-
New fertilizer can be used to grow food – but not build bombs

Ammonium nitrate fertilizer is used in agriculture, but when mixed with a fuel such as diesel, it is highly explosive. It was used in about 65 percent of the 16,300 homemade IEDs in Afghanistan in 2012.About 1,900 troops were killed or wounded in IED attacks in 2012, 60 percent of American combat casualties. There have been more than 17,000 global IED incidents in 123 countries in the past two years. Timothy McVeigh used ammonium nitrate in Oklahoma City in 1995. Scientists have developed a fertilizer that helps plants grow but cannot detonate a bomb.
-
-
Israel's military intelligence: Assad forces used chemical weapons
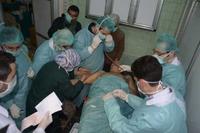
Israeli military intelligence for the first time publicly said that the Syrian military used chemical weapons in an attack on civilians on 19 March. Brig. Gen. Itai Brun, the head of AMAN’s (Israel’s military intelligence) research division, said that information gathered by Israel’s military intelligence, some of it pubic, some of it not, indicates that the weapon used in the attack outside Aleppo was sarin nerve gas. Brun said the Syrian regime has used sarin gas in several other small-scale attacks. Syria has the world’s largest arsenal of chemical weapons.
-
-
Winner announced in the first DARPA FANG Challenge

The Ground Systems team outpaces more than 200 teams and 1,000 participants, submitting the winning mobility in the Fast Adaptable Next-Generation Ground Vehicle (FANG) Mobility/Drivetrain Challenge, and drivetrain subsystem design and claiming the $1 million prize.
-
-
Hagel reassures Israel, discusses large arms deal
U.S. Defense Secretary Chuck Hagel arrived in Israel Sunday for his first visit in the country as secretary of defense. Some elements in the pro-Israel lobby in the United States campaigned against Hagel’s nomination, and Hagel went out of his way to assure Israelis that his position on Israel is not what it was portrayed to be. One of the main reasons for Hagel’s visit is to discuss a major U.S. arms deal that would offer Israel missiles for its fighter aircraft – but also plus KC-135 refueling planes which could be used in a long-range strike on a country such as Iran. Until now, the United States refused to sell refueling tankers to Israel.
-
-
New submarine hunting program reaches milestones
DARPA’s Distributed Agile Submarine Hunting (DASH) Program has tested two complementary prototype systems as part of its Phase 2 development effort. The prototypes demonstrated functional sonar, communications, and mobility at deep depths. The successful tests furthered DASH’s goals to apply advances in deep-ocean distributed sonar to help find and track quiet submarines.
-
-
DARPA shows smaller pixels, smaller thermal cameras for soldiers
The U.S. military uses long-wave infrared (LWIR) cameras as thermal imagers to detect humans at night. These cameras are usually mounted on vehicles as they are too large to be carried by a single soldier and are too expensive for individual deployment. DARPA researchers, however, recently demonstrated a new five-micron pixel LWIR camera that could make this class of camera smaller and less expensive.
-
-
U.S. Army weak on mobile devices security

The U.S. Army has developed a mobile strategy to guide its adoption of mobile devices. A Department of Defense audit found that the Army has been lax in developing security guidelines for the use of the thousands of mobile devices now in service, and that these already-weak and insufficient security guidelines are inconsistently implemented.
-
-
Exploring the human brain to support national security
The other day, at a White House event, President Barack Obama unveiled a new research initiative designed to revolutionize the understanding of the human brain. DARPA plans $50 million in 2014 investments to translate this increased understanding of brain function to create new capabilities.
-
-
Large robotic jellyfish to patrol the oceans

The Office of Naval Research wants to place self-powering, autonomous machines in waters for the purposes of surveillance and monitoring the environment, in addition to other uses such as studying aquatic life, mapping ocean floors, and monitoring ocean currents. Researchers have built a device for that purpose — a life-like, autonomous robotic jellyfish the size and weight of a grown man, 5 foot 7 inches in length and weighing 170 pounds.
-
-
Growing U.S. concern over North Korean miscalculation
U.S. officials are increasingly concerned with the escalating tensions on the Korean Peninsula and the risk of miscalculation. The fear is that North Korea’s young leader, Kin Jong Un, may have launched the harsh rhetorical campaign against South Korea and the United States for domestic reasons – especially the need to establish his leadership credentials in the eyes of the skeptical North Korean military – but that his youth and inexperience may lead him to over-play his hand. “He is 28, 29 years old, and he keeps going further and further out, and I don’t know if he can get himself back in,” Rep. Peter King (R-New York), former chairman of the House Homeland Security Committee, said.
-
-
GAO lauds U.S. Navy's science and technology R&D
The Office of Naval Research (ONR) is the Department of the Navy’s science and technology (S&T) provider, charged with discovering, developing, and transitioning innovative S&T to meet soldier needs. Since its inception in 1946, ONR research efforts have supported the development of the laser, GPS, transistors, fiber optics, radar, cell phones, and more. A recent Government Accountability Office (GAO) report cites ONR’s Future Naval Capabilities (FNC) as an example of efficient, cost-effective program for making science and technology research functional.
-
-
U.S. deploys F-22 stealth fighters to South Korea
As tensions on the Korean Peninsula intensify, and North Korea’s belligerent threats multiply, sources inside the administration said that the United States has deployed F-22 stealth fighter jets to South Korea to take part in large-scale military drills.
-
-
Cost to U.S. of Iraq, Afghanistan wars to exceed $4 trillion

A new study from Harvard University, calculating the cost to the United States of the wars in Iraq Afghanistan, has concluded that that cost will come to between $4 trillion to $6 trillion. This cost includes the spending on medical care for wounded soldiers and repairs to and replacement of military gear used in the two wars. The decision by the Bush administration to pay for the wars with borrowed money has increased their costs, the study says. In all, the two wars have added $2 trillion to the U.S. debt, accounting for about 20 percent of the debt incurred from 2001 to 2012.
-
-
British public divided on merits of drone strikes

Fifty-five percent of the British public would support the U.K. government assisting in a drone missile strike to kill a known terrorist overseas, but support drops substantially if innocent casualties are likely, according to a new study.
-
-
Maintaining U.S. “overwhelming technological advantage” over adversaries
DARPA’s Tactical Technology Office (TTO) creates advanced platforms, weapons, and space systems to help preserve U.S. military superiority through overwhelming technological advantage. DARPA will hold a two-day event aims to spur innovation by gathering potential partners from across TTO’s portfolio.
-
More headlines
The long view
Bookshelf: Smartphones Shape War in Hyperconnected World
The smartphone is helping to shape the conduct and representation of contemporary war. A new book argues that as an operative device, the smartphone is now “being used as a central weapon of war.”
