-
Grid-scale batteries for storing renewable energy have large carbon footprint
Most of the electricity produced in the United States comes from coal- and natural gas-fired power plants. Only about 3 percent is generated from wind, solar, hydroelectric, and other renewable sources. A key problem is that the U.S. electrical grid has virtually no storage capacity, so grid operators cannot stockpile surplus clean energy and deliver it at night, or when the wind is not blowing. Stanford scientists have developed a novel way to calculate the energetic cost of building large batteries and other storage technologies for the electrical grid. The found that the fossil fuel required to build these technologies could negate some of the environmental benefits of installing new solar and wind farms.
-
-
New trends in cybersecurity and information security education

The Federal Information Systems Security Educators’ Association (FISSEA)promotes cybersecurity awareness, training, and education. The annual meeting,to be held 19-21 March 2013 at NIST headquartersin Gaithersburg, Maryland, is geared toward both new and seasoned security officers, IT managers, information security educators and researchers, cybersecurity trainers and teachers, and those involved in instructional design and curriculum development.
-
-
How to predict the progress of technology
MIT researcher finds Moore’s Law and Wright’s Law best predict how technology improves.
-
-
Precious metal recovery technique ideal for rare Earth elements purification
Researchers have come up with a new approach to make the recovery of high value precious metals faster and more economically viable. The new technique could be ideal for the purification of rare earth elements, which are vital commodities for ‘green’ technologies such as hybrid cars and novel batteries.
-
-
Coal and U.S electric power generation

Coal is an important fuel source in the United States today. Responsible for approximately 39 percent of the country’s electrical generation, coal is vital to the day-to-day operation of people’s lives. The United States is rich in coal deposits, with large resources. One of the most important and largest of those deposits is found in the Powder River Basin (PRB) of Wyoming and Montana, which, in 2012, produced more than 42 percent of the nation’s coal.
-
-
Stopping vehicle in their tracks -- remotely
The need to stop vehicles remotely was identified by the law enforcement community. In 2010, the characteristics of a squid’s sticky tendrils were combined with the concept of Spiderman’s super-strong webbing to create a prototype of the first remote device to stop vehicles in their tracks: the Safe, Quick, Undercarriage Immobilization Device (SQUID).
-
-
Arctic ice loss intensified Superstorm Sandy ferocity
If you believe that last October’s Superstorm Sandy was a freak of nature — the confluence of unusual meteorological, atmospheric and celestial events – then Cornell and Rutgers researchers suggest you should think again. The researchers report that the severe loss of summertime Arctic sea ice — attributed to greenhouse warming — appears to enhance Northern Hemisphere jet stream meandering, intensify Arctic air mass invasions toward middle latitudes, and increase the frequency of atmospheric blocking events like the one that steered Hurricane Sandy west into the densely populated New York City area.
-
-
New source for rare earth elements: discarded consumer products
In a new twist on the state’s mining history, a group of Idaho scientists will soon be crushing consumer electronics rather than rocks in a quest to recover precious materials. Two national labs in the state will apply expertise gained in recycling fissionable material from nuclear fuel to separate rare earth metals and other critical materials from crushed consumer products.
-
-
Using plants for herbal defluoridation of drinking water

A filtration system based on a medicinal herb can quickly and easily remove “fluoride” from drinking water, say researchers in India. The technology uses parts of the plant Tridax procumbens as a biocarbon filter for the ion.
-
-
World’s first zero emission sports car is built-at-home electric car

A new partnership has developed the world’s first build at home electric race car kit, an all-electric sports car designed and engineered to support a growing demand for zero emission racing vehicles. The iRacer kit, available from £13,999, can be transformed quickly between hybrid, pure electric, or internal combustion engines.
-
-
Enabling small ships to launch and retrieve long-endurance UAVs
About 98 percent of the world’s land area lies within 900 nautical miles of ocean coastlines. Enabling small ships to launch and retrieve long-endurance UAVs on demand would greatly expand the U.S. military’s situational awareness and ability quickly and flexibly to engage in hotspots over land or water. DARPA is seeking companies to develop these systems.
-
-
Global warming opening new shipping routes in Arctic Ocean
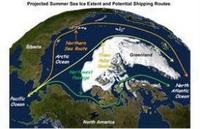
The Arctic Ocean has captured the imagination of explorers because of the possibility it offers for traveling between the Pacific and the Atlantic oceans through the Bering Strait. Until recently, however, sea ice has blocked access to the potential shortcut between Asia and North America or Europe. In the past two years, the ice has begun to melt in late summer to such an extent that even ordinary seagoing vessels have been able to enter its frigid waters. For vessels traveling between Rotterdam in the Netherlands and Yokohama, Japan, the Northern Sea Route is approximately 40 percent shorter than the traditional route through the Suez Canal.
-
-
Arsenic in groundwater in Bangladesh naturally occurring
Human activities are not the primary cause of arsenic found in groundwater in Bangladesh. Instead, a team of researchers found that the arsenic in groundwater in the region is part of a natural process that predates any recent human activity, such as intensive pumping.
-
-
Norfolk, Virginia, tries to cope with sea-level rise
Norfolk, Virginia, is home to the largest U.S. naval base in the country, and the second biggest commercial port on the U.S. Atlantic coast. Floods are an ever-present problem, a problem which has become worse in recent decades. The relative sea level around Norfolk has risen 14.5 inches (.37 meter) since 1930, when the low-lying downtown area routinely flooded. The frequency of storms-induced surges has increased as well.
-
-
The impact of sea-level rise on coastal military installations
The Pentagon says that climate-related effects are already being observed at Department of Defense (DoD) installations in every region of the United States and its coastal waters. The effects of climate change will adversely impact military readiness and DoD natural and built infrastructure unless these risks are considered in DoD decisions. A new white paper developed by the Pentagon’s Strategic Environmental Research and Development Program (SERDP) identifies key climate-related policy questions that need to be addressed.
-
More headlines
The long view
New Technology is Keeping the Skies Safe
DHS S&T Baggage, Cargo, and People Screening (BCP) Program develops state-of-the-art screening solutions to help secure airspace, communities, and borders
Factories First: Winning the Drone War Before It Starts
Wars are won by factories before they are won on the battlefield,Martin C. Feldmann writes, noting that the United States lacks the manufacturing depth for the coming drone age. Rectifying this situation “will take far more than procurement tweaks,” Feldmann writes. “It demands a national-level, wartime-scale industrial mobilization.”
How Artificial General Intelligence Could Affect the Rise and Fall of Nations
Visions for potential AGI futures: A new report from RAND aims to stimulate thinking among policymakers about possible impacts of the development of artificial general intelligence (AGI) on geopolitics and the world order.
Smaller Nuclear Reactors Spark Renewed Interest in a Once-Shunned Energy Source
In the past two years, half the states have taken action to promote nuclear power, from creating nuclear task forces to integrating nuclear into long-term energy plans.
Keeping the Lights on with Nuclear Waste: Radiochemistry Transforms Nuclear Waste into Strategic Materials
How UNLV radiochemistry is pioneering the future of energy in the Southwest by salvaging strategic materials from nuclear dumps –and making it safe.
Model Predicts Long-Term Effects of Nuclear Waste on Underground Disposal Systems
The simulations matched results from an underground lab experiment in Switzerland, suggesting modeling could be used to validate the safety of nuclear disposal sites.
