-
Philippines prepares for worse disasters to come
On average, the Philippines experiences about twenty typhoons a year, including three super-typhoons and many incidents of flooding, drought, earthquakes, tremors, and occasional volcanic eruptions, making the country one of the most naturally disaster-prone areas in the world. Filipino government agencies, with the help of international disaster and relief agencies, have created new strategies for disaster preparedness, response, and mitigation which may well have potential applications in other parts of the world. As the impact of climate change grows more pronounced, the Philippines is becoming a hothouse for developing new methods and systems in the growing business of disaster relief.
-
-
Holograms to help in fighting malaria
Scientists have developed a 3D filming technique that could inform research to stem the spread of malaria. Creating moving digital holograms of malaria sperm has given researchers fresh insights into the behavior of these tiny life forms. Understanding how malaria parasites mate could pave the way for improved prevention and control of this deadly disease, which poses a threat to half of the world’s population.
-
-
Quick ID for water pathogens

New research purports to help people stay healthy by developing a real-time water bug testing that could precisely identify the culprits responsible for waterborne disease.
-
-
Planet’s arable land rapidly degrading

Great civilizations have fallen because they failed to prevent the degradation of the soils on which they were founded. The modern world could suffer the same fate. A new study describes how the productivity of many lands has been dramatically reduced as a result of soil erosion, accumulation of salinity, and nutrient depletion.
-
-
Zapping bugs dead

Restaurants and supermarkets could save millions of dollars by hanging on to bug zapper bulbs instead of tossing them every year as they normally do, a new study has found. What is more, the benefits could extend to the environment by keeping some of the bulbs’ mercury out of the waste stream.
-
-
Rising temperatures threaten Salt Lake City’s water supply
In an example of the challenges water-strapped Western cities will face in a warming world, new research shows that every degree Fahrenheit of warming in the Salt Lake City region could mean a 1.8 to 6.5 percent drop in the annual flow of streams that provide water to the city. By midcentury, warming Western temperatures may mean that some of the creeks and streams that help slake Salt Lake City’s thirst will dry up several weeks earlier in the summer and fall.
-
-
DHS, FDA: Decorative contact lenses for Halloween costumes are risky
Many will celebrate Halloween today, and federal officials are warning the public about the dangers associated with counterfeit decorative contact lenses. Decorative and colored lenses are becoming increasingly popular, especially around this time of year. Several federal agencies have teamed up to launch Operation Double Vision – already underway — to seize illegal, harmful products from store shelves.
-
-
Warming will disturb nutrients balance in drylands, affecting food production
Drylands cover about 41 percent of Earth’s land surface and support more than 38 percent of the world’s population. As the world’s population grows, people will increasingly rely on marginal lands — particularly drylands — for production of food, wood and biofuels. Trouble is, an increase in aridity due to global warming will disturb the balance of nutrients in the soil and reduce productivity of the world’s drylands, a landmark study predicts. Increasing aridity is associated with a reduction in carbon and nitrogen in the soil and an increase in phosphorus.
-
-
Where should U.S. radioactive waste be buried?
In the United States, about 70,000 metric tons of spent commercial nuclear fuel are located at more than seventy sites in thirty-five states. Shales and other clay-rich (argillaceous) rocks have never been seriously considered for holding America’s spent nuclear fuel, but it is different overseas. France, Switzerland, and Belgium are planning to put waste in tunnels mined out of shale formations, and Canada, Japan, and the United Kingdom are evaluating the idea.
-
-
Sharp increase in radioactive water leaks at Fukushima
Tokyo Electric Power(TEPCO) has reported a rise in groundwater radiation levels, saying a tank at the firm’s Fukushima plant leaked 300 metric tons of toxic water in August 2013. Water samples from wells, taken in mid-October, show a record-high concentration of beta-ray emitting substances, and a sharp increase in the presence of radioactive tritium. Japanese prime ministerShinzo Abe, in a tacit admission that Japan cannot effectively handle the continuing radiation leaks from the stricken plant, said Japan would be interested in receiving foreign help to contain widening radioactive water leaks at Fukushima.
-
-
Burping for power: Tapping cow burps for natural gas
Scientists in Argentina have developed a method to transform the gas created by cows’ digestive systems into fuel. The technique channels the digestive gases from bovine stomach cavities through a tube and into a tank, where the gases, called eruptos (burps) in Spanish, are processed to separate methane from other gases such as carbon dioxide.
-
-
More than 500 million people could face increasing water scarcity
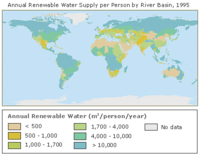
Both freshwater availability for many millions of people and the stability of ecosystems such as the Siberian tundra or Indian grasslands are put at risk by climate change. Even if global warming is limited to 2 degrees above pre-industrial levels, 500 million people could be subject to increased water scarcity.
-
-
New apps to keep you healthy
For those wanting to keep their distance from health threats like E. coli-contaminated lettuce or the flu, there are two upcoming apps for that. The Department of Energy’s Pacific Northwest National Laboratory (PNNL) hosted a competition this summer in which graduate students designed two mobile apps to fight the threats of food-related illnesses and the flu. The apps are called FoodFeed and FL•U (pronounced “flu you”).
-
-
1930s fight against malaria in U.S. a model for today’s global campaign

Malaria killed an estimated 1.24 million people worldwide in 2010 and has decimated economies in the heavily populated, warm climate regions. A new study about the elimination of malaria in the 1930s American South may have significant implications for solving modern day malaria outbreaks in parts of Africa, Central and Latin America, and Asia.
-
-
Small changes in agricultural practices reduce produce-borne illness

Foodborne illness sickens an estimated 9.4 million and kills around 1,300 annually in the United States, according to the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention. Produce accounts for nearly half the illnesses, and 23 percent of the deaths. Researchers have identified some agricultural management practices in the field that can either boost or reduce the risk of contamination in produce from two major foodborne pathogens: salmonella, the biggest single killer among the foodborne microbes, and Listeria monocytogenes.
-
More headlines
The long view
We Ran the C.D.C.: Kennedy Is Endangering Every American’s Health
Nine former leaders of the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC), who served as directors or acting directors under Republican and Democratic administrations, serving under presidents from Jimmy Carter to Donald Trrump, argue that HHS Secretary Roert F. Kennedy Jr. poses a clear and present danger to the health of Americans. He has placed anti-vaxxers and conspiracy theorists at top HHS positions, and he appears to be guided by a hostility to science and a belief in bizarre, unscientific approaches to public health.
