical agents
Organophosphorus agents (OPs) are used both in farm pesticides, and by terrorists and rogue states. About 200,000 people die each year across the world from organophosphorus agents (OP) poisoning, through occupational exposure, unintentional use, and misuse, mostly in developing countries like India, Pakistan, and Sri Lanka and through deliberate terrorist activities. OPs include compounds like Tabun, which was developed in 1936 by German scientists during the Second World War, Sarin, Soman, Cyclosarin, VX, and VR. Researchers develop an enzyme treatment which could neutralize the effects of OPs.
-
-
Catching up: Indian and Chinese companies at the forefront of innovation
In a few short years, the Chinese and Indian share of the world’s research and development centers has increased from 8 to 18 percent. A new study says that India and China invest more than the West in organizational innovation, that is, the implementation of a company structure that creates a favorable climate for new inventions.
-
More headlines
The long view
New Technology is Keeping the Skies Safe
DHS S&T Baggage, Cargo, and People Screening (BCP) Program develops state-of-the-art screening solutions to help secure airspace, communities, and borders
Factories First: Winning the Drone War Before It Starts
Wars are won by factories before they are won on the battlefield,Martin C. Feldmann writes, noting that the United States lacks the manufacturing depth for the coming drone age. Rectifying this situation “will take far more than procurement tweaks,” Feldmann writes. “It demands a national-level, wartime-scale industrial mobilization.”
How Artificial General Intelligence Could Affect the Rise and Fall of Nations
Visions for potential AGI futures: A new report from RAND aims to stimulate thinking among policymakers about possible impacts of the development of artificial general intelligence (AGI) on geopolitics and the world order.
Keeping the Lights on with Nuclear Waste: Radiochemistry Transforms Nuclear Waste into Strategic Materials
How UNLV radiochemistry is pioneering the future of energy in the Southwest by salvaging strategic materials from nuclear dumps –and making it safe.
Model Predicts Long-Term Effects of Nuclear Waste on Underground Disposal Systems
The simulations matched results from an underground lab experiment in Switzerland, suggesting modeling could be used to validate the safety of nuclear disposal sites.
