-
Turning mobile phones into detectors of disease-spreading insects
Insects transmit many of the world’s most infectious diseases, but there has been a decline in the expertise needed to recognize species of insects most likely to transmit illness to people. In a new effort to safeguard human populations, a team of scientists, computer programmers, public health officials, and artists is working to enable mobile phones to link up to computers that automatically identify species of disease-carrying insects.
-
-
The number of labs handling deadly germs grows, and so do calls for regulating lab safety
The number of labs handling dangerous pathogens continues to grow, and so does the number of accidents involving dangerous pathogens. The number of reported accidents involving dangerous microbes grew rapidly from just sixteen in 2004 to 128 in 2008, and 269 in 2010, the last year reported.Experts note that currently there is no single federal agency responsible for assessing overall laboratory needs — instead, departments and agencies only assess the needs for labs relative to their respective missions.
-
-
Concerns grow about CDC’s tracking, securing dangerous pathogens under its supervision
Last week, Centers for Disease Control and Prevention(CDC) officials reported that the same federal scientist who found vials of smallpox in a Food and Drug Administration(FDA) cold storage room at the National Institutes of Healthfacility in Bethesda, Maryland, also found a collection of 327 vials which could contain pathogens like dengue, influenza, and rickettsia. The new revelation adds to growing concerns about the government’s ability to track and secure dangerous pathogens under its supervision.”It is ironic that the institution that sets U.S. standards for safety and security of work with human pathogens fails to meet its own standards,” says a security expert. “It is clear that the CDC cannot be relied upon to police its own select-agent labs.”
-
-
Head of biosecurity advisory panel: Board is stalling as a result of slow fed policy work
The head of a federal biosecurity advisory committee says delays in the development of a national policy on institutional oversight of risky life-sciences research are the main reason the committee has been inactive for close to two years. The dormancy of the National Science Advisory Board for Biosecurity (NSABB) was pushed into the spotlight this week with the revelation that the eleven remaining original members of the 23-member board are being replaced. The board was set up in 2005 to advise the government on biosecurity and dual-use research, meaning research that can be exploited for harm as well as good.
-
-
Investigation finds serious violations of safety rules in CDC’s handling of deadly germs
An investigation by the U.S. Department of Agriculture’s (USDA) Animal and Plant Health Inspection Service(APHIS) conducted a review, from 23 June to 3 July, of the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention(CDC), and cited the agency for failing to follow proper procedures before and after the anthrax scare which led to the potential exposure of more than eighty lab workers to live anthrax viruses in June.APHIS found multiple violations of federal rules for handling dangerous microbes.
-
-
Following accidents, CDC shuts down anthrax, flu labs
Federal officials announced on Friday that they had temporarily closed the flu and anthrax laboratories at the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC) in Atlanta and halted shipments of all infectious agents from the agency’s highest-security labs. The announcement followed revelations about two recent accidents involving deadly agents at the CDC campus in Atlanta. Critics said the accidents highlighted an even greater danger – the efforts at some labs to create superstrains of deadly viruses (what is called “gain of function” research). “You can have all the safety procedures in the world, but you can’t provide for human error,” a critic of gain-of-function research said.
-
-
Smallpox vials found unguarded at NIH campus in Bethesda, Md.
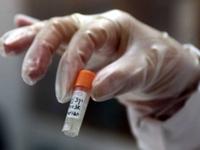
Earlier this month workers clearing out a Food and Drug Administration(FDA) branch office at the National Institutes of Health(NIH) campus in Bethesda, Maryland, discovered vials containing smallpox, an eradicated agent feared for its bioweapons potential. The last smallpox samples in existence were thought to be held at tightly guarded facilities in Atlanta and the State Research Center of Virology and Biotechnologyin Novosibirsk, Russia. The vials appear to date from the 1950s.
-
-
Convergence of chemistry and biology raises concerns about designer toxins
The convergence of chemistry and biology is providing major benefits to humankind, particularly in health care, alternative energy sources, and in environmental control – and when combined with other advances, particularly in nanotechnology, it is also being exploited in developing improved defensive countermeasures against chemical and biological warfare agents. This convergence, however, has also raised concerns that biotechnology could be applied to the production of new toxic chemicals, bioregulators, and toxins. A new report from OPCW says that the potential for scaling up biological processes for large scale production of chemicals of concern is still limited, but biomediated processes might still be effective for producing weaponizable quantities of toxins which are lethal to humans in microgram or lower dosage.
-
-
CDC says anthrax infection “highly unlikely,” but reassigns bioterror lab chief
The U.S. Centers for Disease Control and Prevention(CDC) has advised some of its employees to stop taking antibiotics meant to fight a possible anthrax infection after preliminary tests suggest that it is “highly unlikely” those employees were exposed to live anthrax following an incident in June. Michael Farrell, head of the CDC bioterror lab, has been reassigned.
-
-
Congress debates BioShield funding while medical schools debate bioterrorism training
Just as researchers urge medical schools across the United States to include bioterrorism preparedness courses in their curricula, Congress is debating whether to continue spending on Project Bioshield, an initiative launched in 2004 to incentivize otherwise unprofitable research on treatments for rare outbreaks or bioterror agents such as anthrax and botulinum toxin.
-
-
Better tools for tracing food-borne illness to source
Research could make it easier for public health investigators to determine if a case of food poisoning is an isolated incident or part of a larger outbreak. The study focuses on a test called multi-locus variable number tandem repeats variable analysis (MLVA). The test, which is increasingly used in the detection and investigation of foodborne outbreaks, analyzes specific sequences of DNA (called loci) that change rapidly enough over time to distinguish outbreak strains from other circulating strains of the bacteria but not so rapidly that connections could be masked by changes arising during the course of an outbreak.
-
-
Congress may modify the amount, manner by which Project BioShield procurements are funded
In 2004, Congress passed the Project BioShield Act to provide the federal government with new authorities related to the development, procurement, and use of medical countermeasures against chemical, biological, radiological, and nuclear (CBRN) terrorism agents. Among other things, the authority allows the government to guarantee a market for CBRN medical countermeasures. Under this provision, the secretary of Health and Human Services (HHS) may obligate funds to purchase countermeasures that still need up to ten more years of development. Since 2004, HHS has obligated approximately $3.309 billion to guarantee a government market for countermeasures against anthrax, smallpox, botulism, radiation, and nerve agents. Another provision established a process through which the HHS secretary may temporarily allow the emergency use of countermeasures which lack Food and Drug Administration (FDA) approval. The 113th Congress may also consider modifying the amount and manner by which it funds Project BioShield procurements.
-
-
Advancing microbial forensics to respond to global biological outbreaks
Much as human DNA can be used as evidence in criminal trials, genetic information about microorganisms can be analyzed to identify pathogens or other biological agents in the event of a suspicious disease outbreak. Biological outbreaks can include natural occurrences, accidental, or negligent releases from laboratories, biocrimes aimed at individuals or small groups, or acts of bioterrorism and biowarfare intended to affect large populations. The tools and methods used to investigate such outbreaks belong to an emerging discipline known as microbial forensics, but the field faces substantial scientific and technical challenges, says a new report.
-
-
Scientists: immediate action required to address superbugs’ threat
Scientists warn that drug-resistant superbugs demand an immediate, serious response and that the steps required to plan for these pathogens were not properly taken in previous decades. “[A] world without effective antibiotics would be ‘deadly,’ with routine surgery, treatments for cancer and diabetes and organ transplants becoming impossible,” says one scientist. The scientists warn that if action is not taken immediately, the massive health gains made since Alexander Fleming’s discovery of penicillin in 1928 will be lost forever.
-
-
Canada donates Biosafety Level 3 modular laboratory to Caribbean health authorities
The Biological Security program of Canada’s Global Partnership Program(GPP) has officially transferred a new biological containment laboratory to the Caribbean Public Health Agency(CARPHA). The Biosafety Level 3 (BSL-3) modular laboratory facility, a first in the Caribbean and located in Port of Spain, Trinidad and Tobago, improves diagnostic capabilities for human and veterinary pathogens with high epidemic potential.
-
- All
- Regional
- Water
- Biometrics
- Borders/Immig
- Business
- Cybersecurity
- Detection
- Disasters
- Government
- Infrastructure
- International
- Public health
- Public Safety
- Communication interoperabillity
- Emergency services
- Emergency medical services
- Fire
- First response
- IEDs
- Law Enforcement
- Law Enforcement Technology
- Military technology
- Nonlethal weapons
- Nuclear weapons
- Personal protection equipment
- Police
- Notification /alert systems
- Situational awareness
- Weapons systems
- Sci-Tech
- Sector Reports
- Surveillance
- Transportation
Advertising & Marketing: advertise@newswirepubs.com
Editorial: editor@newswirepubs.com
General: info@newswirepubs.com
2010-2011 © News Wire Publications, LLC News Wire Publications, LLC
220 Old Country Road | Suite 200 | Mineola | New York | 11501
Permissions and Policies
Editorial: editor@newswirepubs.com
General: info@newswirepubs.com
2010-2011 © News Wire Publications, LLC News Wire Publications, LLC
220 Old Country Road | Suite 200 | Mineola | New York | 11501
Permissions and Policies
