DisastersIndian Ocean phenomenon helps in predicting extreme weather
The Indian Ocean Dipole is the difference in sea-surface temperatures between the western and eastern part of the Indian Ocean. A better understanding of the relationship between the Indian Ocean Dipole and extreme weather events will enable farmers, industry, communities, and governments better to anticipate and prepare for droughts and increased bushfire risk, up to six months in advance of the event.
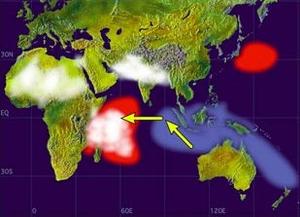
Indian Ocean Dipole in positive mode // Source: albrari.com
A phenomenon in the Indian Ocean that affects events in southeast Australia is helping to predict extreme weather up to six months in advance.
The phenomenon, the Indian Ocean Dipole, is the difference in sea-surface temperatures between the western and eastern part of the Indian Ocean, and until recently has been one of the most influential but the least understood natural forces affecting Australia’s climate. An international team of scientists, led by CSIRO Wealth from Ocean Flagship’s Dr. Wenju Cai, confirmed the link and have published their findings in the journal Nature Geoscience.
A CSIRO release reports that a better understanding of the relationship between the Indian Ocean Dipole and extreme weather events will enable farmers, industry, communities, and governments better to anticipate and prepare for droughts and increased bushfire risk, up to six months in advance of the event.
Just as the El Niño Southern Oscillation (ENSO) affects weather patterns across the Pacific Ocean, the Indian Ocean Dipole influences weather and extreme events across the Indian Ocean.
While ENSO fluctuates between “El Nino,” “neutral,” and “La Nina” phases, the Dipole fluctuates between “positive,” “neutral,” and “negative” phases approximately every three to eight years.
The positive phase is characterized by greater-than-average sea-surface temperatures, more rain in the western Indian Ocean region, and cooler waters in the eastern Indian Ocean. It tends to cause droughts in East Asia and Australia, and flooding in parts of the Indian subcontinent and East Africa.
Positive Dipole activity has, to date, preconditioned major wildfires in southeast Australia, caused coral reef death across western Sumatra, and exacerbated malaria outbreaks in East Africa.
Dr. Cai said the findings provide greater confidence in predicting extreme weather up to two seasons in advance, and furthermore, projecting positive IOD events into the future.
“Over the past 50 years, the Dipole has been trending upwards, increasing the number of positive events, occurring an unprecedented 11 times over the past 30 years,” Dr. Cai said.
“For example, there were three consecutive positive Dipole events between 2006 and 2008, which preconditioned the catastrophic Black Saturday bushfires in Victoria.”
He said the increased frequency is due to the tropical Indian Ocean warming faster in the west than the east, due in part to the increasing temperature of Earth’s surface.
“This warming pattern will continue in the decades to come, according to the state-of-the-art global climate models used in the study,” Cai said.
He said that as the warming pattern continues, future changes will include drier winter and spring seasons over southern Australia, particularly during positive Indian Ocean Dipole years.
— Read more in Wenju Cai et al., “Projected response of the Indian Ocean Dipole to greenhouse warming,” Nature Geoscience 6 (28 November 2013): 999–1007 (doi:10.1038/ngeo2009)
