-
Faster way to spot bacteria-tainted food -- and prevent illness
The regular appearance of food poisoning in the news, including a recent event that led to the recall of more than 33,000 pounds of chicken, drives home the need for better bacterial detection long before meats and produce make it to the dinner table.
-
-
New anthrax-killing virus could offer new ways to detect, treat, and decontaminate anthrax bacillus
From a zebra carcass on the plains of Namibia in Southern Africa, researchers have discovered a new, unusually large virus (or bacteriophage) which infects the bacterium that causes anthrax. The novel bacteriophage could eventually open up new ways to detect, treat, or decontaminate the anthrax bacillus and its relatives that cause food poisoning. Bacteriophages are often highly specific to a particular strain of bacteria, and when they were first discovered in the early twentieth century there was strong interest in them as antimicrobial agents. The discovery of penicillin and other antibiotics, however, eclipsed phage treatments in the West, although research continued in the Soviet Union.
-
-
Salmonella biofilms extraordinarily difficult, if not impossible, to kill
In the United States, an estimated million-plus cases of Salmonella occurs annually, with 23,000 hospitalizations and 450 fatalities reported each year. Researchers find that once Salmonella bacteria get into a food processing facility and have an opportunity to form a biofilm on surfaces, it is likely to be extraordinarily difficult, if not impossible, to kill it.
-
-
U.S. conducted bioweapon tests in Japan in early 1960s
The U.S. Army tested biological weapons in Okinawa, Japan in the early 1960s when the United States ruled the prefecture. U.S documents confirmed that the tests, conducted at least a dozen times occurred between 1961 and 1962. The test involved releasing rice blast fungus over rice paddies in order to measure the agent’s effect on production. With hundreds of millions of people dependent on rice as a staple food, failure of rice production could result in mass starvation. The fungus infects crops naturally, and experts estimate it destroys enough rice to feed sixty million people a year.
-
-
New test for detecting newly emerging strains of drug-resistant superbug
Molecular assays for MRSA are used in active surveillance programs to identify colonized patients rapidly. Active surveillance is a proven strategy to reduce transmission in healthcare settings and it helps prevent infection in vulnerable patients. BD Diagnostics has received FDA clearance to market the BD MAX MRSA XT Assay for use on the BD MAX System. This is the second assay from BD Diagnostics capable of detecting newly emerging MRSA strains with the novel mecC gene.
-
-
Air transportation data helps identify, predict pandemics
Computational model demonstrates how disease spreads in a highly connected world. The computational work has led to a new mathematical theory for understanding the global spread of epidemics. The resulting insights could not only help identify an outbreak’s origin but could also significantly improve the ability to forecast the global pathways through which a disease might spread.
-
-
Quick ID for water pathogens

New research purports to help people stay healthy by developing a real-time water bug testing that could precisely identify the culprits responsible for waterborne disease.
-
-
Innovative salmonella sensing system
Foodborne illnesses making one in six Americans — or forty-eight million people — sick each year. Of these people sickened, 128,000 end up in the hospital, according to the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention, while 3,000 die. A new approach to detecting food contamination enables real-time testing of food and processing plant equipment.
-
-
Innovative device speeds up food-pathogen detection
Researchers have developed a system that concentrates foodborne salmonella and other pathogens faster than conventional methods by using hollow thread-like fibers that filter out the cells, representing a potential new tool for speedier detection. The machine, called a continuous cell concentration device, could make it possible to routinely analyze food or water samples to screen for pathogens within a single work shift at food processing plants.
-
-
Discovery points way to treatment of lethal toxin botulism
Botulinum neurotoxins are produced by Clostridium botulinum and cause the possibly fatal disease botulism, which impedes nerve cells’ ability to communicate with muscles and can lead to paralysis and respiratory failure. The botulinum toxin has also been identified as a potential biological weapon against a civilian population. Scientists have decoded a key molecular gateway for the toxin that causes botulism, pointing the way to treatments that can keep the food-borne poison out of the bloodstream.
-
-
New detectors for chemical, biological threats
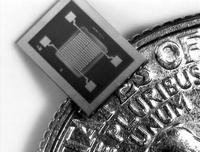
In the late 1990s, Sandia scientists developed a simple-to-use handheld chemical detector for the military, the MicroChemLab. Ever since, Sandia has improved such microfluidics- and microelectromechanical (MEMS) systems-based instruments that identify chemicals based on gas chromatography, or GC, and resonator-style instruments such as surface acoustic wave (SAW) detectors. The lab’s researchers are building on this sensor work to invent tiny detectors that can sniff out everything from explosives and biotoxins to smuggled humans.
-
-
Worries grow about Syria’s biological weapons capabilities, intentions
The debates among experts in Western and Middle Eastern intelligence services and militaries about the use of chemical weapons by the Assad regime revolve around how many times Assad has used chemical weapons, not whether such weapons were used. Neighbors of Syria have become increasingly alarmed – and, in private, have expressed their anxiety in discussions with the United States – about another illicit Syrian WMD program: biological weapons. The readiness of the Assad regime to use one proscribed weapon – chemicals — has led to growing unease among Syria’s neighbors that the regime may not find it too difficult to violate other weapon-related taboos. Biological weapons could give the Assad regime an effective means of retaliation because, if the weapon is well-designed, the lethal contents would spread easily without leaving tell-tale signs about the origin of the attack – or even evidence that there has been an attack.
-
-
Nanoparticles in food pose health risks
Nanomaterials are increasingly used in water treatment, food packaging, pesticides, cosmetics, and other areas. There is a growing concern that these particles could pose a potential health risk to humans and the environment. In a new study, researchers have developed a reliable method for detecting silver nanoparticles in foods.
-
-
New understanding of key step in anthrax infection
Scientists advance A new hypothesis concerning a crucial step in the anthrax infection process. The research teams have explored the behavior of the toxins that rapidly overwhelm the body as the often-fatal disease progresses. Their findings suggest a new possible mechanism by which anthrax bacteria deliver the protein molecules that poison victims. Anthrax is easily weaponized; the findings could help lead to a more effective cure.
-
-
Lawmakers, scientists question FBI’s investigation, conclusion in 2001 anthrax attacks

Twelve years after the fall 2001 anthrax attacks, and six years after the 2007 FBI’s determination that Bruce Ivins, a top government anthrax researcher at the U.S. Army Medical Research Institute of Infectious Diseases (USAMRIID), was the perpetrator of the attacks (Ivins died in 2008 of apparent suicide), lawmakers and USAMRIID scientists insist that the FBI’s conclusions are not supported by scientific evidence – indeed, that some basic scientific facts make the Bureau’s conclusions untenable.
-
- All
- Regional
- Water
- Biometrics
- Borders/Immig
- Business
- Cybersecurity
- Detection
- Disasters
- Government
- Infrastructure
- International
- Public health
- Public Safety
- Communication interoperabillity
- Emergency services
- Emergency medical services
- Fire
- First response
- IEDs
- Law Enforcement
- Law Enforcement Technology
- Military technology
- Nonlethal weapons
- Nuclear weapons
- Personal protection equipment
- Police
- Notification /alert systems
- Situational awareness
- Weapons systems
- Sci-Tech
- Sector Reports
- Surveillance
- Transportation
Advertising & Marketing: advertise@newswirepubs.com
Editorial: editor@newswirepubs.com
General: info@newswirepubs.com
2010-2011 © News Wire Publications, LLC News Wire Publications, LLC
220 Old Country Road | Suite 200 | Mineola | New York | 11501
Permissions and Policies
Editorial: editor@newswirepubs.com
General: info@newswirepubs.com
2010-2011 © News Wire Publications, LLC News Wire Publications, LLC
220 Old Country Road | Suite 200 | Mineola | New York | 11501
Permissions and Policies
