-
“Smart Connector” to detect, pinpoint damage to cellular cables

Researchers have developed the Smart Connector, a new sensor that once installed in the connecting units of coaxial cables can provide information about equipment damage and pinpoint the exact location through self-diagnosing technologies — some of the most advanced in the field today
-
-
A UAV that uses wind power as a bird does

An engineering Ph.D. students wins prizes for the design of an unmanned aerial vehicle (UAV) — dubbed Green Falcon II — which would be powered by the sun and wind; “While all airplanes mimic the shape of birds, the Green Falcon II will literally use the wind to power its movement, just as a bird would,” the young inventor says
-
-
Research may yield more compact antennas for military use
Researchers say that the tall, bulky antennas the U.S. military uses could be scrapped for low-profile, broadband antennas — thanks to a different approach to antenna design that replaces large dipole antennas with a more compact and conformal multi-mode radiator
-
-
Portable wastewater system generates energy, produces drinking water

Researchers are working to develop a portable wastewater treatment system that could improve the military’s efficiency; the solar-bio-nano project also will generate energy and produce drinking water, thus providing a potential blueprint for the future of municipal/agricultural wastewater treatment systems
-
-
Large-scale power storage for the energy grid

The sun does not always shine and the wind does not always blow; Stanford University researchers have used nanoparticles of a copper compound to develop a high-power battery electrode that is inexpensive to make, efficient and durable that it could be used to build batteries big enough for economical large-scale energy storage on the electrical grid
-
-
Insects to become first responders, aid in search and rescue

Researchers are finding ways to harvest energy from insects, holding the promise of using insects to aid in first response and search and rescue, and monitor hazardous situations before sending in humans
-
-
Harvard-designed swarm robots licensed to Swiss company

Harvard researchers developed Kilobot — a low-cost, easy-to-use robotic system for advancing development of “swarms” of robots; robot swarms might one day tunnel through rubble to find survivors, monitor the environment and remove contaminants, and self-assemble to form support structures in collapsed buildings
-
-
Jellyfish-like robot for underwater surveillance

Researchers at the Department of Mechanical Engineering at Virginia Tech built an unmanned underwater vehicle (UUV) inspired by jellyfish morphology and propulsion mechanism
-
-
Ionized plasmas as cheap sterilizer in tough places
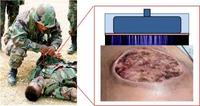
Scientists show that ionized plasmas like those in neon lights and plasma TVs not only can sterilize water, but make it antimicrobial; these plasma devices could be life-savers in developing countries, disaster areas, or on the battlefield where sterile water for medical use is in short supply and expensive to produce
-
-
Terahertz helps detection
Terahertz waves make collecting meteorological data from space, searching for flaws on an aircraft fuselage, or using certain medical diagnostics easier and more accurate
-
-
Nature inspires advances in ultrasound technology
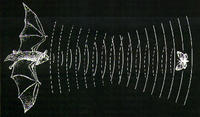
Sonar and ultrasound, which use sound as a navigational device and to paint accurate pictures of an environment, are the basis of many technologies, including medical ultrasound machines and submarine navigation systems; when it comes to more accurate sonar and ultrasound, however, animals’ “biosonar” capabilities still have the human race beat – but not for long
-
-
Brazilian fern inspires waterproof coating
A floating weed that clogs waterways around the world has at least one redeeming feature: it has inspired a high-tech waterproof coating intended for boats and submarines
-
-
Innovative ultrasonic nozzle changes the way water cleans
Scientists have developed a revolutionary ultrasonic attachment for taps, which massively enhances the ability of water to clean; currently, industry uses excessive water, power, and additives for cleaning
-
-
Hybrid power plants: cost effective way to go green
Hybrid cars, powered by a mixture of gas and electricity, have become a practical way to “go green” on the roads; now researchers at Tel Aviv University are using the hybrid approach to power plants as well
-
-
New tech could turn clothes into touch sensors
Everything from clothes and headphone wires to coffee tables could soon become interactive touch devices thanks to the development of new sensor technology; researchers at the University of Munich and the Hasso Plattner Institute are working to integrate technology originally designed to detect damaged underwater cables into touch sensors that can be installed in virtually anything
-
More headlines
The long view
New Technology is Keeping the Skies Safe
DHS S&T Baggage, Cargo, and People Screening (BCP) Program develops state-of-the-art screening solutions to help secure airspace, communities, and borders
Factories First: Winning the Drone War Before It Starts
Wars are won by factories before they are won on the battlefield,Martin C. Feldmann writes, noting that the United States lacks the manufacturing depth for the coming drone age. Rectifying this situation “will take far more than procurement tweaks,” Feldmann writes. “It demands a national-level, wartime-scale industrial mobilization.”
How Artificial General Intelligence Could Affect the Rise and Fall of Nations
Visions for potential AGI futures: A new report from RAND aims to stimulate thinking among policymakers about possible impacts of the development of artificial general intelligence (AGI) on geopolitics and the world order.
Keeping the Lights on with Nuclear Waste: Radiochemistry Transforms Nuclear Waste into Strategic Materials
How UNLV radiochemistry is pioneering the future of energy in the Southwest by salvaging strategic materials from nuclear dumps –and making it safe.
Model Predicts Long-Term Effects of Nuclear Waste on Underground Disposal Systems
The simulations matched results from an underground lab experiment in Switzerland, suggesting modeling could be used to validate the safety of nuclear disposal sites.
