-
Clay-based coating holds promise of green flame retardants
The thick, fast-forming coating has a uniformly high concentration of flame-inhibiting clay particles, and it adheres strongly to the Swiss cheese-like surface of polyurethane foam, which is used in furniture cushions, carpet padding, children’s car seats, and other items
-
-
Container ships as offshore platforms for direct support to disaster zones
DARPA’s Tactically Expandable Maritime Platform (TEMP) program has completed the design of technologies to transform commercial container ships into self-contained floating supply bases during disaster relief operations, without needing port infrastructure
-
-
Biometrics proves 1 percent of applicants to enter U.S. are unsuitable
Chris Archer, the online content editor at IDGA (the Institute for Defense & Government Advancement), talked with James Loudermilk, Senior Level Technologist, FBI Science and Technology Branch, about biometrics and biometrics and homeland security; Loudermilk says that biometrics applications helped the FBI determine that about 1 percent of people who seek visa to visit the United States as tourists have previously done things that make them unsuitable guests; the conversation examines the application of biometrics for homeland security, issues relating to privacy and civil liberties, and what can be learned from international biometrics projects, including India’s UID scheme
-
-
Mega-quake hotspots around the world
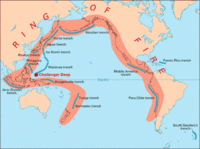
The 2010 earthquake in Haiti killed hundreds of thousands and destroyed large sections of the capital, Port au Prince; the clock is ticking on many earthquake faults throughout the world, and a comprehensive new book points to places around the world that could face the fate of Port au Prince
-
-
Crowd dynamics explains disaster at cultural, sports events
Physicists investigating a recent crowd disaster in Germany found that one of the key causes was that at some point the crowd dynamics turned turbulent, akin to behavior found in unstable fluid flows
-
-
Supreme Court deals near-fatal blow to Arizona SB 1070; states’ immigration efforts now in question

In a major victory for the Obama administration, the U.S. Supreme Court yesterday struck down three of the four main provisions in Arizona’s tough SB 1070 immigration law, saying these provisions were pre-empted by federal law; the Court left in place the fourth provision – the one requiring Arizona local law enforcement during routine stops to check the immigration status of anyone they suspect is in the country illegally – but in reading the provision very narrowly, the Court left its implementation open to legal challenges on grounds that it violates racial profiling prohibition and other laws; in any event, the administration moved quickly to make that remaining provision meaningless by pulling back on a program known as 287(g), which allows the federal government to deputize local officials to make immigration-based arrests; the move means that even if local police step up immigration checks, they will have to rely on federal officials to make the arrests
-
-
Turf wars: math model shows crimes cluster on borders between rival gangs

A mathematical model that has been used for more than eighty years to determine the hunting range of animals in the wild holds promise for mapping the territories of street gangs; among other things, the research demonstrates that the most dangerous place to be in a neighborhood packed with gangs is not deep within the territory of a specific gang, as one might suppose, but on the border between two rival gangs
-
-
Immigration growth in Spain has not caused more crime
Society tends to perceive an increase in the immigrant population with an increase in crime; according to a new study, however, it is not possible to infer this cause-effect relationship in the case of Spain
-
-
Forensic research using DNA sequencing technology
The Ion Personal Genome Machine (PGM) Sequencer translates chemical sequencing information directly into digital form by using semiconductor technology; it enables the analysis of ninety-six samples in one run, allowing forensic practitioners to obtain more information from the samples they process; the sequencer is suitable for a wide array of forensic identification applications, including missing persons identifications, mass disaster work, interpretations of complex mixtures, and bio-defense
-
-
Researchers advance biometric security
Researchers have developed a way for security systems to combine different biometric measurements — such as eye color, face shape, or fingerprints — and create a learning system that simulates the brain in making decisions about information from different sources
-
-
Gun shop which sold gun to Virginia Tech killer closes its doors

Madison, Wisconsin-based online weapon dealer TGSCO, which gained notoriety after it was disclosed that it had sold guns to three individuals – including the Virginia Tech killer — who then went on to commit mass killings, closed its doors last month
-
-
News: Man bites dog
A 22-year old man name Keith Glaspie, running away from police officers in Wilmington, North Carolina was chased and caught by well-trained, 2-year old police dog named Maxx; when Maxx would not let go of the Glaspie’s pants, preventing him from moving, Glaspie tore into Maxx’s ear with his teeth, severing the dog’s ear in two
-
-
New method uses gunshot residue to determine caliber, type of weapon used in crime
Researchers have developed a method to determine the caliber and type of weapon used in a crime by analyzing gunshot residue (GSR); using near-infrared (NIR) Raman microspectroscopy and advanced statistics, the new technique may play a pivotal role in law enforcement cases and forensic investigations
-
-
Smartphone app offers sex offender information
Two of the providers of technology to local sheriffs’ offices have announced a new content publishing agreement that will offer the public information on sex offenders
-
-
Belief in hell associated with reduced crime
A broad study, study following143,197 people in sixty-seven countries over twenty-six years, found that criminal activity is higher in societies in which people’s religious beliefs contain a strong punitive component than in places where religious beliefs are more benevolent; a country where many more people believe in heaven than in hell is likely to have a much higher crime rate than one where these beliefs are about equal
-
More headlines
The long view
AI-Controlled Fighter Jets May Be Closer Than We Think — and Would Change the Face of Warfare
Could we be on the verge of an era where fighter jets take flight without pilots – and are controlled by artificial intelligence (AI)? US R Adm Michael Donnelly recently said that an upcoming combat jet could be the navy’s last one with a pilot in the cockpit.
What We’ve Learned from Survivors of the Atomic Bombs
Q&A with Dr. Preetha Rajaraman, New Vice Chair for the Radiation Effects Research Foundation in Hiroshima and Nagasaki, Japan.
Need for National Information Clearinghouse for Cybercrime Data, Categorization of Cybercrimes: Report
There is an acute need for the U.S. to address its lack of overall governance and coordination of cybercrime statistics. A new report recommends that relevant federal agencies create or designate a national information clearinghouse to draw information from multiple sources of cybercrime data and establish connections to assist in criminal investigations.
Autonomous Weapon Systems: No Human-in-the-Loop Required, and Other Myths Dispelled
“The United States has a strong policy on autonomy in weapon systems that simultaneously enables their development and deployment and ensures they could be used in an effective manner, meaning the systems work as intended, with the same minimal risk of accidents or errors that all weapon systems have,” Michael Horowitz writes.
Twenty-One Things That Are True in Los Angeles
To understand the dangers inherent in deploying the California National Guard – over the strenuous objections of the California governor – and active-duty Marines to deal with anti-ICE protesters, we should remind ourselves of a few elementary truths, writes Benjamin Wittes. Among these truths: “Not all lawful exercises of authority are wise, prudent, or smart”; “Not all crimes require a federal response”; “Avoiding tragic and unnecessary confrontations is generally desirable”; and “It is thus unwise, imprudent, and stupid to take actions for performative reasons that one might reasonably anticipate would increase the risks of such confrontations.”
Luigi Mangione and the Making of a ‘Terrorist’
Discretion is crucial to the American tradition of criminal law, Jacob Ware and Ania Zolyniak write, noting that “lawmakers enact broader statutes to empower prosecutors to pursue justice while entrusting that they will stay within the confines of their authority and screen out the inevitable “absurd” cases that may arise.” Discretion is also vital to maintaining the legitimacy of the legal system. In the prosecution’s case against Luigi Mangione, they charge, “That discretion was abused.”
