-
California community sinking into the ground, and engineers are baffled

Several homeowners in the community of Lake County, California are faced with a problem: their houses are sinking into the ground and they do not know why. The situation has been deteriorating steadily, and now mail delivery has been cancelled in the area, and city and county crews have been forced to change the subdivision’s sewage line to an overland pipe as a result of manhole collapses.
-
-
State agency imposes heavy fine on PG&E for San Bruno blast
The California Public Utilities Commission (CPUC) two weeks ago wrapped up its investigation of a 2010 gas pipeline explosion in San Bruno, California, and recommended that Pacific Gas and Electric (PG&E) pay $2.25 billion for its negligence, which led to the blast.
-
-
Hazard of Western Indian Ocean earthquake, tsunami greater than thought
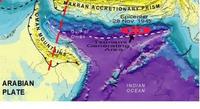
Earthquakes similar in magnitude to the 2004 Sumatra earthquake could occur in an area beneath the Arabian Sea at the Makran subduction zone, according to recent research. The study suggests that the risk from undersea earthquakes and associated tsunami in this area of the Western Indian Ocean — which could threaten the coastlines of Pakistan, Iran, Oman, India, and potentially further afield — has been previously underestimated.
-
-
Japan has an earthquake early-warning system, but California is yet to deploy one
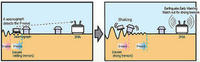
The 2011 Fukushima earthquake claimed many lives, but at least some lives were saved by an early warning system designed ten years ago at Caltech and deployed in Japan in 2007. The system gives people about a minute to prepare for the impending tremor. California is yet to deploy the system.
-
-
Assessing asteroid risk to Earth
Of the more than 600 000 known asteroids in our Solar System, almost 10 000 are classified as near-Earth objects, or NEOs, because their orbits bring them relatively close to Earth’s path. A dramatic proof that any of these can strike Earth came on 15 February, when an unknown object thought to be 17-20 meter in diameter arrived at 66 000 km/h and exploded high above Chelyabinsk, Russia, with 20-30 times the energy of the Hiroshima atomic bomb.
-
-
New grass hybrid helps reduce runoffs, flooding

Scientists use hybridized forage grass to combine fast root growth and efficient soil water retention. Field experiments show Festulolium cultivar reduces water runoff by up to 51 percent against nationally-recommended cultivar. The hybrid captures more water and reduces runoff and likelihood of flood generation.
-
-
Lower waves' impact on coastal communities uncertain
Coastal impacts of climate change studies have predominantly focused on the influence of sea-level rise and, until now, not focused on how changing wave conditions will impact the coastal zone in a changing climate. Scientists note, though, that waves are dominant drivers of coastal change in these sandy environments, and variability and change in the characteristics of surface ocean waves can far exceed the influences of sea-level rise in such environments. Since warmer oceans will see lower waves, the effect of warming on coastal communities is uncertain.
-
-
New technology prevents bridge collapse
Researchers propose a new technology that could divert vibrations away from load-bearing elements of bridges to avoid catastrophic collapses. The researchers propose a “wave bypass” technique that has many similarities to those being used by researchers looking to create Harry Potter-style invisibility cloaks, which exploit man-made materials known as metamaterials to bend light around objects.
-
-
California braces for out-of-control wildfires

The lack of precipitation over the past two winters has California and federal officials concerned about the impact wildfires could have in the summer months. California has already recorded 845 wildfires this year, a 60 percent increase compared with the average for the previous five years.
-
-
Draft of the 2013 U.S. National Climate Assessment is out
As mandated by the U.S. Global Change Research Act (GCRA), the U.S. Global Change Research Program (USGCRP) is currently producing a National Climate Assessment (NCA). The NCA is a report to inform the president, the Congress, and the American people about the current state of scientific knowledge regarding climate change effects on U.S. regions and key sectors, now and in the coming decades. The National Research Council (NRC) says that as the United States continues to engage with the threats, opportunities, and surprises of climate change in its many manifestations, the 2013 NCA should prove to be a valuable resource.
-
-
DHS chemical plant security program hobbled by problems, poor oversight
A DHS program responsible for the security of chemical facilities, such as the West Fertilizer Company plant in Texas, has been ineffective owing to a number of issues, leading federal investigators to wonder “whether it can achieve its mission, given the challenges the program continues to face.”
-
-
Finding the right balance for natural hazard mitigation
Uncertainty issues are paramount in the assessment of risks posed by natural hazards and in developing strategies to alleviate their consequences.Researchers describe a model that estimates the balance between costs and benefits of mitigation — efforts to reduce losses by taking action now to reduce consequences later — following natural disasters, as well as rebuilding defenses in their aftermath.
-
-
Former lawmakers to hold hearings on aliens
Six former member of Congress have agreed to hold a congressional style hearing on the existence of aliens in space. “It’s a huge universe out there,” former Representative Roscoe Bartlett (D-Maryland) said. “You have to be kind of presumptuous and arrogant to assume we’re the only intelligent life in the universe.”
-
-
River beds keep moving, increasing flood risk
A detailed study of shifting river beds could hold the key to more accurate flood prevention. It is commonly believed that the elevation of river beds is more or less constant, so any change in flood risk is due to changes in hydrology. Researchers find, however, that there is a significant trends in the elevation of river beds, an indication that river channels are filling in with sediment or that sediment is being eroded through time.
-
-
Calculating the risk of tsunami for the U.S. East Coast
The greatest threat of a tsunami for the U.S. east coast from a nearby offshore earthquake stretches from the coast of New England to New Jersey. The potential for an East Coast tsunami has come under greater scrutiny after a 2012 earthquake swarm which occurred offshore about 170 miles east of Boston. The largest earthquake in the 15-earthquake swarm, most of which occurred on 12 April 2012, was magnitude (M) 4.0.
-
More headlines
The long view
Risk Assessment with Machine Learning
Researchers utilize geological survey data and machine learning algorithms for accurately predicting liquefaction risk in earthquake-prone areas.
