-
Using gaming to spark kids' STEM interest, improve physical fitness
A team of Purdue University technology researchers will use a $1.2 million National Science Foundation grant to tackle two national challenges: increasing children’s interest in science, technology, engineering, and math (STEM); and decreasing childhood obesity. The three-year project parlays kids’ innate interest in video games and solving big problems to inspire them to gain the STEM skills needed to create technology-based fitness games. The project will also encourage students to create exergames that require players to get up and move.
-
-
Using biological organisms to convert natural gas to liquid transportation fuel

Researchers will use their expertise in protein expression, enzyme engineering, and high-throughput assays as part of a multiproject, $34 million effort by the Advanced Research Projects Agency-Energy (ARPA-E) aimed at developing advanced biocatalyst technologies that can convert natural gas to liquid fuel for transportation.
-
-
U.S. oil production exceeds imports for first time in two decades
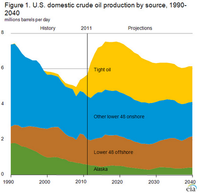
The United States is well on its way to energy independence, with the Obama administration announcing Wednesday that domestic oil production surpassed imports for the first time in nearly two decades. A report by the U.S. Energy Information Administration (EIA) offers proof that the United States has managed both to increase domestic oil and gas drilling and reduce the nation’s carbon emissions, which have dropped to a 20-year low. Since 2008, U.S. crude oil output has increased 50 percent, while imports have fallen about 20 percent.
-
-
Wrong crowd: social networks are key to city violence
A new study of gun violence in Chicago reveals that a person’s social network is a key predictor in whether an individual will become a victim of gun homicide, even more so than race, age, gender, poverty, or gang affiliation. “Risk factors like race and poverty are not the predictors they have been assumed to be,” one of the researchers said. “It’s who you hang out with that gets you into trouble. It’s tragic, but not random.”
-
-
Drive-by charging: Advancing wireless power transfer for vehicles
Researchers have developed new technology and techniques for transmitting power wirelessly from a stationary source to a mobile receiver — moving engineers closer to their goal of creating highway “stations” that can recharge electric vehicles wirelessly as the vehicles drive by.
-
-
The Philippines is victim of geography, poor infrastructure, poverty
Owing to its location and geography, the Philippines is one of the most natural disaster-prone countries in the world. On average the country experiences nine major typhoons and 900 earthquakes annually, and it has twenty-five active volcanoes. Poor infrastructure and pervasive poverty exacerbate the impact of disasters, making them even more deadly and destructive. “In a cruel cycle, poverty and underdevelopment make disasters worse, and disasters make poverty and underdevelopment worse,” one observer notes.
-
-
Past as prologue: Insights from past natural disasters relevant today
The increasing frequency and intensity of natural disasters constitute a daunting challenge to modern society, which is characterized by a heavy infrastructure and increasing population density. Until now, coping with natural disasters has involved expensive state intervention and technology-aided approaches, but researchers believes that the past contains a wealth of unexploited resources which could also provide solutions to the problems communities face when dealing with need to cope with, and recover from, natural disasters.
-
-
Rochester, Minn. wants to stop crime before it happens
The Rochester Police Departmentin Rochester, Minnesota is using IBM’s Infosphere Identity Insightto predict, and combat, crime. InfoSphere Identity Insight is used to identify frequent crime offenders, and even when multiple false identifications belonging to one individual are stored on record, the associated relationships of those identities could lead to the correct individual.
-
-
The Ergonomics of bomb-making at sea

In an effort to stem work-related injuries and speed the assembly of munitions aboard aircraft carriers, the Office of Naval Research (ONR) spearheaded the development of a more efficient and ergonomic way to build bombs at sea. The ONR-sponsored improvements will allow sailors to move around more freely and assemble multiple bombs simultaneously on smaller, individual stands.
-
-
Sequestration already eroding U.S. research capabilities
As congressional budget leaders continue negotiations over Fiscal Year 2014 spending levels, three organizations representing the U.S. leading public and private research universities say that the results of a new survey reveal the pernicious impact of sequestration on scientific research across the country. Budget cuts have already led to fewer grants, cancelled projects, staff reductions, and reduced learning opportunities. “If Congress fails to reverse course and doesn’t begin to value investments in research and higher education, then the innovation deficit this country is facing will worsen as our foreign competitors continue to seize on this nation’s shortfall,” the leader of one of the organizations said.
-
-
Climate scientists say renewables are not enough
Some of the world’s top climatologists have declared their support for nuclear energy as a complementary energy source, alongside wind and solar as energy, which would cut fossil fuel pollution and reduce the growth of global warming. The scientists say that opposing fossil fuels and promoting renewable energy sources offer but a limited solution.
-
-
Emulating stingray movement to build next generation of submarines
Stingrays swim through water with such ease that researchers believe that emulating the fish’s unique way of swimming could improve deep-sea vehicles’ agility and fuel efficiency. “Most fish wag their tails to swim. A stingray’s swimming is much more unique, like a flag in the wind,” says one researcher.
-
-
Insects’ way of flying inspires design of tiny flying robots
Researchers have identified some of the underlying physics that may explain how insects can so quickly recover from a stall in midflight — unlike conventional fixed wing aircraft, where a stalled state often leads to a crash landing. The analysis improves the understanding of how insects fly and informs the design of small flying robots built for intelligence gathering, surveillance, search-and-rescue, and other purposes.
-
-
Chevron contributes $1.5 million to new engineering education initiative
Chevron has contributed $1.5 million to a new National Academy of Engineering (NAE) initiative that will provide expert, research-based guidance to those involved in overseeing engineering education in kindergarten through grade 12. The initiative will create a clearinghouse of curriculum materials and resources and connect engineering education experts with teachers, administrators, and others involved in providing engineering experiences to K-12 students.
-
-
Philippines prepares for worse disasters to come
On average, the Philippines experiences about twenty typhoons a year, including three super-typhoons and many incidents of flooding, drought, earthquakes, tremors, and occasional volcanic eruptions, making the country one of the most naturally disaster-prone areas in the world. Filipino government agencies, with the help of international disaster and relief agencies, have created new strategies for disaster preparedness, response, and mitigation which may well have potential applications in other parts of the world. As the impact of climate change grows more pronounced, the Philippines is becoming a hothouse for developing new methods and systems in the growing business of disaster relief.
-
More headlines
The long view
A Shining Star in a Contentious Legacy: Could Marty Makary Be the Saving Grace of a Divisive Presidency?
While much of the Trump administration has sparked controversy, the FDA’s consumer-first reforms may be remembered as its brightest legacy. From AI-driven drug reviews to bans on artificial dyes, the FDA’s agenda resonates with the public in ways few Trump-era policies have.
Risk Assessment with Machine Learning
Researchers utilize geological survey data and machine learning algorithms for accurately predicting liquefaction risk in earthquake-prone areas.
Foundation for U.S. Breakthroughs Feels Shakier to Researchers
With each dollar of its grants, the National Institutes of Health —the world’s largest funder of biomedical research —generates, on average, $2.56 worth of economic activity across all 50 states. NIH grants also support more than 400,000 U.S. jobs, and have been a central force in establishing the country’s dominance in medical research. Waves of funding cuts and grant terminations under the second Trump administration are a threat to the U.S. status as driver of scientific progress, and to the nation’s economy.
The True Cost of Abandoning Science
“We now face a choice: to remain at the vanguard of scientific inquiry through sound investment, or to cede our leadership and watch others answer the big questions that have confounded humanity for millennia —and reap the rewards.”
Bookshelf: Smartphones Shape War in Hyperconnected World
The smartphone is helping to shape the conduct and representation of contemporary war. A new book argues that as an operative device, the smartphone is now “being used as a central weapon of war.”
New Approach Detects Adversarial Attacks in Multimodal AI Systems
New vulnerabilities have emerged with the rapid advancement and adoption of multimodal foundational AI models, significantly expanding the potential for cybersecurity attacks. Topological signatures key to revealing attacks, identifying origins of threats.
