-
Developing materials for more resilient concrete pavements

Aging roadways pose a growing threat to transportation infrastructure which is critical to the health of economies throughout the world. Beyond the daunting task of funding extensive restoration efforts, there is an equally pressing challenge to find ways to rebuild major roads which are more sustainable. Researchers have been experimenting with what are called phase-change materials to produce more resilient concrete surfaces for roads and bridges. Phase-change materials are substances which respond to temperature variations by changing their state from solid to liquid or vice versa, and can be sourced from petroleum (such as paraffin wax) or be plant-based. A new project is exploring the use of a phase-change material solution for reducing or preventing temperature-related cracks in concrete pavement.
-
-
Self-compacting concrete is now fire resistant as well

Self-compacting high-performance concrete (SCHPC) has till now suffered from one weakness — when exposed to fire it flakes and splits, which reduces the loadbearing capacity of ceilings, walls, and supporting pillars, thus increasing the risk of collapse in a burning building. Scientists have now developed a method of manufacturing fire resistant self-compacting high-performance concrete which maintains its mechanical integrity under these conditions.
-
-
U.K.: Economic costs from flooding could reach £1.5bn, reduce GDP growth

Economic losses caused by the flooding which has devastated parts of Britain in the past few days could exceed 1.5 billion pounds, and shave 0.2-0.3 percent off GDP growth overall in the first quarter of 2016. Insurers will likely shoulder the bulk of the burden after first Storm Desmond and then Storm Eva saw waters swamp large swathes of the country.
-
-
U.K. government rejected flood warnings from own advisers

Critics charge that the U.K. government was warned by both the government’s own climate change experts and outside consultants that there was a need to take urgent action to protect the increasing number areas in Britain which are becoming susceptible to flooding, but that the government rejected the advice. Despite the urging of its own climate experts, the U.K. government in October, just a few weeks before the devastating flooding in Cumbria, decided not to develop comprehensive strategy to address flood risk.
-
-
Climate change losses for Southeast Asia well above previous estimate: ADB
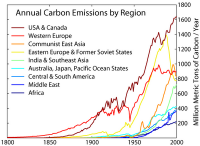
Economic losses from the impacts of climate change in Southeast Asia could be 60 percent higher than previously estimated, reducing the region’s gross domestic product (GDP) by up to 11 percent by 2100, according to a new Asian Development Bank (ADB) study. The analysis is an update to a 2009 ADB report that estimated a 7 percent annual reduction in economic output due to climate change.
-
-
Rail line service disruptions caused by sea level rise to increase dramatically
Rail services to and from the South West of England could be disrupted for more than 10 percent of each year by 2040 and almost a third by 2100, a new study suggests. The cost of maintaining tracks and sea defenses could also soar as predicted sea level rises, coupled with coastal storms and floods, pose major challenges for rail operators and governments.
-
-
Growing risks in flood-prone areas due to economic growth more than climate change
Worldwide economic losses from river flooding could increase 20-fold by the end of the twenty-first century if no further actions on flood risk reduction are taken. There are two contributors to risks associated with river flooding. Floods’ frequency and severity (both influenced by climate change); and the exposure to floods of people and economic assets (determined by economic activity and human residency in flood-prone areas). Researchers calculate that in many flood-prone regions of the world, more than 70 percent of the increase in flood-related risks over the coming decades can be attributed to economic growth and residency patterns in flood prone areas.
-
-
Iranian hackers attacked New York dam

In 2013, Iranian government hackers infiltrated the control system of Bowman Avenue Dam in Rye, New York, located twenty-five miles from New York City. Using a cellular modem, the hackers could have released larger volumes of upstream water without warning. As dams go, the Rye dam is small at about 20ft tall. There was some confusion initially, as DHS and DOE thought a similarly named dam in Oregon — the Arthur R. Bowman Dam – was the one hacked. The Oregon dam, at 245 feet, is much bigger, and hacking its control systems could have had much more serious consequences.
-
-
Fracking-induced earthquakes increase in magnitude over time
A study by geophysicists shows that earthquakes resulting from fracking-related wastewater injection follow several indicative patterns that are starkly different from natural causes. One of the study’s main conclusions is that the likelihood of large-magnitude manmade, or “induced,” earthquakes in areas where fracking activity takes place, increases over time, independent of the previous seismicity rate. The study’s findings could have implications for both the oil and natural gas industry and for government regulators. Under current practices, extraction activities typically shut down in an area if a high-magnitude earthquake occurs. But according to the researchers, a better approach might be to limit production before a large quake occurs.
-
-
Protecting the U.S. electrical grid from cyberattack

Across the United States, 3,200 separate organizations own and operate electrical infrastructure. The widely dispersed nature of the nation’s electrical grid and associated control systems has a number of advantages, but since the late 1990s, cost pressures have driven the integration of conventional information technologies into these independent industrial control systems, resulting in a grid which is increasingly vulnerable to cyberattack, either through direct connection to the Internet or via direct interfaces to utility IT systems. DARPA is soliciting proposal for creating automated systems to restore power within seven days or less after a cyberattack on the grid.
-
-
Contacting ETs: Should we announce our location to an alien force?
While politicians quibble over how to deal with illegal immigration, an ominous group of foreigners goes unaddressed: space aliens. Should humans try to contact creatures from other galaxies? Do we really want that force awakened? For scientists, these are not esoteric questions. The fate of the planet may be at stake. Scientists warn that we should think long and hard about whether we should risk announcing our location to potentially real-life equivalents of Klingons or Stormtroopers. As physicist Stephen Hawking warned in 2010, “If aliens visit us, the outcome would be much as when Columbus landed in America, which didn’t turn out well for the Native Americans.”
-
-
Climate change impacts may appear in some areas sooner than expected
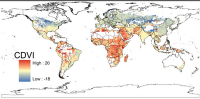
Some impacts of global climate change will appear much sooner than others — with only moderate increases in global temperature. While rising sea levels may one day threaten the commuter tunnels and subway lines of New York City, it will have effects much sooner in other parts of the world – for example, the Marshall Islands and Bangladesh. In countries exposed to the destructive effects of climate change sooner rather than later, there will be little incentives to do something about climate change because the damage has already been done. Thus, once significant portions of the Marshall Islands or Bangladesh are destroyed by rising seas, the rate of damage will reach “saturation” — an inflection point beyond which further temperature increases have little additional effect. Once the Marshall Islands are large sections of Bangladesh are uninhabitable, there is not more damage that can be done there, and the governments of these countries will not have an incentive to participate in global climate efforts because they will not have anything more to lose.
-
-
Concerns over attacks on the U.S. electrical grid increase after Paris attacks
In the aftermath of the 13 November attacks in Paris, U.S. government agencies involved with grid security and utilities are preparing to thwart a major attack on the U.S. electrical grid. Government agencies and utilities believe an attack or series of attacks on the electrical grid of the United States is imminent — more so in the aftermath of the attacks on Paris. They are carrying out drills and exercises to brace for them.
-
-
First code improvements based on NIST Joplin tornado study adopted

Protecting schools and their associated high-occupancy buildings from the most violent tornadoes is the goal of the first approved building code changes based on recommendations from the National Institute of Standards and Technology (NIST) technical investigation into the impacts of the deadly tornado that struck Joplin, Missouri, on 22 May 2011. The new changes, approved at a recent meeting of the International Code Council (ICC), apply to the nation’s most tornado-prone regions.
-
-
Equatorial regions’ power at risk from stormy space weather

Stormy space weather sweeping across the equator is threatening vital power grids in regions long considered safe from such events, ground-breaking new research reveals. The researchers found that these equatorial electrical disruptions threaten power grids in Southeast Asia, India, Africa, and South America, where protecting electricity infrastructure from space shocks has not been a priority.
-
- All
- Regional
- Water
- Biometrics
- Borders/Immig
- Business
- Cybersecurity
- Detection
- Disasters
- Government
- Infrastructure
- International
- Public health
- Public Safety
- Communication interoperabillity
- Emergency services
- Emergency medical services
- Fire
- First response
- IEDs
- Law Enforcement
- Law Enforcement Technology
- Military technology
- Nonlethal weapons
- Nuclear weapons
- Personal protection equipment
- Police
- Notification /alert systems
- Situational awareness
- Weapons systems
- Sci-Tech
- Sector Reports
- Surveillance
- Transportation
Advertising & Marketing: advertise@newswirepubs.com
Editorial: editor@newswirepubs.com
General: info@newswirepubs.com
2010-2011 © News Wire Publications, LLC News Wire Publications, LLC
220 Old Country Road | Suite 200 | Mineola | New York | 11501
Permissions and Policies
Editorial: editor@newswirepubs.com
General: info@newswirepubs.com
2010-2011 © News Wire Publications, LLC News Wire Publications, LLC
220 Old Country Road | Suite 200 | Mineola | New York | 11501
Permissions and Policies
