-
Waste glass cleans up water

A simple method converts waste glass into a material which can be used to remove pollutants from contaminated water; the method uses colored glass which is being stockpiled in the United Kingdom as there is less recycling demand for green and brown bottles than there is for clear bottles
-
-
Rising political, economic tensions over critical minerals

The clean energy economy of the future hinges on many things, chief among them the availability of the scores of rare Earth minerals and other elements used to make everything from photovoltaic panels and cellphone displays to the permanent magnets in cutting edge new wind generators; trouble is, China currently controls about 97 percent of the mining and production of the minerals, and it is using that control to give Chinese companies an advantage and for political pressure on other countries
-
-
Self-repairing composites repair cracks in coating of buildings, bridges
Researchers have developed vascularized structural composites, creating materials that are lightweight and strong with potential for self-healing, self-cooling, metamaterials, and more; these artificial microvascular systems can self-repair of materials damage, such as cracks in a coating applied to a building or bridge
-
-
E-textiles now come with memory-storing fiber
E-textiles could help soldiers, first responders — but also the sick and infirm; the integration of electronics into textiles is a growing field of research that may soon enable smart fabrics and wearable electronics
-
-
Man-made silk mimics spider silk

Spider silk has attracted human interest for thousands of years due to its toughness and ductility; as with most biomaterials, spider silk has evolved over millions of years resulting in a combination of properties that far exceeds any man-made material; until now
-
-
Industrial stent-like repairs for failing pipelines
There are thousands of miles of pipe underground in the United States, some more than 100 years old; gas, oil, water, and sewage seep, and sometimes gush, through corroded joints and defective welds every day; new technology uses carbon and glass laminates to repair and replace failing pipelines
-
-
9/11 legacy: more resilient skyscrapers

Following the 9/11 attacks on the Twin Towers in New York, many predicted that the age of the skyscraper was over; there has been no slowdown in skyscraper orders, however — but the skyscrapers being built today are much stronger than the Twin Towers were; new materials, innovative designs, and attention to safety make today’s skyscraper much more resilient to man-made and natural disasters
-
-
Microbes clean up nuclear waste -- and generate electricity
Researchers have discovered how microbes generate electricity while cleaning up nuclear waste and other toxic metals; the microbes effectively immobilize the radioactive material and prevent it from leaching into groundwater; the discovery could benefit sites changed forever by nuclear contamination
-
-
Studying the effects of fire on steel structures, nuclear plants
Building fires may reach temperatures of 1,000 degrees Celsius, or more than 1,800 degrees Fahrenheit, and the strength of steel structures drops by about 40 percent when exposed to temperatures exceeding 500 degrees Celsius; scientists study precisely what happens to the connections between a floor’s steel beams and the building columns when these connections are exposed to intense heat
-
-
DHS warns copper thefts on the rise

DHS officials warn that copper thefts from critical infrastructure and key resource sectors in the United States are on the rise; in March, a Port of Houston security guard was arrested for giving his friends and families access to the port, where they allegedly stole more than 22,000 pounds of copper
-
-
New material dramatically increases explosive force of weapons

A revolutionary material that will replace steel in warhead casings will bring added lethality and increase the likelihood of a hit on an enemy target; by combining several metals with standard manufacturing techniques, High-Density Reactive Material (HDRM) has the potential dramatically to increase the explosive impact of most weapons with little or no compromise in strength or design
-
-
Self-assembled "micro-robots" designed
Tiny micro-robots — just half a millimeter wide — assemble themselves into star shapes when an alternating magnetic field is applied; the robots can pick up, transport, and put down other non-magnetic particles — potentially enabling fabrication of precisely designed functional materials in ways not currently possible
-
-
New invisibility cloak conceals objects from human view
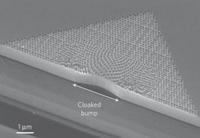
For the first time, scientists have devised an invisibility cloak material that hides objects from detection using light that is visible to humans; the new “carpet cloak” works by concealing an object under layers of silicon oxide and silicon nitride etched in a special pattern, and bending light waves away from the bump that the object makes, so that the cloak appears flat and smooth like a normal mirror
-
-
Transforming acids into bases
Chemists at the University of California, Riverside have accomplished in the lab what until now was considered impossible: transform a family of compounds which are acids into bases; the research offers vast family of new catalysts for use in drug discovery, biotechnology
-
-
Antibacterial stainless steel created
Materials scientists have devised a way of making stainless steel surfaces resistant to bacteria; by introducing silver or copper into the steel surface — rather than coating it on to the surface — the researchers have developed a technique that not only kills bacteria but is very hard and resistant to wear and tear during cleaning
-
- All
- Regional
- Water
- Biometrics
- Borders/Immig
- Business
- Cybersecurity
- Detection
- Disasters
- Government
- Infrastructure
- International
- Public health
- Public Safety
- Communication interoperabillity
- Emergency services
- Emergency medical services
- Fire
- First response
- IEDs
- Law Enforcement
- Law Enforcement Technology
- Military technology
- Nonlethal weapons
- Nuclear weapons
- Personal protection equipment
- Police
- Notification /alert systems
- Situational awareness
- Weapons systems
- Sci-Tech
- Sector Reports
- Surveillance
- Transportation
Advertising & Marketing: advertise@newswirepubs.com
Editorial: editor@newswirepubs.com
General: info@newswirepubs.com
2010-2011 © News Wire Publications, LLC News Wire Publications, LLC
220 Old Country Road | Suite 200 | Mineola | New York | 11501
Permissions and Policies
Editorial: editor@newswirepubs.com
General: info@newswirepubs.com
2010-2011 © News Wire Publications, LLC News Wire Publications, LLC
220 Old Country Road | Suite 200 | Mineola | New York | 11501
Permissions and Policies
