-
Pentagon confirms policy of military response to cyberatacks
In a Pentagon report recently made public, the U.S. military confirmed that it would launch physical strikes in response to cyberattacks
-
-
U.K. banks pass cyberdefense stress test
To bolster cyberdefenses in the financial industry, U.K. banks recently took part in a stress test to determine their ability to cope with a cyberattack; eighty-seven banks took participated in the drill including Barclays, HSBC, and Royal Bank of Scotland
-
-
The increasing risks of GPS systems
During a recent meeting of the National Space-Based Positioning, Navigation, and Timing (PNT) Advisory Board, participants described how U.S. infrastructure is increasingly at risk due to the widespread use of GPS systems and the presence of interdependencies between different sectors
-
-
Building design lessons from the Christchurch earthquake

A leading infrastructure expert believes an assessment needs to be made of the level of “very rare” earthquake that needs to be considered in structural design, perhaps one with a 10,000 year return period or higher, rather than the 500 year return period that is commonly adopted for many buildings in Australia
-
-
Increasing durability, cutting cost of railroad maintenance
Every year, companies that own railroad track across the United States spend millions of dollars maintaining ballast, the crushed rock underneath railroad ties and steel rails; in addition to the high cost, railroads must reroute trains around operations that maintain ballast, delaying the delivery of freight; researchers offer a solution
-
-
DHS investigates attacks on New Jersey water supply

DHS agents and local authorities in New Jersey are investigating a series of attacks on the West Milford water system; since July there have been more than fifteen attacks on local water and sewage facilities that in some instances have resulted in sewage flooding the street or losses in service all together
-
-
Electrical grids in state of “chaos,” report finds
A recent report warned that the world’s electrical grid is in a “state of near chaos,” leaving it vulnerable to a devastating cyberattack; the report, released by Pike Research, found that a simple $60 smart phone app could enable an attack on smart grids due to an aging infrastructure, a lack of standards, and inadequate spending
-
-
Cyber attacks on critical infrastructure reach U.S.
Most of the U.S. critical infrastructure is run by computers which are connected to the Internet; this makes them susceptible to cyber attacks; a few days ago, the control system of a water pump in Illinois was taken over by a hacker’s remote command, and then deliberately destroyed; what critical infrastructure facilities will hackers – nerdy teenagers, terrorists, or intelligence operatives of other nations – target next?
-
-
Serving and protecting – and saving money in the process

As municipalities battle tight budgets and rising gasoline prices, law enforcement fleets across in the United States have found a way to save taxpayer dollars by shifting to clean-burning, American-made propane autogas
-
-
Europe faces rare Earth metal shortages
The EU’s ambitious low-carbon energy production goal depends on five technologies: nuclear, solar, wind, bio-energy, and carbon capture; these technologies, in turn, depend on rare Earth metals; the EU estimates that a large-scale deployment of only one of these technologies — solar energy — will require half the current world supply of tellurium and 25 percent of the supply of indium
-
-
Ionized plasmas as cheap sterilizer in tough places
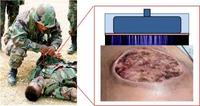
Scientists show that ionized plasmas like those in neon lights and plasma TVs not only can sterilize water, but make it antimicrobial; these plasma devices could be life-savers in developing countries, disaster areas, or on the battlefield where sterile water for medical use is in short supply and expensive to produce
-
-
Sector Report for Monday, 14 November 2011: Infrastructure protection
This report contains the following stories.
Plus 1 additional story.
-
-
Nations could cripple U.S. with retaliatory cyberattack
Last week Richard Clarke, a top adviser to three presidents, sounded a dire warning that the United States should avoid going to war with other nations because its computer networks systems are so vulnerable to attack
-
-
Smart grid security market to jump to $2 billion in 2016
Analysts project that spending on smart grid security will exceed $2 billion in the next five years; according to ABI Research’s report, titled “Smart Grid Security,” $590 million was spent on securing the smart grid in 2010 and by 2016 that number will rocket to $2 billion
-
-
Innovative ultrasonic nozzle changes the way water cleans
Scientists have developed a revolutionary ultrasonic attachment for taps, which massively enhances the ability of water to clean; currently, industry uses excessive water, power, and additives for cleaning
-
More headlines
The long view
Water Wars: A Historic Agreement Between Mexico and US Is Ramping Up Border Tension
As climate change drives rising temperatures and changes in rainfall, Mexico and the US are in the middle of a conflict over water, putting an additional strain on their relationship. Partly due to constant droughts, Mexico has struggled to maintain its water deliveries for much of the last 25 years, deliveries to which it is obligated by a 1944 water-sharing agreement between the two countries.
Trump Is Fast-Tracking New Coal Mines — Even When They Don’t Make Economic Sense
In Appalachian Tennessee, mines shut down and couldn’t pay their debts. Now a new one is opening under the guise of an “energy emergency.”
Smaller Nuclear Reactors Spark Renewed Interest in a Once-Shunned Energy Source
In the past two years, half the states have taken action to promote nuclear power, from creating nuclear task forces to integrating nuclear into long-term energy plans.
Keeping the Lights on with Nuclear Waste: Radiochemistry Transforms Nuclear Waste into Strategic Materials
How UNLV radiochemistry is pioneering the future of energy in the Southwest by salvaging strategic materials from nuclear dumps –and making it safe.
Model Predicts Long-Term Effects of Nuclear Waste on Underground Disposal Systems
The simulations matched results from an underground lab experiment in Switzerland, suggesting modeling could be used to validate the safety of nuclear disposal sites.
