-
Siemens exits nuclear power industry

Siemens, the largest engineering conglomerate in Europe, and the company which built all of Germany’s seventeen nuclear power plants, said Sunday it was existing the nuclear power generation market; Peter Löscher, the chief executive of the Munich-based conglomerate, said: “The [nuclear] chapter for us is closed”
-
-
$90 million contracts for developing anthrax vaccine and antitoxin
HHS awards two companies contracts with potential value of $90 million for the advanced development of a novel next-generation anthrax vaccine and a new type of anthrax antitoxin
-
-
FutureSentry, Sun Surveillance offer solar-powered intrusion detection
Two companies join forces to offer solar-powered automated intrusion detection systems for areas with limited power; the solution enables a cost-effective deployment as there is no need to trench and pull video cable and power, saving on both installation cost and time
-
-
Tyco International acquires Visonic
Tyco International acquires Visonic, a specialist in electronic security systems; the acquisition will strengthen Tyco Security Products’ business in the intrusion security market
-
-
Sector Report for Monday, 19 September 2011: Infrastructure protection
This report contains the following stories.
Plus 1 additional story.
-
-
Cyber attacks on U.S. are becoming more lethal
The head of the U.S. Cyber Command said that cyber attacks on the United States are escalating from large-scale theft and disruption of computer operations to more lethal attacks that destroy systems and physical equipment
-
-
U.S. releases smart grid cybersecurity strategy
Last week the U.S. Department of Energy released its strategic framework for its plan to install and secure the nation’s electrical grid system over the next decade; the report outlines a plan to coordinate efforts by the government and the private sector to begin designing and implementing an electrical grid that is capable of withstanding a cyberattack
-
-
Michigan creates cyber and physical infrastructure protection department
The state of Michigan is now merging responsibility for both physical and digital infrastructure protection under one organization
-
-
Japan nuke accident halves nuclear power growth
The nuclear meltdown at the Fukushima Daiichi plant appears to have caused nations around the world to reconsider nuclear projects; following the accident, demand for future nuclear projects has been halved
-
-
New rail-sensing technology saves time, energy, money
Leaves, as well as snow and rain, cause problems for trains because they reduce traction and cause wheels to spin on acceleration or to lock when slowing down; researchers are working to solve the age-old problem of leaves on the line delaying trains
-
-
Designing a new grid pylon

There are more than 88,000 pylons in the United Kingdom; they stand some 50-meters high, weigh around twenty tons, and carry up to 400,000 volts of electricity over thousands of kilometers of some of the most exposed, weather-beaten parts of Britain; the familiar steel lattice tower has barely changed since the 1920s; National Grid says it is time for a change
-
-
Building codes may underestimate multiple hazard risks
Current building codes consider natural hazards individually — if earthquakes rank as the top threat in a particular area, local codes require buildings to withstand a specified seismic load; if hurricanes or tornadoes are the chief hazard, homes and buildings must be designed to resist loads up to an established maximum wind speed; engineers say that building codes should address multiple hazard scenarios
-
-
Two radiation generators help protect U.S.

One aspect of a nuclear explosion— the electro-magnetic pulse, or EMP — was much discussed during the cold war: scientists argued that exploding a nuclear bomb in the skies high above the United States would create an EMP which would disrupt electronic equipment and paralyze the nation; two remarkable pulsed-power machines used to test the U.S. defenses against atomic weapons have surpassed milestones at Sandia National Laboratories
-
-
U.S., Europe Collaborating on Smart Grid Standards Development
The other day the U.S. Commerce Department’s National Institute of Standards and Technology (NIST) and the European Union’s (EU) Smart Grid Coordination Group (SG-CG) jointly announced their intention to work together on Smart Grid standards development,
-
-
Saltwater intrusion threatens South Florida’s water supplies
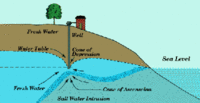
South Florida’s water supply is becoming increasingly endangered by saltwater that is steadily seeping in from the ocean and contaminating supplies; despite the best efforts of local communities to stop the problem, saltwater intrusion is spreading
-
More headlines
The long view
Water Wars: A Historic Agreement Between Mexico and US Is Ramping Up Border Tension
As climate change drives rising temperatures and changes in rainfall, Mexico and the US are in the middle of a conflict over water, putting an additional strain on their relationship. Partly due to constant droughts, Mexico has struggled to maintain its water deliveries for much of the last 25 years, deliveries to which it is obligated by a 1944 water-sharing agreement between the two countries.
Trump Is Fast-Tracking New Coal Mines — Even When They Don’t Make Economic Sense
In Appalachian Tennessee, mines shut down and couldn’t pay their debts. Now a new one is opening under the guise of an “energy emergency.”
Smaller Nuclear Reactors Spark Renewed Interest in a Once-Shunned Energy Source
In the past two years, half the states have taken action to promote nuclear power, from creating nuclear task forces to integrating nuclear into long-term energy plans.
Keeping the Lights on with Nuclear Waste: Radiochemistry Transforms Nuclear Waste into Strategic Materials
How UNLV radiochemistry is pioneering the future of energy in the Southwest by salvaging strategic materials from nuclear dumps –and making it safe.
Model Predicts Long-Term Effects of Nuclear Waste on Underground Disposal Systems
The simulations matched results from an underground lab experiment in Switzerland, suggesting modeling could be used to validate the safety of nuclear disposal sites.
