-
New tool predicts drought
Knowing when to instigate water saving measures in dry times will be easier from now on, following a breakthrough in drought prediction: an Australian researcher has developed a way to predict droughts six months before they begin
-
-
Strong 1Q growth for U.S. solar power, more expected
The United States showed strong first quarter growth in solar panel capacity, increasing installations by 66 percent; the increase in solar capacity is due largely to falling panel prices and developers taking advantage of government incentives that were set to expire in 2010; analysts expect solar panel growth to increase throughout the year
-
-
Mississippi River floods to cause large Gulf of Mexico dead zone
Hypoxia, which creates oceanic dead zones, is caused by excessive nutrient pollution, often from human activities such as agriculture, which results in too little oxygen to support most marine life in bottom and near-bottom water; scientists are predicting the dead zone area in the Gulf could measure between 8,500 and 9,421 square miles, or an area roughly the size of New Hampshire; the largest hypoxic zone measured to date occurred in 2002 and encompassed more than 8,400 square miles
-
-
Arizona wildfire now largest in state's history

The Wallow wildfire in Arizona has continued to burn out of control and is now the largest fire in Arizona’s history; on Tuesday firefighters in Arizona reported that they had 18 percent of the fire contained; so far the blaze has burned 479,407 acres in the White Mountains of eastern Arizona; officials have evacuated thousands of residents from mountain towns and are urging residents to stay clear as the smoke has created dangerous air conditions
-
-
Report warns falling crop yields could spell disaster
A recent study found that as temperatures continue to rise the geographical range of staple crops like corn and beans will become increasingly limited, potentially resulting in massive food shortages; there are currently fifty-six million people who lack food security as temperatures are expected to rise above 86° Fahrenheit; at that temperature, beans are no longer a viable crop, while rice and corn yields suffer
-
-
Virtual water would not remedy global fresh water shortage

More than 80 percent of humanity currently lives in regions where water security is threatened, meaning that as the global population grows against a finite volume of freshwater, a more equal distribution of water use between countries will be needed; virtual water — that is, the amount of water it takes to produce goods or a service — has been suggested as a possible solution to this growing problem by using virtual water values to inform international trade deals; a new study suggests that it may not be as revolutionary as first thought
-
-
Climate change and cities: a wake-up call

More than half the world’s population live in cities, many of which are increasingly vulnerable to the impacts of climate change; cities, however, are also emerging as the innovative “first responders” in dealing with climate change; climate change will stress cities in many ways — there will be more heat waves, threatening the health of the elderly and infirm; droughts will also become more commonplace in many cities, while in coastal communities too much water may be the problem, due to sea-level rise and more extreme coastal flooding
-
-
Deadly tornado kills four in Massachusetts

On Wednesday, as many as seven tornadoes tore through Massachusetts resulting in the state’s first twister related deaths in sixteen years; the tornadoes touched down in the western and central part of the state, but hit Springfield, located ninety miles west of Boston, the hardest; more than forty people have been admitted to hospitals after sustaining injuries from the tornado and four people have been confirmed dead so far; emergency responders are currently picking through the wreckage to rescue any survivors trapped in the rubble
-
-
Ports unprepared for increase in Katrina-like storms

A recent report by Stanford University researchers found that the majority of seaports around the world are unprepared for rising sea levels and increasingly violent storms; a majority of ports surveyed listed sea level rise and increasing extreme storms as some of their top concerns; only 6 percent of respondents said they have plans to build hurricane barriers in the next ten years, and less than 18 percent said they had plans to build dikes or other storm protection structures; to ease uncertainty among port authorities, researchers developed a computer model to provide cost estimates that take into account a port’s specific location as well as the cost of labor, materials, and equipment for fortifying a structure against rising sea levels
-
-
Former world leaders say global water crisis must be addressed
In March 2008, the U.K. intelligence services, in a report to then-prime minister Gordon Brown, warned that the deteriorating fresh water situation around the world would soon lead not only to tensions over water between states, but to “water wars”; world leaders, at least former world leaders, agree that the global water situation is dire, and twenty of them, led by Bill Clinton, meet to discuss solutions
-
-
Human impact of rising oceans will extend well beyond coasts

Identifying the human impact of rising sea levels is far more complex than just looking at coastal cities on a map; rather, estimates that are based on current, static population data can greatly misrepresent the true extent — and the pronounced variability — of the human toll of climate change; a new study focuses on four regions identified as highly susceptible to flooding: the tip of the Florida peninsula, coastal South Carolina, the northern New Jersey coastline, and the greater Sacramento region of northern California; the study finds that by 2030, more than nineteen million people will be affected by rising sea levels just in their four study areas
-
-
Germany to scrap nuclear power by 2022

Germany yesterday announced plans to become the first major industrialized power to shut down all its nuclear plants in the wake of the disaster in Japan; phase-out due to be wrapped up by 2022; it means that the country will have to find the 22 percent of its electricity needs currently covered by nuclear reactors from another source; Monday decision is a U-turn for Chancellor Angela Merkel, and means that the current government has adopted the timetable for a nuclear phase-out set by the previous Social Democrat-Green coalition government a decade ago; it also cancels Merkel’s decision from November 2010 to extend the lifetime of Germany’s seventeen reactors by an average of twelve years, which would have kept them open until the mid-2030s
-
-
Global carbon emissions at record high
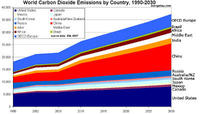
Global carbon emissions are at their highest ever levels, increasing fears of a global temperature rise over the “dangerous” two degrees Celsius threshold; unpublished estimates from the International Energy Agency revealed that the world economy’s return to growth in 2010 coincided with a 1.6 gigaton rise in carbon dioxide emissions, the highest ever recorded jump
-
-
Global warming: Arctic access by land will diminish, but improve by sea

Global warming over the next forty years will cut through Arctic transportation networks like a double-edged sword, limiting access in certain areas and vastly increasing it in others in absolute terms; winners are expected to be coastal communities, coastal resource-extraction operations, tourism, fishing, and shipping concerns; potential losers include inland mining and timber operations, inland oil and gas drilling, and smaller inland communities, often inhabited by indigenous peoples; Canada and Russia stand to lose the most winter-road potential as rising temperatures will prevent up to 400,000 square miles from hardening into potential roadways
-
-
More tornadoes headed to Joplin, Missouri
As emergency responders pick through the wreckage from Sunday’s massive tornado in Joplin, Missouri, residents are preparing for another monstrous storm that could generate more deadly tornadoes; meteorologists anticipate that thunderstorms will hit Joplin once again on Tuesday night; rescue workers raced to sift through the rubble in search of survivors before the next storm hits; it is estimated that 30 percent of the city has been destroyed after the tornado carved a three-quarter mile wide path of destruction; so far officials have confirmed that at least 117 people are dead, more than 600 injured, and approximately 1,500 are still missing from one of the country’s deadliest tornadoes in over sixty years; initial projections rate the monstrous tornado as an EF-4 with wind speeds of 166 to 200 miles per hour; it is reported that the mile-wide funnel contained two cyclones inside; President Obama is currently overseas in the United Kingdom, but plans to visit Missouri this weekend after returning from Europe
-
- All
- Regional
- Water
- Biometrics
- Borders/Immig
- Business
- Cybersecurity
- Detection
- Disasters
- Government
- Infrastructure
- International
- Public health
- Public Safety
- Communication interoperabillity
- Emergency services
- Emergency medical services
- Fire
- First response
- IEDs
- Law Enforcement
- Law Enforcement Technology
- Military technology
- Nonlethal weapons
- Nuclear weapons
- Personal protection equipment
- Police
- Notification /alert systems
- Situational awareness
- Weapons systems
- Sci-Tech
- Sector Reports
- Surveillance
- Transportation
Advertising & Marketing: advertise@newswirepubs.com
Editorial: editor@newswirepubs.com
General: info@newswirepubs.com
2010-2011 © News Wire Publications, LLC News Wire Publications, LLC
220 Old Country Road | Suite 200 | Mineola | New York | 11501
Permissions and Policies
Editorial: editor@newswirepubs.com
General: info@newswirepubs.com
2010-2011 © News Wire Publications, LLC News Wire Publications, LLC
220 Old Country Road | Suite 200 | Mineola | New York | 11501
Permissions and Policies
