-
ONR’s augmented-reality project progresses

The Office of Naval Research (ONR) yesterday demonstrated the next phase of an augmented-reality project which will change the way soldiers view operational environments — literally
-
-
NYPD monitoring of Muslim communities did not produce a single terrorist lead

An NYPDunit which gathers information on Muslim communities and businesses in order to uncover links to terrorist plots has been unable to do so in six years of engaging in monitoring Muslim communities in New York and New Jersey
-
-
Napa Valley hospital employees fearful of new, wearable security system
Employees at a Napa Valley, California hospital are required to carry an alarm device on a lanyard around their necks; the alarm device is about the size of a smart phone and can send and receive signals during an emergency; after incidents in which psychiatric patients tried to choke employees by grabbing and twisting the lanyards, employees want other options for carrying the alarm device
-
-
Electronic nose detects airborne toxins down to the parts per billion level
Research create an electronic nose device with applications in agriculture, industry, homeland security, and the military; the device can detect small quantities of harmful airborne substances
-
-
How to act if there is a fire on a high-speed train

Researchers have used computer models to analyze the best way to evacuate the Spanish High Speed Train (AVE) in the case of fire; the involvement of the crew in organizing the fast transfer of passengers, completing the process before the train comes to a halt, and collective collaboration to assist those with reduced mobility are just some of the strategies to be followed
-
-
Y-12 and operator error
Three anti-nuclear activists, led by an 82-year old nun, breached the perimeter security system of the supposedly highly secure Y-2 nuclear facility at Oak Ridge, Tennessee, where nuclear weapons components are manufactured (note that the Oak Ridge National Laboratory [ONRL] is not affiliated with the Y-12 National Security Complex); they then spent several hours in a secure area of the facility, leisurely spray-painting slogans on the facility’s walls – without the facility’s security staff, or the sophisticated $500 million security cameras and sensors, detecting them; to understand what happened at Y-2, we must accept that operator error is an essential problem in national security, and that the problem is pervasive and normal; the only way to deal with the operator error phenomenon is to build redundancies into the system
-
-
Long Beach Police Department purchases underwater inspection system for port
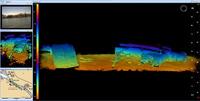
The Port of Long Beach is the second busiest seaport in the United States and is a major gateway for trade with Asia, handling more than six million containers annually; to enhance port security, the City of Long Beach Police Department has purchased an Underwater Inspection System (UIS) from Cod Octopus
-
-
Homeland security films informational but costly
Over the last four years the mayor’s office of Public Safety and Homeland Security in Houston, Texas, has spent $540,000 dollars to produce three short videos teaching people how to react in public safety emergencies; the price tag has some people upset
-
-
Court: Kentucky can continue to credit God for homeland security
The Kentucky Supreme Court has declined to hear a challenge to a state law that mandated that the commonwealth give credit to God for Kentucky’s homeland security; the Court let stand a 2011 Kentucky Court of Appeals ruling which found that a 2006 law, requiring the Kentucky Office of Homeland Security to publicize dependence on “Almighty God” in agency training and educational materials, did not violate the establishment clause in the Constitutional
-
-
Border Patrol kiosk detects liars trying to enter U.S.

The U.S. Customs and Border Protection (CBP) is using border crossing stations in Arizona to test new technology to detect liars as they attempt to enter the country; travelers are subjected to a 5-minute interview with the kiosk, while microphones monitor vocal pitch frequency and quality, an infrared camera monitors eye movement and pupil dilation, and a high definition camera monitors facial expression
-
-
New device dismantles pipe bombs safely, preserving forensic evidence
Thousands of pipe bombs are made each year, and thousands of pipe bomb threats are called into local police and FBI authorities across the country; many are false alarms, but those that are not can be deadly; dismantling a pipe bomb is tricky and serious business, and missteps during the dismantling process can produce catastrophic results
-
-
Home, office WiFi could be used by emergency responders
Wireless routers for homes and offices could be knitted together to provide a communications system for emergency responders if the mobile phone network fails
-
-
Drone use spreads to more areas and missions

As security challenges in the United State and around the globe change, many countries have one thing in common: unmanned drones will be a significant part of the future of security; advancements in technology are driving the use of UAVs into newareas
-
-
Concerns over terrorist groups gaining foothold in Latin America
At the moment, Islamic militant and terrorist groups do not seem to have a presence in Latin America, but concerns are growing that these groups could develop strategic links with drug organizations, posing a serious threat to security in the hemisphere
-
-
Unmanned civilian drones vulnerable to hijacking
Unmanned drones have become the eyes and ears of the military in recent years, giving them an advantage in intelligence gathering and in operations without risking soldiers’ lives; the drones’ versatility and low price have made them an attractive tool for domestic law enforcement and first response missions; there is one glitch, though: drones can be hijacked; if that happens, these swift, unmanned aircrafts could become weapons for terrorists
-
More headlines
The long view
Why Ukraine’s AI Drones Aren’t a Breakthrough Yet
Machine vision, a form of AI, allows drones to identify and strike targets autonomously. The drones can’t be jammed, and they don’t need continuous monitoring by operators. Despite early hopes, the technology has not yet become a game-changing feature of Ukraine’s battlefield drones. But its time will come.
