-
Mississippi man arrested for sending ricin letters to Obama, Sen. Wicker
The FBI confirmed yesterday (Wednesday) that a letter addressed to President Obama was found to contain the toxin ricin. As is the case with all the mail sent to the White House, the letter was screened in a remote mail sorting facility in Anacostia, a neighborhood in southeast Washington, D.C., and intercepted. The FBI arrested a man from Tupelo, Mississippi, on suspicion that he was behind the ricin letters to the White House and to Senator Roger Wicker (R-Mississippi), who lives in Tupelo.
-
-
Experts will meet in September for the bi-annual anthrax research conference
More than 300 scientists and researchers from all over the world who work on Bacillus anthracis, the causative agent of anthrax, and B. cereus and B. thuringiensis, two closely related bacilli, will be heading to Victoria, British Columbia for the Bacillus ACT 2013 conference, which will be held 1-5 September.
-
-
Footwear safety reflectors help in detecting bioterror threats

Tiny versions of the reflectors on sneakers and bicycle fenders that help ensure the safety of runners and bikers at night are moving toward another role in detecting bioterrorism threats and diagnosing everyday infectious diseases, scientists said the other day.
-
-
Arsenic contamination in food and water supplies
After virtually eliminating arsenic as a useful tool for homicide, science now faces challenges in doing the same for natural sources of this fabled old “inheritance powder” that contaminates water supplies and food, threatening more than thirty-five million people worldwide.
-
-
Concerns grow over repeated safety failures at U.S. BioLabs
According to a report that was released by the Government Accountability Office (GAO) late last month, the United States is at a high risk for accidents at laboratories which conduct research on potential bioterror germs such as anthrax because federal officials have failed to develop national standards for lab design, construction, and operation.
-
-
Finding the right tools to respond to suspicious powder incidents

HazMat teams across the United States respond to hundreds of white powder calls each year in large cities where quick decision-making is critical. DHS makes it easier to buy the right technology for bio-threat incidents.
-
-
New device will quickly detect botulinum, ricin, other biothreat agents
Researchers are developing a medical instrument which will be able quickly to detect a suite of biothreat agents, including anthrax, ricin, botulinum, shiga, and SEB toxin. The device, once developed, approved by the Food and Drug Administration (FDA), and commercialized, would most likely be used in emergency rooms in the event of a bioterrorism incident.
-
-
Same-day water test keeps beaches open, swimmers’ health protected

With warm summer days at the beach on the minds of millions of winter-weary people, scientists are reporting that use of a new water quality test this year could prevent unnecessary beach closures, while better protecting the health of swimmers.
-
-
Nanobiotechnology kills listeria, other food-borne pathogens, dead
Researchers, using nature as their inspiration, successfully attached cell lytic enzymes to food-safe silica nanoparticles, and created a coating with the demonstrated ability selectively to kill listeria — a dangerous foodborne bacteria that causes an estimated 500 deaths every year in the United States. The coating kills listeria on contact, even at high concentrations, within a few minutes without affecting other bacteria.
-
-
U.S. Army helps in chemical testing of meat product

When a South Dakota beef producer voiced concerns over the safety of its product to a meat inspection staff, the Animal Disease Research and Diagnostic Laboratory at South Dakota State University, called on the U.S. Army Research, Development and Engineering Command’s chemical-biological center (ECBC) – and the ECBC answered.
-
-
June workshop on approaches to CBRNE incidents
NIST-organized workshop will explore ways to improve an all-of-government approach that increases resilience to international chemical, biological, radiological, nuclear, or explosive (CBRNE) incidents.
-
-
Audits find “troubling” security flaws in CDC labs
Laboratories at the Centers for Disease Control Prevention (CDC) have been cited in government audits for failing to secure bioterror agents such as anthrax and plague. The audits also found that employees handling these agents have not been trained properly to do so.
-
-
DHS awards contract for utility plant at the Kansas biolab
DHS has awarded a $40 million contract to build a utility plant at a $1.15 billion animal research lab in Kansas. The 87,000 square foot facility will replace an animal research lab on Plum Island in New York and will be used to research deadly animal diseases that affect livestock.
-
-
Improving detection of, responses to biological warfare
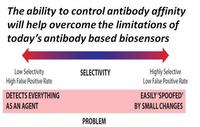
Biological warfare agents pose more than a hypothetical threat to U.S. soldiers. Troops operate in hostile areas where they could come under attack from adversaries wielding bio-agents like anthrax and toxins. The first step in reacting to any such attack is knowing that it occurred. Quickly and accurately identifying the presence of airborne antigens can be difficult given their complexity, the presence of numerous similar microorganisms in the environment, and the fact that even minute quantities of a threat agent can cause infection. Researches seek to advance sensitivity and durability of antibody-based biosensors better to protect soldiers.
-
-
Promising substance for better cyanide antidote for terrorist attacks
In an advance toward closing a major gap in defenses against terrorist attacks and other mass casualty events, scientists are reporting discovery of a promising substance that could be the basis for development of a better antidote for cyanide poisoning.
-
- All
- Regional
- Water
- Biometrics
- Borders/Immig
- Business
- Cybersecurity
- Detection
- Disasters
- Government
- Infrastructure
- International
- Public health
- Public Safety
- Communication interoperabillity
- Emergency services
- Emergency medical services
- Fire
- First response
- IEDs
- Law Enforcement
- Law Enforcement Technology
- Military technology
- Nonlethal weapons
- Nuclear weapons
- Personal protection equipment
- Police
- Notification /alert systems
- Situational awareness
- Weapons systems
- Sci-Tech
- Sector Reports
- Surveillance
- Transportation
Advertising & Marketing: advertise@newswirepubs.com
Editorial: editor@newswirepubs.com
General: info@newswirepubs.com
2010-2011 © News Wire Publications, LLC News Wire Publications, LLC
220 Old Country Road | Suite 200 | Mineola | New York | 11501
Permissions and Policies
Editorial: editor@newswirepubs.com
General: info@newswirepubs.com
2010-2011 © News Wire Publications, LLC News Wire Publications, LLC
220 Old Country Road | Suite 200 | Mineola | New York | 11501
Permissions and Policies
