-
HHS awards $24.9 million contract to accelerate development of Ebola drug
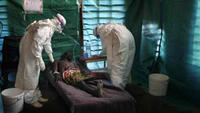
The development of a medication to treat illness from Ebola will be accelerated under a contract with the U.S. Department of Health and Human Services’ Office of the Assistant Secretary for Preparedness and Response (ASPR). HHS says that this contract supports the government-wide response to the Ebola outbreak in West Africa. The $24.9 million, 18-month contract with Mapp Biopharmaceutical Inc., of San Diego, California, may be extended up to a total of $42.3 million. HHS notes that it is seeking additional proposals for the advanced development of antibody treatments, antiviral drugs, and vaccines against the Ebola and Marburg viruses.
-
-
Atlanta’s rapid transit deploys AI video analytics to bolster public safety
The Metropolitan Atlanta Rapid Transit Authority (MARTA) is deploying Behavioral Recognition Systems’ AISight, an artificial intelligence-based analytics solution that teaches itself to recognize and alert on unexpected patterns within massive volumes of data.
-
-
Neumedicines receives $14m for acute radiation exposure countermeasures
Neumedicines receives $14 million from BARDA to support advanced development of HemaMax, including advanced GMP manufacturing activities and a Phase 2 clinical safety study in 200 healthy human volunteers. The company says its efficacy studies have shown that a single, low-dose, subcutaneous injection of HemaMax at twenty-four hours after exposure to lethal radiation increases survival by an average of more than 2-fold without any supportive care or antibiotics.
-
-
The CDC contracts Emergent BioSolutions for $18.9 million smallpox treatment
The CDC has contracted Emergent BioSolutions for the supply of Vaccinia Immune Globulin Intravenous (VIGIV) into the U.S. Strategic National Stockpile (SNS). VIGIV is a therapeutic licensed by the U.S. Food and Drug Administration (FDA) for the treatment of complications due to smallpox vaccination. The contract options are valued at $18.9 million over three years.
-
-
Fire shuts down nuclear repository, but DOE still recognizes operator for “excellent” performance
Five days after an underground truck fire closed the Waste Isolation Pilot Plant (WIPP), the Energy Department (DOE) awarded Nuclear Waste Partnership (NWP), the operating contractor of the nuclear repository, $1.9 million for “excellent” performance during the past year.Shortly after the truck fire, WIPP was shut down because of radiation leak, Still, “No federal or contractor official has lost their job, been transferred, been moved off the WIPP contract or otherwise held accountable. No leadership has changed at the federal level. No company has lost a contract,” noted an industry observer.
-
-
DHS urged to investigate use of DHS grants for Motorola emergency comm. devices
Three senior House Democrats have requested DHS’s Office of Inspector Generalto investigate allegations claiming Motorola’s contracting tactics have led state and local governments unnecessarily to spend millions of dollars on the company’s proprietary devices, including its two-way emergency radio systems.
-
-
Urgent need: Dirty bomb detection technology which does not rely on helium
It has taken 4.7 billion years for Earth to accumulate our helium reserves, but these reserves are dwindling at an alarming rate, and will be exhausted by around 2025. The supplies we have originated in the very slow radioactive alpha decay that occurs in rocks, and there is no chemical way to manufacture helium. The Department of Defense and other agencies use Helium-3 (He-3) to detect neutrons emanating from Special Nuclear Material (SNM) in order to counter the threat of nuclear-fueled explosives such as dirty bombs. Since the supply of He-3 is rapidly drying up, the Defense Threat Reduction Agency (DTRA) awarded a $2.8 million contract to Alion Science and Technology to develop a replacement technology which will detect neutrons without relying on He-3.
-
-
Leidos awarded DHS Plum Island biolab contract
DHS awarded Reston, Virginia-based Leidos a prime contract to support and supplement the Science and Technology (S&T) Agricultural Scientific Program at the Plum Island Animal Disease Center (PIADC). The single-award time and materials (T&M) contract has a one-year base period of performance, four one-year options, and a total contract value of approximately $12 million if all options are exercised. Work will be performed in Orient Point, New York.
-
-
New Mexico demands clarifications, reassurances on WIPP radiation leaks

New Mexico’s environment secretary Ryan Flynn has ordered the Department of Energy (DOE) to explain how it will protect public health and the environment while it investigates a radiation leak at the underground Waste Isolation Pilot Plant (WIPP). The plant has not been in compliance with various permit requirements since the February underground fire and radiation leak, which eventually led to a plant shutdown.
-
-
Doing business with DHS: Ranking DHS’s contracting officers
Firms bidding on federal contracts often have to deal with changing requirements and shifting deadlines. In order to provide more clarity to the process, a new app ranks the contracting officers at different federal agencies based on how frequently they award contracts, the length of the procurement process, the average dollar value of the contracts awarded, and the officers’ “annoyance factor,” which is based on how often the contracting officer modifies a solicitation after it has been posted and how often deadlines are changed.
-
-
DHS cancels acquisition of BioWatch’s Generation 3 technology
Owing to concerns about BioWatcheffectiveness and high cost, DHS has canceled plans to install an automated technology meant to speed the 24-hour operations of the program, the nation’s system for detecting a biological attack.ASeptember 2012 GAO report estimated that annual costs to operate the Generation 3 technology would be “about four times more” than the existing BioWatch system.
-
-
Washington, D.C. area leads nation in cybersecurity jobs

The Washington, D.C metropolitan area had more than 23,000 cybersecurity job postings in 2013, making the region the leading destination for cybersecurity jobs, followed by the New York metro area with 15,000 cybersecurity job postings in 2013. On a state-by state basis, Virginia ranks second and Maryland ranks sixth, with Virginia reporting 25.1 cybersecurity job postings per 10,000 residents and Maryland posting 18.1 jobs per 10,000 residents.
-
-
Two politicians insisting on more congressional oversight of DHS
The lawmakers who support the proposed DHS Acquisition Accountability and Efficiency Act, authored by Representative Jeff Duncan (R-South Carolina), are doing exactly what they were sent to Washington to do: they are attempting to provide fiscal oversight over one of our largest federal agencies. Hopefully, politicians on both sides of the aisle will join Representatives Duncan and Michael McCaul (R-Texas) in passing legislation forcing DHS to use tax payer money in the most efficient ways possible, including demanding contractors meet the terms of their contracts, not rewarding contractors who have a record of poor performance, and completing their security-related projects in a timely manner.
-
-
Cost of plutonium disposal facility skyrockets
The Mixed Oxide (MOX) nuclear fuel factory at the Savannah River Site in South Carolina, being built to help dispose of cold war-era weapon-grade plutonium, would cost up to $30 billion in addition to the $4 billion spent on construction so far. The staggering cost overruns have led many to call for a new, less expensive solution. Matthew Bunn, a former Clinton White House official who helped develop the plutonium disposal program, agrees that the cost of the MOX factory is excessive. “The things we’re trying to accomplish aren’t worth that amount of money,” he said.
-
-
Security check contractor defrauded U.S. of millions of dollars
The Department of Justice said Wednesday that U.S. Investigations Services (USIS), the company which conducted the background checks on Edward Snowden and Aaron Alexis, has defrauded the government of millions of dollars. The government charges that between 2008 and 2012, 650,000 background investigations – about 40 percent of the company’s investigations in that period – were submitted to the government as having been completed although, in fact, they were not. Several former and current USIS employees said the company had an incentive to rush background check work because it was paid only after a file is marked “FF,” for fieldwork finished, and sent to the government. Two senior managers said that toward the end of the month, investigations were closed in order to meet financial quotas, without a required review by the quality control department.
-
- All
- Regional
- Water
- Biometrics
- Borders/Immig
- Business
- Cybersecurity
- Detection
- Disasters
- Government
- Infrastructure
- International
- Public health
- Public Safety
- Communication interoperabillity
- Emergency services
- Emergency medical services
- Fire
- First response
- IEDs
- Law Enforcement
- Law Enforcement Technology
- Military technology
- Nonlethal weapons
- Nuclear weapons
- Personal protection equipment
- Police
- Notification /alert systems
- Situational awareness
- Weapons systems
- Sci-Tech
- Sector Reports
- Surveillance
- Transportation
Advertising & Marketing: advertise@newswirepubs.com
Editorial: editor@newswirepubs.com
General: info@newswirepubs.com
2010-2011 © News Wire Publications, LLC News Wire Publications, LLC
220 Old Country Road | Suite 200 | Mineola | New York | 11501
Permissions and Policies
Editorial: editor@newswirepubs.com
General: info@newswirepubs.com
2010-2011 © News Wire Publications, LLC News Wire Publications, LLC
220 Old Country Road | Suite 200 | Mineola | New York | 11501
Permissions and Policies
