-
Badly engineered missile defense systems deployed “because there was a rush”
In 1983 President Ronald Reagan launched the Strategic Defense Initiative (SDI) to build space- and ground-based missile defense systems. The space-based component was abandoned as impractical, and the focus shifted to Ground-based Midcourse Defense systems (GMD). Despite disappointing results and program test failures, Congress and the George W. Bush administration pressed forward with spending billions on acquiring systems of questionable reliability. “We recognize the problems we have had with all the currently fielded interceptors,” Undersecretary of Defense Frank Kendall old an industry gathering in February 2014. “The root cause was a desire to field these things very quickly and very cheaply; we are seeing a lot of bad engineering, frankly, and it was because there was a rush.”
-
-
Inexpensive seismic alert device may help Mexico City residents

Mexico City has been experiencing an unusually large number of tremors within the past few months, and though the country has one of the most advanced seismic alert systems in the world, many residents are unable to receive notifications before tremors occur. Mexican regulations limit the sale of government-issued earthquake alert receivers to one private company, but since the receivers cost an average of $310, most families are unable to afford them. Andres Meira, a 39-year-old architect, has designed an earthquake alert receiver, which costs only $54 at retail, which taps into the government’s earthquake alert frequency to notify its users of a pending earthquake.
-
-
The real reason for a decline in violent crime
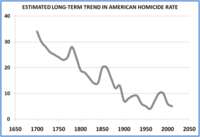
A scientific analysis of twenty million words recorded during 150 years of criminal trials at London’s Old Bailey reveals how changes in culture rather than law helped to reduce violent crime, according to a new study. “What we have been able demonstrate through analyzing the language used in court is that the decline in less serious forms of violence, such as assault, was not led by legislation or moments of dramatic change in the law, but by social attitudes,” says one of the authors.
-
-
Number of world’s nuclear weapons reduced, but modernization continues
The overall number of nuclear weapons in the world continues to decline, but none of the nuclear weapon-possessing states are prepared to give up their nuclear arsenals for the foreseeable future. At the start of 2014 nine states — the United States, Russia, the United Kingdom, France, China, India, Pakistan, Israel, and North Korea — possessed approximately 4000 operational nuclear weapons. If all nuclear warheads are counted, these states together possessed a total of approximately 16,300 nuclear weapons compared to 17,270 in early 2013.
-
-
How has Iraq lost a third of its territory to ISIS in three days?

The Islamic State of Iraq and the Levant (ISIL), also known as ISIS, has about 12,000 fighters in its ranks. About 8,000 needed only forty-eight hours to take Mosul, Iraq’s second largest city, although it was defended by more than 27,000 government troops. It took ISIL another twenty-four hours to gain control of about one-third of Iraq – facing little, if any, resistance from Iraq’s one-million-strong security apparatus. The reasons: After the U.S. occupation force, in 2003, dismantled Iraq’s professional military, a new Iraqi army was re-established from militia members and low-ranking members of the Ba’ath army. Senior officers in Saddam Hussein’s forces were dismissed, which gave rise to at least two security issues. Firstly, military officers of the previous army were steered toward terrorist groups. Secondly, Iraq’s new military suffered from the loss of expertise and military discipline instilled by their former officers. In addition, poor governance has led to widespread corruption in both political and military spheres. Military personnel are routinely reported to be soliciting bribes, especially in Sunni areas of Iraq.
-
-
Close air support technology helps in fire suppression
In the heat of battle, lives can depend on being able to coordinate troop positions safely while directing aircraft to provide close air support for ground forces. DARPA’s Persistent Close Air Support (PCAS) program aims to help overcome those challenges by providing soldiers with advanced digital tools for situational awareness and targeting in place of legacy communications systems and traditional paper maps. Firefighters battling wildfires face challenges very similar to those that troops face in battle — the need for situational awareness, precise coordination of airborne water drops and ensuring fellow firefighters are kept safe from rapidly moving and shifting flames. Technology developed for air-to-ground warfare has been adapted to help firefighters combat deadly forest blazes.
-
-
Free app alerts CPR-trained individuals to a heart attack case in their immediate vicinity
Speed and timeliness is instrumental to saving the life of a victim of cardiac arrest, so Santa Clara Countyagencies have adopted PulsePoint, a free mobile application (app) which uses location-based technology to alert CPR-trained residents and bystanders if someone in their immediate area is experiencing sudden cardiac arrest. Once alerted, residents can decide whether they are available to reach the victim and begin resuscitation until official emergency responders arrive.
-
-
World Cup security teams focus more on crime, protests – less on terrorism

During the 2014 FIFA World Cup, currently being held across twelve different venues across Brazil, security teams have extensively prepared for measures to be taken against crime and protest related to heated political unrest. American bomb-busting robots, Israeli surveillance drones, and German anti-aircraft tanks — an international assortment of security officials and measures – are just some of the pieces of the greater security apparatus protecting both players and fans.
-
-
New generation of aerial robots for high-risk missions
The need for robots able to carry out high-risk service tasks, such as the inspection of power plants and the cleaning of skyscrapers, is growing. Robots which actively interact with the environment without being constrained on the ground are well suited to such tasks.
-
-
Defense in terror case challenges exclusion from court session on surveillance records
The defense for Adel Daoud, a young Muslim man who was arrested outside a Chicago bar in an undercover FBI operation and charged with attempting to blow up the bar, has submitted a motion objecting to a private court session held to discuss the defense’s access to classified records. “Not only do I not get to be there, but I didn’t even get to object,” defense attorney Thomas Durkin said. “I had to object over the fact that I couldn’t even make an objection.”
-
-
Laser weapon developed for Marine vehicles

As the U.S. Navy prepares to deploy its first laser weapon on a ship later this summer, Office of Naval Research (ONR) officials announced that they have finished awarding contracts to develop a similar weapon to be used on ground vehicles. The Ground-Based Air Defense Directed Energy On-the-Move program, commonly referred to as GBAD, aims to provide an affordable alternative to traditional firepower to keep enemy unmanned aerial vehicles (UAVs) from tracking and targeting Marines on the ground.
-
-
A first: Armed robber convicted based on Chicago’s facial recognition technology
Pierre Martin became the first person in Chicago to receive a prison sentence after being convicted based on evidence from the city’s facial recognition technology, NeoFace. Martin was sentenced Monday to twenty-two years for two armed robberies carried out on the Chicago Transit Authority(CTA) train system in January and February 2013. A few weeks after the incidents, Chicago Police Department officials announced that Marin was identified using facial recognition software.
-
-
NNSA says security at Y-12 National Security Complex has improved
Retired Air Force lieutenant-general and now National Nuclear Security Administration(NNSA) chief Frank Klotz asserted last week that security at the Y-12 National Security Complexat Oak Ridge National Laboratory(ORNL) has improved significantly since a 28 July 2012 break-inat the plant when three aging peace activists, led by an 82-year old nun, managed to breach the facility’s supposedly impregnable perimeter security systems.
-
-
Feds, rail operators, Washington State embroiled in crude oil shipment disclosure dispute

Last month the U.S. Department of Transportation(DOT) ordered rail carriers with trains carrying crude oil to notify state officials in the states through which the trains pass about the volume, schedule, and routes of these trains. The amount of crude oil transported by trains has grown dramatically – from 6,000 carloads in 2005 to more than 400,000 carloads in 2013. The increase in the volume of crude oil shipping has been accompanied by a sharp rise in the number of accidents and derailments. DOT’s order was meant to allow states’ first responders to be prepared, but the railways treat shipping information as “security sensitive” and refuse to share it with states’ officials unless the information is distributed to emergency response groups for planning purposes only. Washington State says that state laws require that such information be made public.
-
-
Improved performance of facial recognition software
Who is that stranger in your social media photo? A click on the face reveals the name in seconds, almost as soon as you can identify your best friend. While that handy app is not quite ready for your smart phone, researchers are racing to develop reliable methods to match one person’s photo from millions of images for a variety of applications.
-
More headlines
The long view
Are We Ready for a ‘DeepSeek for Bioweapons’?
Anthropic’s Claude 4 is a warning sign: AI that can help build bioweapons is coming, and could be widely available soon. Steven Adler writes that we need to be prepared for the consequences: “like a freely downloadable ‘DeepSeek for bioweapons,’ available across the internet, loadable to the computer of any amateur scientist who wishes to cause mass harm. With Anthropic’s Claude Opus 4 having finally triggered this level of safety risk, the clock is now ticking.”
“The Federal Government Is Gone”: Under Trump, the Fight Against Extremist Violence Is Left Up to the States
As President Donald Trump guts the main federal office dedicated to preventing terrorism, states say they’re left to take the lead in spotlighting threats. Some state efforts are robust, others are fledgling, and yet other states are still formalizing strategies for addressing extremism. With the federal government largely retreating from focusing on extremist dangers, prevention advocates say the threat of violent extremism is likely to increase.
Luigi Mangione and the Making of a ‘Terrorist’
Discretion is crucial to the American tradition of criminal law, Jacob Ware and Ania Zolyniak write, noting that “lawmakers enact broader statutes to empower prosecutors to pursue justice while entrusting that they will stay within the confines of their authority and screen out the inevitable “absurd” cases that may arise.” Discretion is also vital to maintaining the legitimacy of the legal system. In the prosecution’s case against Luigi Mangione, they charge, “That discretion was abused.”
Autonomous Weapon Systems: No Human-in-the-Loop Required, and Other Myths Dispelled
“The United States has a strong policy on autonomy in weapon systems that simultaneously enables their development and deployment and ensures they could be used in an effective manner, meaning the systems work as intended, with the same minimal risk of accidents or errors that all weapon systems have,” Michael Horowitz writes.
Ukraine Drone Strikes on Russian Airbase Reveal Any Country Is Vulnerable to the Same Kind of Attack
Air defense systems are built on the assumption that threats come from above and from beyond national borders. But Ukraine’s coordinated drone strike on 1 June on five airbases deep inside Russian territory exposed what happens when states are attacked from below and from within. In low-level airspace, visibility drops, responsibility fragments, and detection tools lose their edge. Drones arrive unannounced, response times lag, coordination breaks.
Shots to the Dome—Why We Can’t Model US Missile Defense on Israel’s “Iron Dome”
Starting an arms race where the costs are stacked against you at a time when debt-to-GDP is approaching an all-time high seems reckless. All in all, the idea behind Golden Dome is still quite undercooked.
