-
Global marine analysis: Food chain collapse likely
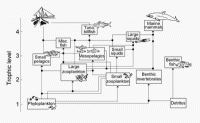
A world-first global analysis of marine responses to climbing human CO2 emissions has painted a grim picture of future fisheries and ocean ecosystems. Marine ecologists say the expected ocean acidification and warming is likely to produce a reduction in diversity and numbers of various key species that underpin marine ecosystems around the world. The researchers found that there would be “limited scope” for acclimation to warmer waters and acidification. Very few species will escape the negative effects of increasing CO2, with an expected large reduction in species diversity and abundance across the globe.
-
-
Instant water heater offers energy, cost savings
Traditional water heaters take time to reach preferred temperatures, thus wasting water and energy. A new instant hot water solution, developed through the EU-funded RAPIDHEAT project, successfully optimized heating and control technologies to develop a lightweight low thermal mass heater that provides full temperature output within two seconds of switch-on.
-
-
An app alerts people, law enforcement about potential crime risk
You are walking home after a night out on a dark autumn evening. Suddenly, you get the feeling that someone is following you. You look over your shoulder, and see a shadow between the trees in the park. You quicken your steps. When you glance behind you again, you see the shadow disappear in between two houses. This is when you could press the “help” button on the app that you have downloaded. It sends a message to everyone in the area who also has the app, with information about your phone number and where you are. This way they are able to call you, alert emergency services, or get to your location if need be. The app has been developed by a group of student entrepreneurs.
-
-
DYI experiment demonstrates the physics of climate change for students

There are two main causes of rising sea levels — thermal expansion and melting land-based ice. Thermal expansion is responsible for most of the rising sea levels during the past century, but an increasing amount of rising levels into the future will be due to the melting Greenland and Antarctic ice sheets, as well as melting glaciers across the globe, especially the Himalayas, experts say. The rising sea level is a global phenomenon and will affect all coastal cities, but some places are more vulnerable than others. For example, the sea level on the North American Atlantic coast north of Cape Hatteras is rising three to four times faster than the global average, which has been attributed to a reduction in the strength of the Atlantic Meridional Overturning Current.
-
-
Math story time at home markedly improves math achievement in school

Adding math talk to story time at home is a winning equation for children’s math achievement, according to new research. The study shows a marked increase in math achievement among children whose families used Bedtime Math, an iPad app that delivers engaging math story problems for parents and children to solve together. A recent study found that math-anxious parents who help their children with math homework actually undermine their children’s math achievement – but the new findings demonstrate that structured, positive interactions around math at home can cut the link between parents’ uneasiness about math and children’s low math achievement.
-
-
NSF awards $74.5 million to 257 interdisciplinary cybersecurity research projects
The NSF the other day announced the awarding $74.5 million in research grants through the NSF Secure and Trustworthy Cyberspace (SaTC) program. In total, the SaTC investments include a portfolio of 257 new projects to researchers in thirty-seven states. The largest, multi-institutional awards include research better to understand and offer reliability to new forms of digital currency known as cryptocurrencies, which use encryption for security; invent new technology to broadly scan large swaths of the Internet and automate the detection and patching of vulnerabilities; and establish the “science of censorship resistance” by developing accurate models of the capabilities of censors.
-
-
Tony Blair: Many Muslims support Islamic extremists' ideology
Tony Blair has warned that the ideology which drives Islamic extremists has significant support from Muslims around the world. Blair said that unless religious prejudice in Muslim communities is rooted out, the threat from the extremists will not be defeated. Blair, speaking at the 9/11 Memorial Museum in New York City, said that while the number of people engaging in violence by joining groups like Islamic State is relatively small, many of their views are widely shared.
-
-
ISIS, al-Qaeda, al-Nusra share near identical ideologies: Report
A just-published report analyzes a cross-section of 114 propaganda sources over two years from the three main Salafi-jihadi groups: ISIS, Jabhat al-Nusra, and al-Qaeda in the Arabian Peninsula. The three groups share near identical ideologies, challenging the concept that “ISIS is more extreme than al-Qaeda.” Built upon distorted Islamic religious principles, the propaganda produces single-minded focus on violent jihad. The report finds explicit references to these principles throughout the propaganda:
-
-
To “see” climate change, check your thermometer

Scientists often use satellites, supercomputers, or high-tech arrays of instruments to show how the climate is changing. But now researchers have shown how climate change can be visible, even at just one location, with the simplest instrument of all: a thermometer.
-
-
Climate change will soon make atolls in the Pacific, Indian oceans uninhabitable

More than half a million people live on atolls throughout the Pacific and Indian Oceans. A new study shows that the combined effect of storm-induced wave-driven flooding and sea level rise on island atolls may be more severe and happen sooner than previous estimates of inundation predicted by passive “bathtub” modeling for low-lying atoll islands, and especially at higher sea levels forecasted for the future due to climate change.
-
-
New flame retardant is naturally derived, nontoxic
Flame retardants are added to foams found in mattresses, sofas, car upholstery, and many other consumer products. Once incorporated into foam, these chemicals can migrate out of the products over time, releasing toxic substances into the air and environment. Inspired by a naturally occurring material found in marine mussels, researchers have created a new flame retardant to replace commercial additives that are often toxic and can accumulate over time in the environment and living animals, including humans.
-
-
History shows more big wildfires likely as climate warms

The history of wildfires over the past 2,000 years in a northern Colorado mountain range indicates that large fires will continue to increase as a result of a warming climate, according to a new study. Researchers examined charcoal deposits in twelve lakes in and near the Mount Zirkel Wilderness of northern Colorado, finding that wildfires burned large portions of that area during a documented spike in temperatures in North America starting about 1,000 years ago. That period, known as the Medieval Warm Period (MWP), lasted about 300 years, when temperatures rose just under 1 degree Fahrenheit.
-
-
Immigrants account for a larger share of U.S. science and engineering workforce
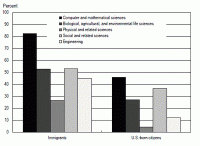
From 2003 to 2013, the number of scientists and engineers residing in the United States rose from 21.6 million to 29 million. An important factor in that increase: over the same time period, the number of immigrant scientists and engineers went from 3.4 million to 5.2 million. Immigrants went from making up 16 percent of the science and engineering workforce to 18 percent, according to a new report.
-
-
Government climate pledges, if implemented, would warm world by 2.7°C
The combination of government climate action plans – or Intended Nationally Determined Contributions (INDCs) — if implemented, would bring global warming down to 2.7°C, according to a new analysis. This is the first time since 2009, when the Climate Action Tracker (CAT) began calculating temperature estimates from climate action pledges, that projected warming has dipped below 3°C.
-
-
Recovering rare earth materials from electric and hybrid vehicle motors
China currently supplies about 97 percent of rare earth materials used in manufacturing around the world. In an effort to help develop a sustainable domestic supply of rare earth elements and lessen the U.S. dependence on China for materials that are vital to the production of electronics, wind turbines, and many other technologies, researchers have developed a method of extracting rare earths from the drive units and motors of discarded electric and hybrid cars.
-
More headlines
The long view
A Shining Star in a Contentious Legacy: Could Marty Makary Be the Saving Grace of a Divisive Presidency?
While much of the Trump administration has sparked controversy, the FDA’s consumer-first reforms may be remembered as its brightest legacy. From AI-driven drug reviews to bans on artificial dyes, the FDA’s agenda resonates with the public in ways few Trump-era policies have.
Risk Assessment with Machine Learning
Researchers utilize geological survey data and machine learning algorithms for accurately predicting liquefaction risk in earthquake-prone areas.
Foundation for U.S. Breakthroughs Feels Shakier to Researchers
With each dollar of its grants, the National Institutes of Health —the world’s largest funder of biomedical research —generates, on average, $2.56 worth of economic activity across all 50 states. NIH grants also support more than 400,000 U.S. jobs, and have been a central force in establishing the country’s dominance in medical research. Waves of funding cuts and grant terminations under the second Trump administration are a threat to the U.S. status as driver of scientific progress, and to the nation’s economy.
The True Cost of Abandoning Science
“We now face a choice: to remain at the vanguard of scientific inquiry through sound investment, or to cede our leadership and watch others answer the big questions that have confounded humanity for millennia —and reap the rewards.”
Bookshelf: Smartphones Shape War in Hyperconnected World
The smartphone is helping to shape the conduct and representation of contemporary war. A new book argues that as an operative device, the smartphone is now “being used as a central weapon of war.”
New Approach Detects Adversarial Attacks in Multimodal AI Systems
New vulnerabilities have emerged with the rapid advancement and adoption of multimodal foundational AI models, significantly expanding the potential for cybersecurity attacks. Topological signatures key to revealing attacks, identifying origins of threats.
