-
Safe, efficient cookstoves for earthquake survivors

316,000 people were killed and more than one million made homeless by the 12 January 2010 magnitude 7.0 quake that left the capital city of Port-au-Prince in ruins; many of the displaced Haitians still live in tent cities, where even simple tasks such as cooking are a challenge; scientists hope to find the safest and most energy-efficient way for earthquake survivors to cook
-
-
Self-repairing composites repair cracks in coating of buildings, bridges
Researchers have developed vascularized structural composites, creating materials that are lightweight and strong with potential for self-healing, self-cooling, metamaterials, and more; these artificial microvascular systems can self-repair of materials damage, such as cracks in a coating applied to a building or bridge
-
-
Solar UV disinfects drinking water

More than 800 million people around the world lack access to clean water; the water available for people to drink in many developing countries has not been treated to remove contaminants, including pathogenic microorganisms; half of the world’s hospital beds are occupied by people who are sickened by the water they drink; Purdue University researchers have invented a water-disinfection system that uses the sun’s ultraviolet radiation to inactivate waterborne pathogens
-
-
Protecting structures against firebrand attack
NIST engineers have built a device that bellows showers of glowing embers, or firebrands, to test how structures can withstand this destructive aspects of wild fires; in Japan, where the device is now used in a test facility, firebrands are a growing peril that accounts for half of the nation’s ten most costly fires
-
-
Connecticut town considers charging centers for power outages
Following Hurricane Irene which left thousands without power up and down the East Coast, a town in Connecticut is considering building several charging stations for residents to power up their hand held electronics during a natural disaster or prolonged power outage
-
-
Pentagon expends cyber networks security project
The Pentagon plans to extend a cyber defense pilot program intended to help protect U.S. defense contractors from cyberattacks to more private companies, subcontractors, and industries such as power plants
-
-
MIT to help develop a nuclear reactor concept
MIT has been awarded $7.5 million to help develop a new nuclear reactor concept — the high-temperature salt-cooled reactor (also called a Fluoride-salt High-Temperature Reactor, or FHR); the FHR combines high-temperature graphite-matrix coated particle fuel developed for high-temperature gas-cooled reactors (fuel failure temperature > 1600 degrees C), liquid salt developed for the molten salt reactors (boiling point > 1400 degrees C), and safety systems originate from sodium fast reactors
-
-
NIST offers comprehensive risk assessment guidance for federal information systems
NIST has released two new publications dealing with risk assessment; one is the authoritative source of comprehensive risk assessment guidance for federal information systems, the other, an update to a March 2011 publication, focuses exclusively on risk assessments
-
-
InfraGard launches EMP SIG
InfraGard has launched a nationwide special interest group (SIG) — named the EMP SIG, after electromagnetic pulse — which will focus on threats that could cause nationwide long-term critical infrastructure collapse
-
-
Global water market could hit $800 billion by 2035
Analysts are predicting that the global market for water could grow dramatically over the next two decades, with some projecting a $1 trillion market in 2020; “Water is the fastest growing market at the moment, with a size of $500 billion globally,” said Harri Kerminen, the president and CEO of Finnish chemical firm Kemira
-
-
X-ray machine operators lack proper training, says explosives expert
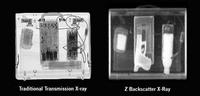
Even with the increasing ubiquity of X-ray machines and other explosives detection devices, many dangerous contraband items are still passing through security checkpoints at government buildings, airports, and businesses as a result of poor training; in 2009 Government Accountability Office (GAO) investigators successfully smuggled bomb making materials into ten high-security federal buildings
-
-
Why the Twin Towers collapsed: new theory
Materials scientist says that a mixture of water from sprinkler systems and molten aluminum from melted aircraft hulls created explosions that led to the collapse of the Twin Towers on 9/11
-
-
Speeding skyscraper construction -- and making them stronger
Researchers are working on a new technique that could speed construction of skyscrapers while also providing enough stiffness and strength to withstand earthquakes and forces from high winds
-
-
French nuke industry struggles to boost public image
In an effort to curry favor with the public, for the first time France has opened the doors of its nuclear power plants for the country’s annual “heritage” event; public opinion polls indicate the French public have turned increasingly against nuclear power following the accident at Japan’s Fukushima Daiichi nuclear power plant
-
-
Maintaining water quality
Scientists at Kansas State University and seven other collaborating institutions were recently awarded $3.3 million from the National Science Foundation (NSF) to conduct a-large scale study of how stream organisms influence water quality across North America
-
More headlines
The long view
Water Wars: A Historic Agreement Between Mexico and US Is Ramping Up Border Tension
As climate change drives rising temperatures and changes in rainfall, Mexico and the US are in the middle of a conflict over water, putting an additional strain on their relationship. Partly due to constant droughts, Mexico has struggled to maintain its water deliveries for much of the last 25 years, deliveries to which it is obligated by a 1944 water-sharing agreement between the two countries.
Trump Is Fast-Tracking New Coal Mines — Even When They Don’t Make Economic Sense
In Appalachian Tennessee, mines shut down and couldn’t pay their debts. Now a new one is opening under the guise of an “energy emergency.”
Smaller Nuclear Reactors Spark Renewed Interest in a Once-Shunned Energy Source
In the past two years, half the states have taken action to promote nuclear power, from creating nuclear task forces to integrating nuclear into long-term energy plans.
Keeping the Lights on with Nuclear Waste: Radiochemistry Transforms Nuclear Waste into Strategic Materials
How UNLV radiochemistry is pioneering the future of energy in the Southwest by salvaging strategic materials from nuclear dumps –and making it safe.
Model Predicts Long-Term Effects of Nuclear Waste on Underground Disposal Systems
The simulations matched results from an underground lab experiment in Switzerland, suggesting modeling could be used to validate the safety of nuclear disposal sites.
