-
Precision agriculture using military technology: drones
Drones are military aircraft currently being repurposed for everyday use, especially within the growing field of precision agriculture; these flying robots allow farmers to detect changes in water content, plant health, and pesticide dispersal in their fields
-
-
Threat-recognition technology incorporates mind, machine

For soldiers operating in the field, the ability to detect threats from standoff distances can be life-saving; when advanced radar and drone coverage is not available, soldiers typically rely on their own vision to scan their surroundings; DARPA links human brainwaves, improved sensors, and cognitive algorithms to improve target detection
-
-
Tasered youth fare as well as adults: study

Adolescents who are tasered by law enforcement officers do not appear to be at higher risk for serious injury than adults, according to new a new study; the conclusions are based on a retrospective study of Taser use from law enforcement data collected by the largest, independent multicenter database established in 2005
-
-
First responders train to deal with a new threat: zombie attack

A company specializing in training military units, federal, and state agencies in security, force protection, emergency response,and disaster management, has a new threat incorporated into its disaster-crisis scenario, which is part of the firm’s annual counterterrorism summit in San Diego: a zombie attack
-
-
Sharp drop in illegal crossers notwithstanding, “border industrial complex” keeps growing
Since 1986, U.S. immigration enforcement has cost the U.S. government $219 billion dollars; almost 80,000 workers now depend on immigration enforcement for their employment; illegal immigration has dropped sharply over the last four years, and is now at a 1971 level — but the what some call the “border industrial complex” keeps growing and growing
-
-
Four-legged “pack mule” robots demonstrate their capabilities

Two completed prototype robotic “pack mules” exhibit reduced noise, new gaits, and improved perception, the two functioning platforms have started to run through the paces similar to what they could one day experience carrying gear for a squad of Marines or Soldiers
-
-
DARPA’s legged robot beats Usain Bolt’s speed record

Usain Bolt, Olympic gold medalist and world record-holder sprinter, set the world speed record for a human in 2009 when he reached a peak speed of 27.78 mph for a 20-meter split during the 100-meter sprint; DARPA’s Cheetah robot, already the fastest legged robot in history, bested Bolt recently by clocking at 28.3 mph for a 20-meter split
-
-
More cyber-secure UAVs
The software that runs complex military systems such as UAVs contains tens of thousands of lines of code; this code is designed by human beings, and human beings make mistakes; DARPA wants military systems to be run by fail-safe software, ad for this purpose has created the High-Assurance Cyber Military Systems (HACMS) program; Rockwell Collins has been selected as the prime contractor for the unmanned air vehicle portion of the HACMS
-
-
Security education is becoming a central part of security hiring, promotion
There is a growing emphasis on homeland security-related education in security hiring in both the private and government sectors; this growing demand has lead to a rapid growth in college and university degree programs in homeland security – the number of such programs is now estimated to be 350; trouble is, those programs do not have a commonly agreed upon curriculum, and as a result, the classes chosen to be part of an individual’s curriculum are based on the available faculty, rather than proven value to the students
-
-
Radiation-enabled computer chips allow low-cost security imaging systems
With homeland security on high alert, screening systems to search for concealed weapons are crucial pieces of equipment; these systems, however, are often prohibitively expensive, putting them out of reach for public spaces such as train and bus stations, stadiums, or malls, where they could be beneficial; until now
-
-
Forensic science in the dock
Two members of O. J. Simpson’s defense team founded the Innocence Project in 1992; since then, the project has helped exonerate almost 300 innocent people by challenging improper use of DNA testing and other elements of forensic science
-
-
Serious limitations make boost-phase missile interception impractical
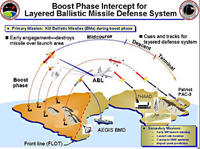
One of the central elements of President Reagan’s 1983 “Star Wars” ballistic missile defense initiative was boost-phase defense: boost-phase defense systems are intended to shoot down enemy missiles immediately following launch while the rocket engine is still firing; a new congressionally mandated study by the National Research Council study says that to defend against ballistic missile attacks more effectively, the United States should concentrate on defense systems that intercept enemy missiles in midcourse and stop spending money on boost-phase defense systems of any kind
-
-
DHS submersible Pluto mimics the real narco-subs
In the early 1990s, South American drug cartels came up with a new tactic to transport narcotics destined for the United States: small, radar-dodging, self-propelled, semi-submersibles (SPSSs); better to address the submersible problem, DHS Science and Technology Directorate created its own submersible and called it Pluto, after the planet which is difficult to spot
-
-
Apple rejects app which tracks drone strikes against militants
Apple has rejected an app, developed by a New York student, which tracks U.S. drone strikes in Pakistan; Apple said the app violated rule 16.1 of its guidelines, which bans “excessively objectionable or crude content”
-
-
New search-and-rescue tool: remotely controlled cockroaches

Researchers have developed a technique that uses an electronic interface to remotely control, or steer, cockroaches; remotely controlling cockroaches would allow first responders to create a mobile web of smart sensors that uses cockroaches to collect and transmit information, such as finding survivors in a building that has been destroyed by an earthquake
-
More headlines
The long view
Why Ukraine’s AI Drones Aren’t a Breakthrough Yet
Machine vision, a form of AI, allows drones to identify and strike targets autonomously. The drones can’t be jammed, and they don’t need continuous monitoring by operators. Despite early hopes, the technology has not yet become a game-changing feature of Ukraine’s battlefield drones. But its time will come.
