-
List of most-at-risk L.A. buildings to be released
Scientists have compiled a list of concrete buildings in Los Angeles which could be at risk of collapsing in a major earthquake. The list identifies about 1,500 concrete structures built before 1980 which need further study to determine their risk level. Structural engineers insist that hundreds could die if any of the buildings collapsed.
-
-
Sea-level rise could exceed one meter in this century: experts
Sea-level rise in this century is likely to be 70-120 centimeters by 2100 if greenhouse-gas emissions are not mitigated, a broad assessment of the most active scientists who research in the area, and who are the most prolific publishers on that topic, has revealed. In contrast, for a scenario with strong emissions reductions, experts expect a sea-level rise of 40-60 centimeters by 2100. Ninety international experts, all of whom published at least six peer-reviewed papers on the topic of sea-level during the past five years, provided their probabilistic assessment.
-
-
Understanding Greenland Ice Sheet melting helps sea-level forecasts
New insight into how glacier movement is affected by melting ice in summer could help predictions of sea level rise. In 2012, an exceptionally warm summer caused the Greenland Ice Sheet to undergo unprecedented rates of melting. Researchers have found, however, that fast summer ice flow caused by significant melting is cancelled out by slower motion the following winter.
-
-
Research funding and reward structure contributes to formation “science bubbles”
Fashions in research funding, reward structures in universities, and streamlining of scientific agendas undermine traditional academic norms and may result in science bubbles. New research shows how the mechanisms that set off the financial crisis might be replicating in the field of science. The prevailing scientific reward structure thus amplifies social phenomena like “pluralistic ignorance” and “lemming effects,” which have been shown to have significant impact on information processing and assessment in populations of interacting persons — including in one of the most rational enterprises of modern social life.
-
-
Winners announced in NY, NJ coastal protection ideas competition
Ten of the ideas submitted to the Rebuild by Designcompetition, launched by the Hurricane Sandy Rebuilding Task Force, were selected as the most promising concepts for sustainable ways to protect Sandy-affected regions from future catastrophes.
-
-
Government, private sector prioritize cybersecurity education
As government and private sector organizations transmit and store more information electronically, the need for professionals with skills to protect and evaluate sensitive information is increasing. American companies and government agencies are expanding various initiatives aimed at increasing the number of cybersecurity professionals in the country.
-
-
Marines test latest battlefield IT at Agile Bloodhound ‘13
Marines in Hawaii last week demonstrated that using handheld devices and special software automatically to sift through loads of data can help ease information overload and deliver made-to-order intelligence to the front lines. “We’re trying to create a user-oriented world view for Marines,” said Col. William Zamagni. “Whether they’re in command centers with PCs, in vehicles with laptops or on foot with smartphones, Marines need access to the most pertinent information possible.”
-
-
Smaller asteroids could cause bigger problems

On 15 February an asteroid burst over the Russian city of Chelyabinsk. Scientists estimate that the Chelyabinsk event was equivalent to an explosion of about 500 kilotons of TNT. At its peak, the airburst appeared to be thirty times brighter than the sun. The asteroid fireball that injured about 1,500 people and damaged more than 7,000 buildings, collapsing roofs, and breaking thousands of windows. Scientists say that because the frequency of a strike of an asteroid of this size has exceeded expectations, with three such strikes in just over a century – Chelyabinsk in 2013, Tunguska in 2008, and a large airburst in the South Atlantic in 1963 — the number of similar-sized asteroids capable of causing damage may be greater than suspected.
-
-
Study finds more spending on fire suppression may lead to bigger fires
Researchers found that fire management can fall into the firefighting trap: Energy and resources are spent mostly on fire suppression — putting out fires in the moment — while less attention is devoted to fire prevention, such as clearing brush and building fire lanes during the off-season. After severe fires, policymakers funnel even more funds into fire suppression for the next season, but this attention to fire suppression may undermine prevention efforts. The result, counterintuitively, is even worse fires the following season, due to the buildup of fire-prone materials such as dried tinder and dead trees. The researchers emphasize balancing fire suppression with prevention measures.
-
-
Financial decision making, risk taking in the face of changing climate
Maximizing returns on financial investments depends on accurately understanding and effectively accounting for weather and climate risks, according to a new study by the American Meteorological Society. An AMS report concludes that financial investments face a range of risks due to existing weather patterns and climate variability and climate change. Even small changes in weather can impact operations in critical economic sectors. At the same time, climate variability and change can either exacerbate existing risks or cause new sources of risk to emerge.
-
-
Fashion scouts and cops: the logic behind stop-and-frisk
New research compares practices used by fashion industry casting directors to the New York City Police Department’s controversial stop-and-frisk program. Fashion casting directors belong to a select group of mediators responsible for shaping the pool of modeling talent by scouring familiar territory for the young and beautiful. These casting directors had been similarly indoctrinated into the industry and the talent they would choose often resulted in over-representation of certain kinds of people. Similarly, police officers are a select group responsible for making a city safer. Their training — reinforced daily through the institutionalization and public acceptance of such practices — disposes them to scour familiar geographical and social territory for potential criminals, often resulting in over-representation of people from certain groups.
-
-
Security agencies concerned about plastic guns
The Undetectable firearms Act of 1988, which makes it illegal to manufacture, import, sell, ship, deliver, process, transfer, or receive a firearm which is not detectable by walk-through metal detection, is set to expire on 9 December 2013. If Congress fails to reauthorize the law, plastic guns will no longer require metal components which are detectable by metal detectors. “When these 3D firearms are manufactured, some of the weapons can defeat normal detection such as metal detectors, wands, and it could present a problem to public safety in a venue such as an airport, an arena, a courthouse,” says ATF assistant director Richard Marianos.
-
-
Using gaming to spark kids' STEM interest, improve physical fitness
A team of Purdue University technology researchers will use a $1.2 million National Science Foundation grant to tackle two national challenges: increasing children’s interest in science, technology, engineering, and math (STEM); and decreasing childhood obesity. The three-year project parlays kids’ innate interest in video games and solving big problems to inspire them to gain the STEM skills needed to create technology-based fitness games. The project will also encourage students to create exergames that require players to get up and move.
-
-
Using biological organisms to convert natural gas to liquid transportation fuel

Researchers will use their expertise in protein expression, enzyme engineering, and high-throughput assays as part of a multiproject, $34 million effort by the Advanced Research Projects Agency-Energy (ARPA-E) aimed at developing advanced biocatalyst technologies that can convert natural gas to liquid fuel for transportation.
-
-
U.S. oil production exceeds imports for first time in two decades
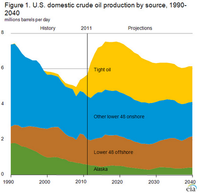
The United States is well on its way to energy independence, with the Obama administration announcing Wednesday that domestic oil production surpassed imports for the first time in nearly two decades. A report by the U.S. Energy Information Administration (EIA) offers proof that the United States has managed both to increase domestic oil and gas drilling and reduce the nation’s carbon emissions, which have dropped to a 20-year low. Since 2008, U.S. crude oil output has increased 50 percent, while imports have fallen about 20 percent.
-
More headlines
The long view
Autonomous Vehicle Technology Vulnerable to Road Object Spoofing and Vanishing Attacks
Researchers have demonstrated the potentially hazardous vulnerabilities associated with the technology called LiDAR, or Light Detection and Ranging, many autonomous vehicles use to navigate streets, roads and highways. The researchers have shown how to use lasers to fool LiDAR into “seeing” objects that are not present and missing those that are – deficiencies that can cause unwarranted and unsafe braking or collisions.
Tantalizing Method to Study Cyberdeterrence
Tantalus is unlike most war games because it is experimental instead of experiential — the immersive game differs by overlapping scientific rigor and quantitative assessment methods with the experimental sciences, and experimental war gaming provides insightful data for real-world cyberattacks.
Prototype Self-Service Screening System Unveiled
TSA and DHS S&T unveiled a prototype checkpoint technology, the self-service screening system, at Harry Reid International Airport (LAS) in Las Vegas, NV. The aim is to provide a near self-sufficient passenger screening process while enabling passengers to directly receive on-person alarm information and allow for the passenger self-resolution of those alarms.
Falling Space Debris: How High Is the Risk I'll Get Hit?
An International Space Station battery fell back to Earth and, luckily, splashed down harmlessly in the Atlantic. Should we have worried? Space debris reenters our atmosphere every week.
Testing Cutting-Edge Counter-Drone Technology
Drones have many positive applications, bad actors can use them for nefarious purposes. Two recent field demonstrations brought government, academia, and industry together to evaluate innovative counter-unmanned aircraft systems.
Strengthening the Grid’s ‘Backbone’ with Hydropower
Argonne-led studies investigate how hydropower could help add more clean energy to the grid, how it generates value as grids add more renewable energy, and how liner technology can improve hydropower efficiency.
