-
Rapid test strips detect swimming water contamination
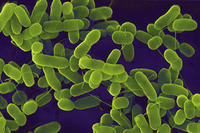
Water-testing technology has never been fast enough to keep up with changing conditions, nor accessible enough to check all waters; researchers have developed a rapid testing method using a simple paper strip that can detect E. coli in water within minutes; the new tool can close the gap between outbreak and detection, improving public safety
-
-
Efficiency of multi-hop wireless networks boosted
Multi-hop wireless networks can provide data access for large and unconventional spaces, but they have long faced significant limits on the amount of data they can transmit; now researchers have developed a more efficient data transmission approach that can boost the amount of data the networks can transmit by 20 to 80 percent
-
-
Cellphones could soon see through walls
Researchers have designed an imager chip that could turn mobile phones into devices that can see through walls, wood, plastics, paper, and other objects; the chip exploits the terahertz band of the electromagnetic spectrum, which is one of the wavelength ranges that falls between microwave and infrared, and which has not been accessible for most consumer devices
-
-
Robust nanosponges soak up oil again and again
Researchers show that nanotube blocks hold promise for environmental cleanup following oil spills or other disasters; the robust sponge can be used repeatedly and stands up to abuse; a sample nanosponge remained elastic after about 10,000 compressions in the lab; the sponge can also store the oil for later retrieval
-
-
E-beam technology to keep food supply safe
More than two million people a year, most of them children, die from food-borne or water-borne illness; more than one-third, or 1.3 billion tons, of the food produced for human consumption every year is wasted or lost because of spoilage; the UN nuclear weapons watch dog, the IAEA, says that irradiating food is a more effective solution for preventing death, illness, and food spoilage than techniques currently in use: heating, refrigerating, freezing, or chemical treatment
-
-
Researchers use electricity to generate alternative fuel
Scientists show that we can use electricity to power our cars — even if these cars are not electric vehicles; the researchers demonstrated a method for converting carbon dioxide into liquid fuel isobutanol using electricity
-
-
Containing a tunnel flood with an inflatable giant plug

Researchers have developed a giant plug to contain tunnel floods; the plug inflates (with water or air) to dimensions of roughly 32-feet-long and by 16-feet-wide, and holds 35,000 gallons, about the same capacity as a medium-sized backyard swimming pool
-
-
Test strip detects TNT and other explosives in water
Scientists developed a new explosives detector that can sense small amounts of TNT and other common explosives in liquids instantly with a sensitivity that rivals bomb-sniffing dogs, the current gold standard in protecting the public from terrorist bombs
-
-
Rapid, low-cost, point-of-care flu detection demonstrated

The novel H1N1 flu pandemic in 2009 underscored weaknesses in methods widely used to diagnose the flu, from frequent false negatives to long wait times for results; scientists demonstrate a prototype rapid, low-cost, accurate, point-of-care device that promises a better standard of care
-
-
A swarm of small satellites to deflect menacing asteroids
New research suggests that the best way to divert an asteroid hurtling toward Earth is using a swarm of relatively small satellites flying in formation and cooperatively firing solar-powered lasers onto an asteroid; this would be a more effective way than the current methods being contemplated, which are focused on large unwieldy spacecraft
-
-
Machine can tell when a human being is lying
In a study of forty cases, a computer correctly identifies liars more than 80 percent of the time, a better rate than humans with the naked eye typically achieve in lie-detection exercises
-
-
New plastics mimic human skin: they “bleed” when scratched, then heal
Plastics have become so common, replacing steel, aluminum, glass, paper, and other traditional materials because they combine desirable properties such as strength, light weight, and corrosion resistance; a new genre of plastics that mimic the human skin’s ability to heal scratches and cuts offers the promise of endowing military and first response gear – and consumer goods – with self-repairing surfaces
-
-
Firefly technology sheds new light
A new device, employing the same chemical which lights up fireflies, can easily detect food contamination; the researchers who developed the system hope it will soon be used to test for other diseases, including HIV-AIDS
-
-
Robot jellyfish for underwater search and rescue
Researchers have built a robotic swimmer that mimics the motion of a jellyfish; the device will because for underwater search and rescue missions
-
-
Breakthrough in next gen nuclear detectors

Researchers have long struggled to develop radiation detectors that can spot a nuclear device hidden away in a shielded case, but a recent breakthrough could change all that
-
More headlines
The long view
New Technology is Keeping the Skies Safe
DHS S&T Baggage, Cargo, and People Screening (BCP) Program develops state-of-the-art screening solutions to help secure airspace, communities, and borders
Factories First: Winning the Drone War Before It Starts
Wars are won by factories before they are won on the battlefield,Martin C. Feldmann writes, noting that the United States lacks the manufacturing depth for the coming drone age. Rectifying this situation “will take far more than procurement tweaks,” Feldmann writes. “It demands a national-level, wartime-scale industrial mobilization.”
How Artificial General Intelligence Could Affect the Rise and Fall of Nations
Visions for potential AGI futures: A new report from RAND aims to stimulate thinking among policymakers about possible impacts of the development of artificial general intelligence (AGI) on geopolitics and the world order.
Keeping the Lights on with Nuclear Waste: Radiochemistry Transforms Nuclear Waste into Strategic Materials
How UNLV radiochemistry is pioneering the future of energy in the Southwest by salvaging strategic materials from nuclear dumps –and making it safe.
Model Predicts Long-Term Effects of Nuclear Waste on Underground Disposal Systems
The simulations matched results from an underground lab experiment in Switzerland, suggesting modeling could be used to validate the safety of nuclear disposal sites.
