-
Russia meteor a “once every 100 years” event

The meteor which disintegrated in the skies over Chelyabinsk, Russia, early Friday morning entered the atmosphere at about 40,000 mph (18 kilometers per second). The energy released by the impact was in the hundreds of kilotons.The meteor is the largest reported since 1908, when a meteor hit Tunguska, Siberia.
-
-
System to vaporize asteroids that threaten Earth
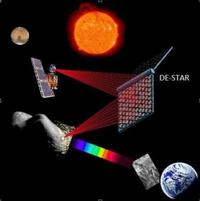
As an asteroid roughly half as large as a football field — and with energy equal to a large hydrogen bomb – flew by Earth on Friday, two California scientists unveiled their proposal for a system that could eliminate a threat of this size in an hour. The same system could destroy asteroids ten times larger than the one known as 2012 DA14 in about a year, with evaporation starting at a distance as far away as the Sun.
-
-
Quantum cryptography to secure electric grid
Novel methods for controlling the electric grid are needed to accommodate new energy sources such as renewables whose availability can fluctuate on short time scales. This requires transmission of data to and from control centers; but for grid-control use, data must be both trustworthy and delivered without delays. The Los Alamos National Laboratory quantum cryptography team successfully completed the first-ever demonstration of securing control data for electric grids using quantum cryptography.
-
-
Infrastructure renewal in regional Australia
New research in Australia calls for the establishment of a new national organization to tackle the shortfall in infrastructure investment and boost the regions’ capacity to contribute to national economic growth. Expert say the new organization, to be called Local Infrastructure Australia, would be the most effective way of overcoming the backlog in local government infrastructure investment now estimated at between $12 and $15.5 billion.
-
-
Lessons from the 2010-11 Australia floods
New research has come up with ways quickly to assess flood damage to houses while also showing most people did not intend to make changes to reduce their vulnerability after the 2010-11 Australia floods. Two separate reports show how lessons learned from households affected by the 2010-11 Australian floods can minimize damage under current and future climates.
-
-
Sediment carried by 2011 Mississippi flood shored up Louisiana’s wetlands

The spring 2011 flood on the Mississippi was among the largest floods ever, the river swelling over its banks and wreaking destruction in the surrounding areas. A new study also shows, however, that the floods reaped environmental benefits — transporting and laying down new sediment in portions of the Delta — that may help maintain the area’s wetlands.
-
-
Obama to issue cybersecurity executive order today
President Barack Obama is expected to issue an executive order tomorrow to dealing protecting U.S. critical infrastructure from cyberattacks. The order will be issues one day after the president’s State of the Union address. The order will establish a critical infrastructure council which will be run by DHS and will include members of the Departments of Defense, Justice, and Commerce as well as the National Intelligence Office. The council will be tasked with formulating new regulations for federal agencies, or broadening regulations already in place. The regulations will most likely include the sharing of data between private corporations and the federal government.
-
-
Infrastructure sees drop in funding last year
Infrastructure investments in roads, bridges, and power stations have dropped significantly in 2012 as banks struggled to offer long-term debt and governments targeted cost savings. There were hopes that infrastructure spending would boost the world economy in 2012, but funding fell from $159 billion worldwide in 2011 to $99 billion.
-
-
Northeast U.S. digs out after deadly snowstorm

About 250,000 homes and businesses in northeast United States remain remained without power this morning as a blizzard dumped more than three feet of snow on north-mid-Atlantic and New England states, and parts of Canada. The death toll was at fifteen. Utilities in New England said the storm could leave some customers in the dark at least until Tuesday. About 650,000 lost power in eight states at the height of the storm.
-
-
Tiny organisms in oceans can save islands from rising sea levels: study

Warming climate is causing sea levels to rise, posing a special threat to low-lying island nations. The government of the Maldive Islands, an island nation in the Indian Ocean consisting of a chain of twenty-six atolls, has begun exploring the possibility of purchasing land in Africa to relocate the entire population – about 330,000 – once rising sea water begin to swallow the small atolls. Scientists found out, though, that the warming temperature of the seas is causing tiny single-cell organisms to are spreading rapidly through the world’s oceans, where they just might be able to mitigate the consequences of climate change.
-
-
New internally cured concrete increases bridge life span
Concrete is normally made by mixing portland cement with water, sand, and stone. In the curing or hardening process, water helps the concrete mixture gain strength by reacting with the cement. Traditionally, curing is promoted by adding water on top of the bridge deck surface. The new technology for internal curing provides additional water pockets inside the concrete, enhancing the reaction between the cement and water, which adds to strength and durability. This new technology is enabling Indiana to improve bridges in the state with a new “internally cured” high-performance concrete.
-
-
NY to buy, demolish beachfront homes, make way for storm buffers

New York governor Andrew Cuomo plans to use $400 million in federal funding to buy beachfront homes as part of a broader plan to reshape the New York coastline so the state is better prepared for sea level rise, surges, and storms. The plan is to raze the purchased homes and leave to shore front vacant. Some properties would be turned into dunes, wetlands, or other natural buffers. Other parcels could be combined and turned into public parkland.
-
-
Miles tax may soon replace gas tax as a way to fund infrastructure maintenance
With infrastructure around the country in a state of disrepair, many states and lawmakers are trying to find a way to fund improvement of roads and bridges. The federal gasoline tax brings in fewer dollars each year, and now some lawmakers and transportation experts are considering the idea of taxing citizens by how far they drive each year instead of the amount of gasoline they buy each year.
-
-
Springfield, Illinois, faces infrastructure woes
As is the case with other cities, the infrastructure of Illinois’ capital, Springfield, is decaying. Experts told the city council that it would take $86.6 million over the next three years to shore up the city’s streets and sewer system, and $22.5 million a year thereafter to maintain it. The city is now grappling with how to raise the necessary funds.
-
-
Climate change threatens public health, safety, economy along U.S. coasts
A new technical study from the U.S. National Oceanic and Atmospheric Agency (NOAA) and the U.S. Geological Survey (USGS) reports that the effects of climate change will continue to threaten the health and vitality of U.S. coastal communities’ social, economic, and natural systems. All U.S. coasts are highly vulnerable to the effects of climate change such as sea-level rise, erosion, storms, and flooding, especially in the more populated low-lying parts of the U.S. coast along the Gulf of Mexico, Mid-Atlantic, northern Alaska, Hawaii, and island territories. The report says that the financial risks associated with both private and public hazard insurance are expected to increase dramatically.
-
- All
- Regional
- Water
- Biometrics
- Borders/Immig
- Business
- Cybersecurity
- Detection
- Disasters
- Government
- Infrastructure
- International
- Public health
- Public Safety
- Communication interoperabillity
- Emergency services
- Emergency medical services
- Fire
- First response
- IEDs
- Law Enforcement
- Law Enforcement Technology
- Military technology
- Nonlethal weapons
- Nuclear weapons
- Personal protection equipment
- Police
- Notification /alert systems
- Situational awareness
- Weapons systems
- Sci-Tech
- Sector Reports
- Surveillance
- Transportation
Advertising & Marketing: advertise@newswirepubs.com
Editorial: editor@newswirepubs.com
General: info@newswirepubs.com
2010-2011 © News Wire Publications, LLC News Wire Publications, LLC
220 Old Country Road | Suite 200 | Mineola | New York | 11501
Permissions and Policies
Editorial: editor@newswirepubs.com
General: info@newswirepubs.com
2010-2011 © News Wire Publications, LLC News Wire Publications, LLC
220 Old Country Road | Suite 200 | Mineola | New York | 11501
Permissions and Policies
