-
Killing bugs dead: “Attract-and-kill” technique tackles Argentine ants

After being inadvertently introduced in the United States from South America, Argentine ants have successfully invaded urban, agricultural, and natural settings nationwide. In urban California, the Argentine ant is among the primary pest ants. For example, this particular species of ants makes up 85 percent of ants sampled by commercial pest control companies in just the Greater San Diego Area. UC Riverside entomologists devise a novel “attract-and-kill” technique, which involves mixing a synthetic pheromone in insecticide sprays, to tackle the pest.
-
-
Preoccupation with bioterrorism hobbles preparations for natural spread of deadly viruses
Preoccupation with hypothetical bioterrorism attacks is leaving America more vulnerable to the threat of natural spread of deadly viruses. Since the 9/11 attacks, the federal government has poured billions of dollars to prevent and monitor threats of bioterrorism, yet the United States was ill-prepared for the swine flu outbreak of 2009. Experts say it is time to rebalance public health priorities so that preparations for the real threat of the outbreak of infectious diseases will not take a back seat to preparations for the more remote threat of bioterrorism.
-
-
Central African Republic, already mired in ethnic violence, faces another threat: famine

Since last year, when they had to flee the intensifying violence across the Central African Republic, farming communities had to abandon their fields along the main roads to replant deep in the bush. This disruption led them to produce much less than in previous years, with a major impact on their food reserves, which will last till February instead of July. The success of the next planting season crucially hinges on the return of farming families to the fields. Families who are unable to plant in March will have to wait one whole year before they can hope to harvest again. Failure to plant in March will have dire consequences for the food security of the Central African Republic’s population.
-
-
Extensive use of antibiotics in agriculture creating public health crisis
In the United States, 80 percent of the antibiotics are consumed in agriculture and aquaculture for the purpose of increasing food production. This flood of antibiotics released into the environment — sprayed on fruit trees and fed to the likes of livestock, poultry, and salmon, among other uses — has led bacteria to evolve.Mounting evidence shows resistant pathogens are emerging in the wake of this veritable flood of antibiotics — resulting in an increase in bacteria that is immune to available treatments. Scientists say that if the problem is left unchecked, this will create a health crisis on a global scale.
-
-
Breed-specific legislation does not protect the public from dangerous dogs

Research conducted by animal behavior experts challenges the basis of breed-specific legislation designed to protect the public from “dangerous” dogs.The researchers concluded that rather than making people safer, current legislation in the United Kingdom could be lulling them into a false sense of security.
-
-
Freshwater loss compounds climate change’s detrimental effects on agriculture
A warmer world is expected to have severe consequences for global agriculture and food supply, reducing yields of major crops even as population and demand increases.Agricultural models estimate that given the present trajectory of greenhouse gas emissions, climate change will directly reduce food production from maize, soybeans, wheat, and rice by as much as 43 percent by the end of the twenty-first century. Now, a new analysis combining climate, agricultural, and hydrological models finds that shortages of freshwater used for irrigation could double the detrimental effects of climate change on agriculturedue to the reversion of twenty to sixty million hectares of currently irrigated fields back to rain-fed crops.
-
-
Uranium found to be mobile in a natural wetland

Because they are known to mop up pollutants, artificial wetlands are considered to be an efficient strategy to contain waterborne uranium. Studying a natural wetland near a former uranium-mining site in the French region of Limousin, however, researchers have found that under certain circumstances, uranium can be partly remobilized into the surrounding water. The researchers show how it becomes mobile again by binding to tiny metallic and organic compounds with a little help from ambient bacteria.
-
-
Superbugs discovered to be breeding in sewage plants
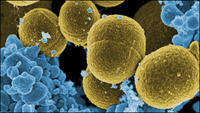
Rice University study finds that two wastewater treatment plants in China fail to kill antibiotic-resistant bacteria. The bacteria were not only escaping purification but also breeding and spreading their dangerous cargo.
-
-
Upper Rio Grande to experience growing gap between water supply and demand
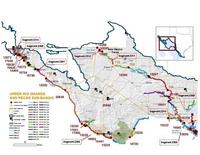
Increasing temperatures and changes in the timing of snowmelt runoff could impact the amount of water available on the upper Rio Grande in the future, says a news study. Temperatures will increase four to six degrees Fahrenheit by the end of the twenty-first century, according to the climate modeling used in the study. Although the modeling projects that total annual average precipitation in the basin will not change considerably, we are likely to see a decreasing snowpack, an earlier and smaller spring snowmelt runoff and an increase in the frequency, intensity and duration of both droughts and floods.
-
-
Survey of deep-sea chemical munitions dump off California finds no chemical weapons

Since the Second World War, U.S. nautical charts have shown seven “chemical munitions dumping areas” along the Pacific Coast between San Francisco and the Mexican border. Little or no information, however, is available about the amount, location, or nature of the materials that were dumped at most of these sites. Researchers from the Monterey Bay Aquarium Research Institute (MBARI) conducted a detailed survey of one supposed deep‐water dump site off Southern California, and found that it contained no chemical munitions. The researchers conclude that not all sites marked as chemical munitions dumps may actually have been used for this purpose.
-
-
James Bond drank too much to perform at the level depicted in books, movies
A detailed examination of James Bond’s books shows that Bond’s weekly alcohol intake is over four times the recommended limit for an adult male, putting him at high risk of several alcohol related diseases, such as alcoholic liver disease, cirrhosis, impotence, and alcohol-induced tremor, and an early death. The medical team concluded that it would not be realistic to expect Bond to have the capacity to perform (in all aspects of life) at his high level of alcohol intake.
-
-
India-Pakistan nuclear war would lead to world-wide famine: study
An India-Pakistan nuclear war may see the use of about 100 Hiroshima-size bombs – about half of India and Pakistan’s nuclear arsenals. A new study says that a nuclear exchange on such a scale would “probably cause the end (of) modern industrial civilization as we know it” by subjecting about two billion people to the risk of starvation, and causing massive economic and social disruptions far away from the theater of war. Among the consequences of a nuclear exchange: Chinese winter wheat production could decline by 50 percent during the first year and by more than 30 percent over ten years; there would be a 21 percent decline in Chinese middle-season rice production during the first four years and an average 10 percent decline in the following six years; corn and soybean production in the United States would decline by 10 percent on average for ten years.
-
-
Air transportation data helps identify, predict pandemics
Computational model demonstrates how disease spreads in a highly connected world. The computational work has led to a new mathematical theory for understanding the global spread of epidemics. The resulting insights could not only help identify an outbreak’s origin but could also significantly improve the ability to forecast the global pathways through which a disease might spread.
-
-
Food security and self-provision of major cities
Wealthy capital cities vary greatly in their dependence on the global food market. The Australian capital Canberra produces the majority of its most common food in its regional hinterland, while Tokyo primarily ensures its food security through import. The Copenhagen hinterland produces less than half of the consumption of the most common foods. For the first time, researchers have mapped the food systems of capital cities, an essential insight for future food security if population growth, climate change, and political instability will affect the open market.
-
-
U.K. tightens animal disease surveillance
The U.K. Animal Health and Veterinary Laboratories Agency(AHVLA) has introduced a new surveillance system to detect new and re-emerging animal disease threats in England and Wales. The new system is expected to improve the geographical and species-specific coverage of disease.The new system will rely more on private sector laboratories for gathering surveillance intelligence and less on government laboratories.
-
More headlines
The long view
We Ran the C.D.C.: Kennedy Is Endangering Every American’s Health
Nine former leaders of the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC), who served as directors or acting directors under Republican and Democratic administrations, serving under presidents from Jimmy Carter to Donald Trrump, argue that HHS Secretary Roert F. Kennedy Jr. poses a clear and present danger to the health of Americans. He has placed anti-vaxxers and conspiracy theorists at top HHS positions, and he appears to be guided by a hostility to science and a belief in bizarre, unscientific approaches to public health.
