-
Restoring and sustaining Louisiana’s eroding coast

Measures taken over the last ninety years to prevent a repetition of the 1927 New Orleans flood — the construction of improved levees, spillways, and dams as well as associated flood and additional navigation management structures designed to contain overflows and manage and stabilize a deep-water channel – have starved adjacent wetlands of the freshwater and sediment needed to stave off the Gulf of Mexico’s rising tides. The resulting land loss across the Delta is leading toward catastrophic collapse. Over the last century, almost 1,900 square miles of deltaic wetlands, an area approximately the size of Delaware, have disappeared from Louisiana. Every hour, a football field-sized swath of land drowns in the Gulf’s advancing tides. A Louisiana independent initiative, with the support and participation of the State of Louisiana and U.S. Army Corps of Engineers, has called on experts from the private sector to develop and assess new designs for the Lower Mississippi River (below New Orleans). The winning proposals were announced last week.
-
-
Coastal uplift along Pacific Coast lower than expected, exacerbating sea-level rise impact
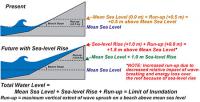
A new study shows that uplift rates across the Pacific Coast of the United States and northern Mexico have been overestimated by an average of more than 40 percent. These lower uplift rates this may have important implications for coastal management, including earthquake hazards and the potential impact of sea-level rise to coastlines across the Pacific Coast. If the Pacific Coast’s uplift rate is lower than had been estimated, this means that sea-level rise would have an even greater impact on coastal communities and infrastructure. Higher coastal uplift rates would have negated some of the effects of rising sea levels, something lower uplift rate will not do.
-
-
Draft guide to help energy companies reduce cyber risk

DHS reported that 5 percent of the cybersecurity incidents its Industrial Control Systems Cyber Emergency Response Team responded to in fiscal year 2014 were tied to weak authentication. Four percent were tied to abuse of access authority. The National Cybersecurity Center of Excellence (NCCoE) is requesting comments on a draft guide to help energy companies better control who has access to their networked resources, including buildings, equipment, information technology, and industrial control systems.
-
-
Post-Katrina flood damage resulted from Corps of Engineers' errors, was preventable
A decade after hurricane Katrina hit New Orleans, experts say the flooding that caused over 1,800 deaths and billions of dollars in property damage could have been prevented had the U.S. Army Corps of Engineers retained an external review board to double-check its flood-wall designs. Researchers contend that the main fault in the failure of the flood walls along the city’s principal drainage canals was the misinterpretation of a full-scale load test carried out by the Corps in the Atachafalaya Basin a few years prior to Katrina. After these so-called E-99 tests, it was determined that flood walls in the city should be installed at a depth of 17 feet, instead of the initially estimated depths of 31 to 46 feet.
-
-
U.S. coastal communities face increasing risk of compound floods

In 2010, 39 percent of the U.S. population lived in coastal communities — a number which is expected to continue to increase in the next five years. The confluence of storm surges and heavy precipitation can bring dangerous flooding to low-lying coastal regions, including major metropolitan areas. A new study of the United States coastline has found the risk of such flooding is higher on the Atlantic coast than the Pacific, and the number of these compound events has increased significantly in many major cities in the past century.
-
-
California levees face risk of catastrophic failure as a result of historic drought

Earthen levees protect dry land from floods and function as water storage and management systems. Over 21,000 kilometers of earthen levees deliver approximately two-thirds of potable water to more than twenty-three million Californians and protect more than $47 billion worth of homes and businesses from flooding. Scientists say that the ongoing extreme drought in the state poses a risk of catastrophic failure to California’s levee systems and highlights an urgent need to invest in research regarding the vulnerabilities of these systems under extreme climatic events.
-
-
Climate change and Hurricane Katrina: what have we learned?
Theory and computer models show that the incidence of the strongest hurricanes — those that come closest to achieving their potential intensity — will increase as the climate warms, and there is some indication that this is happening. Global warming, however, is occurring far too fast for effective human adaptation. Adapting to the myriad changes expected over the next 100 years is such a daunting prospect that otherwise intelligent people rebel against the idea even to the extent of denying the very existence of the risk. This recalcitrance, coupled with rising sea levels, subsiding land, and increased incidence of strong hurricanes, all but guarantees that New Orleans will have moved or have been abandoned by the next century.
-
-
Drought causing California’s San Joaquin Valley land to sink, damaging infrastructure

Californians continue pumping groundwater in response to the historic drought, and as a result, land in the San Joaquin Valley is sinking faster than ever before, nearly two inches per month in some locations. Sinking land, known as subsidence, has been occurring for decades in California because of excessive groundwater pumping during drought conditions, but the sinking is happening faster. The increased subsidence rates can damage local, state, and federal infrastructure, including aqueducts, bridges, roads, and flood control structures. Long-term subsidence has already destroyed thousands of public and private groundwater well casings in the San Joaquin Valley. Over time, subsidence can permanently reduce the underground aquifer’s water storage capacity.
-
-
New facility will be center of research to make U.S. grid more robust, smarter

The U.S. electric power grid is the most complex machine ever built. Transforming it from an early twentieth century machine to a twenty-first century engine for innovation is a demanding scientific and technical challenge. The Pacific Northwest National Laboratory has launched its new Systems Engineering Building (SEB), in which industry, academia, and leading scientists will conduct research which will change the future of the U.S. power grid. “The private sector and the government must work together to ensure that we can prevent and recover from grid disruptions, whether they come from cyberattack, physical attack, or severe weather that is brought on by climate change,” Deputy Energy Secretary Elizabeth Sherwood-Randall said at the building’s dedication.
-
-
U.S. coastal flood risk on the rise ten years after Hurricane Katrina
A decade after Hurricane Katrina caused $41 billion in property and casualty insurance losses, the most expensive catastrophe ever experienced by the global insurance industry, rising sea levels are driving up expected economic and insurance losses from hurricane-driven storm surge in coastal cities across the United States. Rising sea levels contributing to increased risk of severe economic damage from flood following a hurricane – and Miami, New York, and Tampa now face greater risk than New Orleans.
-
-
World’s most at-risk coastal regions should adopt Louisiana’s post-Katrina protection plans
A decade after Hurricane Katrina hammered America’s Gulf Coast, measures are being taken there to protect against similar devastation from natural disasters — as well as against long-term, gradual impacts resulting from climate change. Other coastal regions across the world, however, remain vulnerable to damaging storms, and providing similar protection for the tens of millions of people living in those areas — around 38 percent of the global population, or 2.5 billion people, lives within 100 kilometers (62 miles) of the coast — will require international action. Experts say that the world’s most at-risk nations should implement coastal protection plans like those adopted by Louisiana.
-
-
New tools increase Palestinians’ capacity to face earthquakes
A massive earthquake would lead to the devastation of 70 percent of houses in the Palestinian territories, and the death of 16 000 people. As the Palestinian territories are located in the Rift Valley — right at the frontier between the Arabian and African plates which are moving farther apart — the likelihood of earthquakes is expected to keep increasing. Two projects aim to make the next generation of citizens and researchers better equipped to face this growing threat.
-
-
New technology solves city pipelines leakage problem without excavation

In Mexico City there are twenty-six thousand kilometers of water pipes and drainage, of which about 8,000 are useless, with risk of collapse and resulting cuts in service. The water pipes infrastructure of many other cities is not much better. A Mexican start-up has created a technology to renew piping without the need for excavation, ensuring it lasts fifty years, twice as long as traditional piping.
-
-
Inspired by bats, sensor technology detects dangerous structural cracks

Researchers have developed an ultrasound sensor for detecting dangerous cracks in structures such as aircraft engines, oil, and gas pipelines, and nuclear plants. The device, known as a transducer, identifies structural defects with varying ultrasonic frequencies and overcomes the limits of other, similar devices, which are based on rigid structures and have narrow ranges. It is thought to be the first device of its kind in the world.
-
-
Geoengineering technique would not stop sea level rise

Researchers used computer model experiments to test how the Greenland Ice Sheet would react to albedo modification, also called solar radiation management geoengineering, a proposed technology to cool down the Earth’s temperature by reflecting some sunlight away from the planet. They found the ice sheet might contribute to sea-level rise for decades to centuries after albedo modification began. The researchers say that albedo modification should not be counted on as a short-term solution to stop rising global sea levels.
-
- All
- Regional
- Water
- Biometrics
- Borders/Immig
- Business
- Cybersecurity
- Detection
- Disasters
- Government
- Infrastructure
- International
- Public health
- Public Safety
- Communication interoperabillity
- Emergency services
- Emergency medical services
- Fire
- First response
- IEDs
- Law Enforcement
- Law Enforcement Technology
- Military technology
- Nonlethal weapons
- Nuclear weapons
- Personal protection equipment
- Police
- Notification /alert systems
- Situational awareness
- Weapons systems
- Sci-Tech
- Sector Reports
- Surveillance
- Transportation
Advertising & Marketing: advertise@newswirepubs.com
Editorial: editor@newswirepubs.com
General: info@newswirepubs.com
2010-2011 © News Wire Publications, LLC News Wire Publications, LLC
220 Old Country Road | Suite 200 | Mineola | New York | 11501
Permissions and Policies
Editorial: editor@newswirepubs.com
General: info@newswirepubs.com
2010-2011 © News Wire Publications, LLC News Wire Publications, LLC
220 Old Country Road | Suite 200 | Mineola | New York | 11501
Permissions and Policies
