-
Rebuilding dried-up swamps to protect New Orleans from hurricanes
During the past four decades, swamps and wetlands which used to offer New Orleans a natural defense against hurricane, were dried and paved over. The city has launched a new project to restore a key area of cypress swampland near the Lower 9th Ward, an effort they called essential to protecting the metro area in the event of another major hurricane.
-
-
White House: no evidence of, contact with extra terrestrials

Two petitions, signed by 17,000, were submitted to the White house; the first demanded immediate disclosure of the U.S. government’s knowledge of and communications with extraterrestrial beings, the second a formal acknowledgement from the White House that extraterrestrials have been engaging the human race; in response, the White House Office of Science & Technology Policy wrote that the U.S. government has no evidence that any life exists outside our planet, or that an extraterrestrial presence has contacted or engaged any member of the human race
-
-
Leeds sludge experts target nuclear waste
Researchers from the University of Leeds have teamed up with Sellafield Ltd. to clean up radioactive sludge produced by the U.K. nuclear industry; the newly formed Sludge Center of Expertise will play a key role in describing the behavior of the sludge wastes that have arisen after years of operation at Sellafield and other nuclear sites across the United Kingdom
-
-
A new pest threatens U.S. agriculture -- iPhone owners can help
A new meandering pest — the brown marmorated stink bug (BMSB) — is feasting on many of North America’s most important crops, posing an unprecedented threat to U.S. agriculture; the value of susceptible crops in the thirty-three states where BMSB has been established or sighted exceeds $21 billion
-
-
Environmentalists in arms over border decision
Yesterday, House Natural Resources Committee 26-17 vote to approve H.R. 1505, the National Security and Federal Lands Protection Act; the proposed legislation would waive thirty-six environmental and other laws for U.S. Customs and Border Patrol activities on public lands within 100 miles of U.S. borders; environmentalists are angry
-
-
Protecting structures against firebrand attack
NIST engineers have built a device that bellows showers of glowing embers, or firebrands, to test how structures can withstand this destructive aspects of wild fires; in Japan, where the device is now used in a test facility, firebrands are a growing peril that accounts for half of the nation’s ten most costly fires
-
-
Global water market could hit $800 billion by 2035
Analysts are predicting that the global market for water could grow dramatically over the next two decades, with some projecting a $1 trillion market in 2020; “Water is the fastest growing market at the moment, with a size of $500 billion globally,” said Harri Kerminen, the president and CEO of Finnish chemical firm Kemira
-
-
Environmentalists worry border environment protection
Environmentalists have taken aim at an amendment to the Senate appropriations bill for DHS that would allow border enforcement agencies ultimate authority within 100-miles of the U.S. border
-
-
Designing a new grid pylon

There are more than 88,000 pylons in the United Kingdom; they stand some 50-meters high, weigh around twenty tons, and carry up to 400,000 volts of electricity over thousands of kilometers of some of the most exposed, weather-beaten parts of Britain; the familiar steel lattice tower has barely changed since the 1920s; National Grid says it is time for a change
-
-
Earth's largest environmental catastrophe: 250 million year anniversary
The eruption of giant masses of magma in Siberia 250 million years ago led to the Permo-Triassic mass extinction when more than 90 percent of all species became extinct
-
-
Saltwater intrusion threatens South Florida’s water supplies
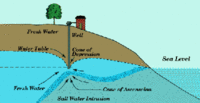
South Florida’s water supply is becoming increasingly endangered by saltwater that is steadily seeping in from the ocean and contaminating supplies; despite the best efforts of local communities to stop the problem, saltwater intrusion is spreading
-
-
Texas drought forces military to change training

A particularly severe drought in Texas has forced the military to change the way it trains its soldiers due to the risk of starting fires; law enforcement agencies would benefit from taking note of additional safety measures put into place
-
-
Severe drought in Georgia, 150 counties declared disaster areas
A severe drought and excessive heat has forced the U.S. Department of Agriculture to declare 150 counties in Georgia as primary natural disaster areas; the drought began on 15 April and has caused farmers to lose more than 30 percent of their pasture, grain crops, cotton, peanuts, tobacco, and forage crops
-
-
Sea level rise to take economic toll on California coast
California beach towns could face hefty economic losses caused by sea level rise, according to a new state-commissioned study; the study estimates the cost of coastal storm damage and erosion, both of which are expected to increase as sea levels rise
-
-
Carbon abatement technologies compete for prizes
The U.K. Technology Strategy Board is investing up to £4.5 million in carbon abatement technologies (CATs), centered mainly on innovative projects with strong elements of technology demonstration; to select the technologies, the TSB is holding a competition
-
- All
- Regional
- Water
- Biometrics
- Borders/Immig
- Business
- Cybersecurity
- Detection
- Disasters
- Government
- Infrastructure
- International
- Public health
- Public Safety
- Communication interoperabillity
- Emergency services
- Emergency medical services
- Fire
- First response
- IEDs
- Law Enforcement
- Law Enforcement Technology
- Military technology
- Nonlethal weapons
- Nuclear weapons
- Personal protection equipment
- Police
- Notification /alert systems
- Situational awareness
- Weapons systems
- Sci-Tech
- Sector Reports
- Surveillance
- Transportation
Advertising & Marketing: advertise@newswirepubs.com
Editorial: editor@newswirepubs.com
General: info@newswirepubs.com
2010-2011 © News Wire Publications, LLC News Wire Publications, LLC
220 Old Country Road | Suite 200 | Mineola | New York | 11501
Permissions and Policies
Editorial: editor@newswirepubs.com
General: info@newswirepubs.com
2010-2011 © News Wire Publications, LLC News Wire Publications, LLC
220 Old Country Road | Suite 200 | Mineola | New York | 11501
Permissions and Policies
