-
Standardizing small, self-sustaining electric microgrids
When Department of Energy and Oak Ridge National Laboratory researchers talk about “islanding,” or isolating, from the grid, they are discussing a fundamental benefit of microgrids — small systems powered by renewables and energy storage devices. The benefit is that microgrids can disconnect from larger utility grids and continue to provide power locally.
-
-
Lights out: Experts say instability of world’s power supplies must be urgently addressed
A new study reveals the urgent need to address instabilities in the supply of electrical power to counteract an increase in the frequency and severity of urban blackouts. The work builds on previous studies which examined a sharp increase in electrical usage over recent years, and warned the world to prepare for the prospect of coping without electricity as instances of complete power failure become increasingly common.
-
-
Coastal towns build resilience to prepare for future storms
Sea Bright, New Jersey is one of several communities affected by Superstorm Sandy which is actively building resiliency against the next major storm. The town, set on a narrow strip of sand between the Atlantic Ocean and the Shrewsbury River, frequently floods, and during Sandy, its entire downtown business district was damaged, as were 75 percent of the town’s homes.
-
-
Upgrading infrastructure could reduce future flood damage

From 1980 to 2007, about 90 percent of all global disasters were caused by flooding either by rain, tsunami, hurricane, or some other natural event. At the same time, the American Society of Civil Engineer’s 2013 Report Card for America’s Infrastructure gave the country a dismal D+. The group said $3.6 trillion was needed by 2020 to address the most serious problems. In Colorado, the report card says, 70 percent of major roads are poor or mediocre and 566 bridges are structurally deficient. A new study argues that the severe flooding that devastated a wide swath of Colorado last year might have been less destructive if the bridges, roads, and other infrastructure had been upgraded or modernized.
-
-
Texas acts to reduce number of man-made earthquakes
The number of disposal wells in Texas has surged along with the number of drilling projects. Texas has more than 3,600 active commercial disposal wells. In 2013, the Railroad Commission approved 668 disposal well permits, twice the number of approvals in 2009. The growing number of disposal wells corresponds with an increase in earthquakes in communities where such seismic activity rarely existed.Officials in Texas have now taken steps to reduce the number of earthquakes caused by wells drilled for the disposal of oilfield waste.
-
-
Many victims of Hurricane Sandy are still waiting for government aid

It has been two years since Hurricane Sandy destroyed thousands of homes and businesses along the Jersey Shore yet many affected homeowners are still waiting for federal and state aid to rebuild. Of the $3.26 billion the U.S. Department of Housing and Urban Development (HUD) has provided to New Jersey, only $802 million has been paid out as of 30 September. The federal government’s first allocation of Sandy funds to New Jersey came seven months after the storm. The state has yet to issue any of the $1.46 billion approved by HUD in May, and New Jersey officials expect a final round of $880 million next spring.
-
-
State regulators discuss the connection between fracking and earthquake
Regulators from states with significant petroleum and natural gas exploration activities met last week in Columbus, Ohio as part of the 2014 Interstate Oil and Gas Compact Commission conference.One key topic of discussion at the conference wasthe potential implications of a study which found that numerous, unnoticeable earthquakes in Harrison County, Ohio, likely were linked to oil and natural gas exploration. 190 of the quakes which ranged from magnitude 1.7 to 2.2, occurred in the thirty-nine hours after fracking activity occurred at one well in late September and early October 2013.
-
-
States invest in resilience in the face of mounting extreme-weather challenges
Months after Superstorm Sandy devastated the New York coast line, Governor Andrew Cuomo’s Office of Storm Recovery launched a $17 billion strategy to transform the state’s infrastructure. Project Reimagining New York for a New Reality sought to make the state’s transportation networks, energy supply, coastal protection efforts, weather warning systems, and emergency management more resilient. The strategy is just one example of a trend in investments toward resilience efforts post Hurricane Katrina, Irene, Lee, and Sandy.
-
-
Resting place of 2 million barrels of oil missing from Deepwater Horizon accident found
Where is the remaining oil from the 2010 Deepwater Horizon disaster in the Gulf of Mexico? The location of two million barrels of oil thought to be trapped in the deep ocean has remained a mystery. Until now. Scientists have discovered the path the oil and followed it to its resting place on the Gulf of Mexico sea floor. By analyzing data from more than 3,000 samples collected at 534 locations over twelve expeditions, the researchers identified a 1,250-square-mile patch of the sea floor on which four to 31 percent of the oil trapped in the deep ocean was deposited. This is the equivalent of 2 to 16 percent of the total oil discharged during the accident.
-
-
Building a network of canals to save Boston from sea level rise
By the end of the century, sea-level rise on the U.S. east coast is predicted to reach six feet, so city planners in Boston recently met to discuss how to live with rising waters along the city’s historic streets. One suggestion is to turn Boston’s Back Bay district into a network of canals. The canals would alleviate sea-level rise by draining water into lower-lying back alleys and some main streets, but the proposed plan would have to contend with freezing temperatures in the winter.
-
-
Insurance companies now write Ebola exclusions into policies; offer Ebola-related products
U.S. and British insurance companies have begun to write Ebola exclusions into their policies for hospitals, event organizers, airliners, and other businesses vulnerable to disruption from the disease. As a result, new policies and renewals will become more expensive for firms looking to insure business travel to West Africa or to cover the risk of losses from Ebola-driven business interruptions (BI).The cost of insuring an event against Ebola, for example, would likely be triple the amount of normal cancellation insurance — if the venue was in a region not known to be affected by the virus.
-
-
Seismometers to measure Washington, D.C. shaking
On 23 August 2011, a relatively modest 5.8 magnitude in Virginia was felt from central Georgia to central Maine, and west to Detroit and Chicago. It is estimated that approximately one-third of the U.S. population could have felt the earthquake, which damaged the Washington National Cathedral and the Washington Monument. The tremor raised questions on how much seismic shaking is amplified by local geological conditions. Thirty seismometers are being installed in the U.S. capital this winter to monitor ground tremors better to estimate the intensity of ground shaking that can be expected during future earthquakes in the area.
-
-
South Florida wants to secede from Florida over sea level rise
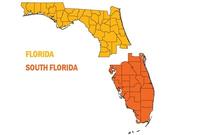
When people talk of “secession” in the United States they typically have Texas, Vermont, or the former Confederate states in mind, and the reasons for driving secession typically have to do with politics or money. Not anymore. The city of South Miami earlier this month passed a resolution which called for southern Florida to secede from the rest of the state, citing climate change as the reason. There are many differences between north and south Florida: South Florida is largely urban and politically tends to lean left, while the north is mostly rural and much more conservative. If south Florida reminds people of New York, the Florida panhandle resembles Alabama. Then there is this: The northern part of the state is, on average, 120 feet above sea level, but much of the southern section averages only fifteen feet above sea level. South Floridian say that the state government in Tallahassee ignores the perils of sea level rise, which are particularly acute in south Florida, so the time has come to separate from the aloof north.
-
-
Napa Valley residents debate necessity of earthquake insurance
Many residents of the Napa Valley in California are weighing the benefits and costs of earthquake insurance in the wake of the 24 August quake, which heavily damaged many homes and businesses in the region. The high premiums of earthquake insurance are deterring many home and business owners, despite the real threat of intensive damage.Only 6 percent of Napa Valley residents had earthquake insurance, andonly 9 percent of California businesses have coverage.
-
-
U.S insurance sector showing “profound lack of preparedness in addressing climate-related risks”: Report
Amid growing evidence that climate change is having wide-ranging global impacts which will worsen in the years ahead, a new report ranks the nation’s 330 largest insurance companies on what they are saying and doing to respond to escalating climate risks. The report found strong leadership among fewer than a dozen companies but generally poor responses among the vast majority. “Despite being on the ‘front line’ of climate risks, most of the company responses show a profound lack of preparedness in addressing climate-related risks and opportunities,” says the president of the organization sponsoring the report.
-
More headlines
The long view
The Surprising Reasons Floods and Other Disasters Are Deadlier at Night
By Kate Yoder
It’s not just that it’s dark and people are asleep. Urban sprawl, confirmation bias, and other factors can play a role.
Why Flash Flood Warnings Will Continue to Go Unheeded
By Rebecca Egan McCarthy
Experts say local education and community support are key to conveying risk.
