-
Solar UV disinfects drinking water

More than 800 million people around the world lack access to clean water; the water available for people to drink in many developing countries has not been treated to remove contaminants, including pathogenic microorganisms; half of the world’s hospital beds are occupied by people who are sickened by the water they drink; Purdue University researchers have invented a water-disinfection system that uses the sun’s ultraviolet radiation to inactivate waterborne pathogens
-
-
Global water market could hit $800 billion by 2035
Analysts are predicting that the global market for water could grow dramatically over the next two decades, with some projecting a $1 trillion market in 2020; “Water is the fastest growing market at the moment, with a size of $500 billion globally,” said Harri Kerminen, the president and CEO of Finnish chemical firm Kemira
-
-
Maintaining water quality
Scientists at Kansas State University and seven other collaborating institutions were recently awarded $3.3 million from the National Science Foundation (NSF) to conduct a-large scale study of how stream organisms influence water quality across North America
-
-
Saltwater intrusion threatens South Florida’s water supplies
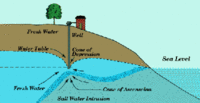
South Florida’s water supply is becoming increasingly endangered by saltwater that is steadily seeping in from the ocean and contaminating supplies; despite the best efforts of local communities to stop the problem, saltwater intrusion is spreading
-
-
Simple solution for removing arsenic from water

Almost 100 million people in developing countries are exposed to dangerously high levels of arsenic in their drinking water, unable to afford complex purification technology; scientists developed a simple, inexpensive method for removing arsenic based on chopped up pieces of ordinary plastic beverage bottles coated with a nutrient found in many foods and dietary supplements
-
-
Wastewater recycling adds to greenhouse gas emissions

New research shows that wastewater recycling processes may generate more greenhouse gases than traditional water-treatment processes; still, there are good reasons to continue keep wastewater recycling among the water-resource tools for urban areas
-
-
Thermopower waves advance a new energy future
Thermopower waves in thermoelectric materials can convert heat from solid fuels into electrical energy, in research that advances the vision of “smartdust” and other truly autonomous micro and nanomachines; “smartdust” systems are micro-electromechanical systems that are networked wirelessly for sensing and receiving data, for example testing pH of soil in large agricultural fields or quality of water reserves
-
-
Bacteria--Energy Producers of the Future?
A lot of the water we use daily goes to waste — whether it goes down drains, sewers, or toilets, much of it ends up at a wastewater treatment plant where it undergoes rigorous cleaning before it flows back to the environment; researchers are looking at processes which would turn wastewater into energy
-
-
Tap water in Copenhagen contaminated with E.coli
Parts of the Danish capital Copenhagen were without clean drinking water Saturday after high levels of the E.coli bacteria were detected in the municipal tap water system
-
-
Cleaning water while generating energy
A fuel cell system that can generate electricity from organic compounds and clean up wastewater at the same time has been developed by scientists in China; the cell uses light energy to degrade organic compounds in wastewater, generating electrons that pass through to the cathode, which converts the chemical energy into electrical energy
-
-
Towing icebergs to provide fresh water for parched regions

A third of the world’s population — more than two billion people — lives without access to clean drinking water, and studies show that the situation will only get worse; a French innovator has an idea: towing icebergs from the Greenland and Antarctica to regions most in need of fresh water; a computer simulation shows this solution to be viable and affordable
-
-
Solar-based method to provide safe water

A revolutionary low-cost technique that uses sunshine to provide safe drinking water; solar disinfection (SODIS) of drinking water is an effective way of preventing water-borne diseases such as cholera, dysentery or polio — especially important in developing countries, where safe drinking water is often a precious rarity
-
-
New desalination technology to help solve world's water shortage

Over one-third of the world’s population already lives in areas struggling to keep up with the demand for fresh water. By 2025, that number will nearly double; a new study argues that seawater desalination should play an important role in helping combat worldwide fresh water shortages once conservation, reuse, and other methods have been exhausted
-
-
New device identifies unknown liquids instantly
Materials scientists and applied physicists have invented a new device that can instantly identify an unknown liquid; the 3D-nanostructured chip offers a litmus test for surface tension (and doubles as a carrier for secret messages); the researchers are currently developing more precisely calibrated chips and conducting field tests with government partners for applications in quality assurance and contaminant identification
-
-
Water purification unit generates its own energy
A new biological water purification facility developed by Siemens generates enough methane gas to power its own operations; it also produces much less sludge than conventional systems; the test facility is mlocated in Singapore, and the city state is building a much larger pilot facility — one that will process 300 times more effluent than its predecessor, or about as much sewage water as is produced by around 1,000 people
-
More headlines
The long view
Water Wars: A Historic Agreement Between Mexico and US Is Ramping Up Border Tension
As climate change drives rising temperatures and changes in rainfall, Mexico and the US are in the middle of a conflict over water, putting an additional strain on their relationship. Partly due to constant droughts, Mexico has struggled to maintain its water deliveries for much of the last 25 years, deliveries to which it is obligated by a 1944 water-sharing agreement between the two countries.
