-
Massachusetts takes steps to withstand climate change impacts
Governor Deval Patrick of Massachusetts earlier this week unveiled a $50 million plan to help prepare Massachusetts for the challenges climate change poses to energy supplies, public health, transportation, and basic infrastructure in his state. A $40 million grant from the state’s Department of Energy Resources will help cities and towns develop protections around energy services, and $10 million will go toward shoring up critical coastal infrastructure and dam repair.
-
-
Time to replace GDP with new metrics: experts
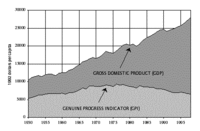
Gross Domestic Product is a misleading measure of national success, say public policy experts. “When it was instituted seven decades ago, GDP was a relevant signpost of progress,” they say. “Increased economic activity was credited with providing employment, income and amenities to reduce social conflict and prevent another world war. But the world today is very different compared to how it was then.”
-
-
NRC: storing spent nuclear fuel in cooling pools is safe
The nuclear reactors now in service in the United States were built with the assumption that the spent fuel would be removed from nuclear the facilities after a few years, but because the government has failed to provide a centralized place to store the spent fuel, utility companies have had to store an ever-growing quantity of it in spent fuel pools on the grounds of the facilities. Scientists argue that it would be safer to move some of the spent fuel into giant steel and concrete casks, where it can be stored dry, with no reliance on water, pumps, or filters to keep them cool. The nuclear industry and the NRC do not agree.
-
-
California bill would restrict selling, access to LPR-collected data
A bill before the California State Senate would to prohibit law enforcement agencies and private firms in California from selling data collected by automatic license plate readers. (LPRs). The proposed Senate Bill 893 would prohibit LPR operators from selling data to non-law enforcement agencies or to non-law enforcement officials. Law enforcement access to LPR data retained for more than five years would require a court order.
-
-
Stimulating plant growth and increasing crop yields
Plants naturally slow their growth or even stop growing altogether in response to adverse conditions, such as water shortage or high salt content in soil, in order to save energy. They do this by making proteins that repress the growth of the plant. Growth repression can be problematic for farmers as crops that suffer from restricted growth produce smaller yields. Scientists have discovered a natural mechanism in plants that could stimulate their growth even under stress and potentially lead to better crop yields.
-
-
Thinking outside the box: Free public education that pays for itself
A U.K. researcher proposes an innovative way to pay for college and graduate education: students would not pay for their education while at school. Rather, they will commit to paying a fixed percentage of their income (say, 6 percent) during their prime earning years (35-54, for example) to the university that awarded their degree. These student promises for a given university cohort will be bundled and sold to investors as “education securities.” Investors would receive a share of the average income for the cohort. Because average income moves with inflation, investors would be assured of getting their initial investment back plus whatever amount is necessary to cover changes in the value of their money. The securities could even be designed to include a real return (over inflation) of as much as 3 percent.
-
-
Palo Alto Networks acquires Morta Security
Palo Alto Networks has acquired Morta Security, a Silicon Valley-based cybersecurity company operating in stealth mode since 2012. Financial terms of the acquisition were not disclosed. Palo Alto Networks says that the acquisition of Morta Security further strengthens its position as a provider of next-generation enterprise security.Palo Alto Network says that most organizations still rely on legacy point technologies that address only specific types of attacks, or phases of the attack. Because of the singular nature of these technologies, they are ill-equipped to detect and prevent today’s advanced cyberattacks.The company says that to address these challenges, a new approach is required.
-
-
2013 natural catastrophes dominated by extreme weather in Europe, Supertyphoon Haiyan

Exceptionally high losses from weather-related catastrophes in Europe and Supertyphoon Haiyan dominated the overall picture of natural catastrophes in 2013. Floods and hailstorms caused double-digit billion-dollar losses in central Europe, and in the Philippines one of the strongest cyclones in history, Supertyphoon Haiyan, resulted in a human catastrophe with over 6,000 fatalities.
-
-
Improper use of biocides in food production poses public health risks
Biocides used in the food industry at sublethal doses may be endangering, rather than protecting, public health by increasing antibiotic resistance in bacteria and enhancing their ability to form harmful biofilms, according to a new study.
-
-
DNA data management specialist DNAnexus secures $15 million in Series C financing
Mountain View, California-based DNAnexus, a specialist in cloud-based solutions for large-scale DNA data management and analysis, on Friday announced that it has closed a $15 million Series C funding led by Claremont Creek Ventures, Google Ventures, TPG Biotech, and First Round Capital. The company says that its Platform-as-a-Service (PaaS) is being adopted by more customers seeking a solution to the needs of global enterprises face when building clinically compliant analysis pipelines for DNA sequence data.
-
-
FireEye acquires Mandiant in a deal worth about $1 billion
The combination of the two companies creates one of the cybersecurity industry leading vendor. The combined competencies of the two companies would allow them to find and stop attacks at every stage of the attack life cycle. “The reason for this deal is that we now live in a world of constant compromise. When you know you will be compromised, you can’t just continue trying to keep the bad guys out; you also need to investigate every compromise, figure out what happened, prevent it from ever happening again and clean up the mess,” says one analyst.
-
-
Nations' nuclear ambitions not discouraged by few suppliers
Twenty-nine countries are considering constructing their first nuclear power plant. There are doubts as to which of these nuclear “newcomer” countries can actually succeed and join the thirty-one countries that already operate nuclear reactors. If even half of the national plans for nuclear power plants materialize, the geography of nuclear energy would radically change and could revitalize a stagnant industry. But given the obstacles to starting a national nuclear power program even for rich and stable countries, it’s not likely to happen quickly elsewhere.
-
-
Minimizing power grid disruptions from wind power
Researchers have found that an increase in the use of wind power generation can make the power grid more fragile and susceptible to disruptions. The researchers, however, did not just identify the problem — they have also devised a technique for coordinating wind power generation and energy storage in order to minimize the potential for such power disruptions.
-
-
FAA approves testing, developing standards for commercial use of drones
The Federal Aviation Administration(FAA) yesterday (Monday) has authorized test sites for UAVs. The FAA has selected six institutions to run the tests and operate the test sites. The test sites are part of a program to develop safety and operational rules for drones by the end of 2015, as mandated by Congress. Experts anticipate an exponential growth of drone use in the agriculture and law enforcement sectors. Analysts predict that more than 70,000 jobs would be created in the first three years after Congress approves drone use in U.S. skies, and that the global commercial drone market will reach $89 billion in the next decade.
-
-
Small, portable, fast TLC unit for explosives, drugs analysis
Field Forensics of St. Petersburg, Florida, unveiled its microTLC, a portable and easy to use solution for pre-screening and presumptive identification of drugs and explosive mixtures. Thin layer chromatography (TLC) is an established laboratory procedure which identifies compounds belonging to the same general chemical class. The microTLC makes it possible for both laboratory and field analysis to be performed by first responders and forensics scientists.
-
- All
- Regional
- Water
- Biometrics
- Borders/Immig
- Business
- Cybersecurity
- Detection
- Disasters
- Government
- Infrastructure
- International
- Public health
- Public Safety
- Communication interoperabillity
- Emergency services
- Emergency medical services
- Fire
- First response
- IEDs
- Law Enforcement
- Law Enforcement Technology
- Military technology
- Nonlethal weapons
- Nuclear weapons
- Personal protection equipment
- Police
- Notification /alert systems
- Situational awareness
- Weapons systems
- Sci-Tech
- Sector Reports
- Surveillance
- Transportation
Advertising & Marketing: advertise@newswirepubs.com
Editorial: editor@newswirepubs.com
General: info@newswirepubs.com
2010-2011 © News Wire Publications, LLC News Wire Publications, LLC
220 Old Country Road | Suite 200 | Mineola | New York | 11501
Permissions and Policies
Editorial: editor@newswirepubs.com
General: info@newswirepubs.com
2010-2011 © News Wire Publications, LLC News Wire Publications, LLC
220 Old Country Road | Suite 200 | Mineola | New York | 11501
Permissions and Policies
