-
DARPA launches Biological Technologies Office
DARPA has established a new technology office — the Biological Technologies Office (BTO) — which will merge biology, engineering, and computer science to harness the power of natural systems for national security. With the establishment of the new office last week, biology takes its place among the core sciences that represent the future of defense technology.
-
-
New group formed to monitor Savannah River Site, nuclear waste issues in SE U.S.
Savannah River Site Watch (SRS Watch), a new public-interest watchdog group, was launched last week in what it said was a response to the need for increased monitoring of the nuclear projects carried out by the U.S. Department of Energy (DOE). The group says it has been formed to focus on an array of nuclear projects now underway at Savannah River Site (SRS), the sprawling 310-square mile complex located near Aiken, South Carolina.
-
-
Los Alamos National Lab resumes transuranic waste shipments
The waste was received at Waste Control Specialists in Andrews, Texas, where it will be temporarily staged until it can be shipped to the Waste Isolation Pilot Plant (WIPP) near Carlsbad, New Mexico for final disposal. WIPP has been closed since mid-February as a result of radiation leaks in underground storage tunnels. The shipments keep LANL on track to complete 3,706 Campaign on schedule. The campaign aims to remove 3,706 cubic meters of nuclear waste from LANL by 30 June 2014.
-
-
Lead ammunition should be replaced by steel in shooting sports: experts
Researchers say that Olympic athletes specializing in shooting use one thousand cartridges per week and scatter some 1.3 tons of lead yearly, with harmful effects for surrounding animals and agricultural land. The researchers urge the International Olympic Committee and other sports organizations to replace lead ammunition with steel, which is non-toxic and contains similar technical characteristics.
-
-
New center will work to improve methods to detect, prevent the spread of nuclear weapons
The National Nuclear Security Administration (NNSA) has awarded the University of Michigan $25 million to establish the Center for Verification Technology. A team from thirteen universities will work with eight national labs to analyze nuclear nonproliferation efforts, improve technologies for monitoring weapons-grade materials and detecting secret weapon tests, and train the next generation of nonproliferation experts.
-
-
U.K. prisons serve as recruitment centers for jihadi causes

A recent report details the growing population of Muslims in British jails, many of whom are declared Islamic extremists. Top-security prison Whitemoor, home to many extremists serving life sentences for plotting acts of terror in the United Kingdom, is considered a recruitment center for al-Qaeda, according to prison inspectors. Roughly 42 percent of prisoners at Whitemoor are Muslims, a stark contrast to the overall U.K. population in which only 5 percent practice Islam.In all, there are 11,729 Muslims in British jails, about one in seven of all inmates.
-
-
Possibility of “dirty bombs” a major terrorism threat
The International Atomic Energy Agency (IAEA) has warned that there were 140 cases of missing or unauthorized nuclear and radioactive material in 2013 — a pressing reminder that the possibility of possession of nuclear materials by terrorist organizations is both real and current.
-
-
Making hunches better than 50-50 propositions
Detecting roadside bombs while in a moving vehicle; sensing impending danger based on something unusual at local café; deciding whether that object just launched off the coast is a missile or airliner — these are just a few of many scenarios where there is not a lot of time to make a decision, and where we have to rely on hunches. Hunches are 50-50 propositions, but U.S. Navy researchers want to know whether those facing the unexpected in the heat of battle can be trained to guess right more often than not.
-
-
Invisibility cloaks, stealth technology a step closer

It may seem easy in Hollywood movies, but is hard to create invisibility cloaks in real life because no material in nature has the properties necessary to bend light in such a way. Scientists have managed to create artificial nanostructures that can do the job, called metamaterials. The challenge, however, has been making enough of the material to turn science fiction into a practical reality.
-
-
Obscure element shows promise for nuclear waste storage

One of the least known elements of the periodic table, californium, may hold the key to the safe and effective long-term storage of nuclear waste, according to new research. The researchers have demonstrated that californium (Cf) has an “amazing” ability to bond and separate other materials, as well as being extremely resistant to radiation damage.
-
-
Prosecutors ask for confidentiality in NY “Death Ray” case

Glendon Scott Crawford,a former General Electric Co. industrial mechanic, is standing trails in Albany, New York, for developed a radiological dispersal device which he tried to sell to both the KKK and to Jewish organizations so they could use it to kill Muslims. Several experts argued the device would not work since it would require massive amounts of electricity, weigh enough to crush most vehicles and would require victims to remain still in order to face prolonged exposure from close-range radiation.
-
-
Connecticut mulls regional 911 authority
Connecticut House Bill 5531, if passed, would authorize the towns of East Lyme, New London, and Waterford to establish a municipal body to operate all 911 call centers in region. Creating a unified authority will allow for more efficient dispatch operations, reduce operating cost among the three towns, and will also equalize the towns’ liability should a lawsuit stem from a 911 call response. Critics disagree.
-
-
Real-life CSI: The stories gunshot residue tell
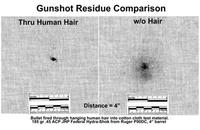
The popular TV series “CSI” is fiction, but every day, real-life investigators and forensic scientists collect and analyze evidence to determine what happened at crime scenes. In a new study, scientists say they have developed a more rapid and accurate method that could allow crime scene investigators to tell what kind of ammunition was shot from a gun based on the residue it left behind.
-
-
New tool makes scanning the Internet for illegal images possible
Researchers have developed a system that makes it possible to scan traffic on the Internet for illegal photographs. The system can, for example, help trace child pornography on the Internet without infringing on the privacy of Internet users. Internet service providers could use the tool to keep their network “clean.”
-
-
Turkey shoots down Syrian military jet

Turkish fighter jets on Sunday shot down a Syrian warplane after it violated Turkey’s airspace. The Syrian military confirmed the incident, saying the plane was downed in Syrian airspace while strafing rebel positions. Syrian state TV described the incident as a “blatant aggression,” and said the pilot safely ejected from the aircraft. In 2012 Turkey changed its rules of engagement after Syria shot down a Turkish military plane, saying that any Syrian military plane approaching the Turkish border would be treated as a legitimate target.
-
More headlines
The long view
Why Was Pacific Northwest Home to So Many Serial Killers?
Ted Bundy, Gary Ridgway, George Russell, Israel Keyes, and Robert Lee Yates were serial killers who grew up in the Pacific Northwest in the shadow of smelters which spewed plumes of lead, arsenic, and cadmium into the air. As a young man, Charles Manson spent ten years at a nearby prison, where lead has seeped into the soil. The idea of a correlation between early exposure to lead and higher crime rates is not new. Fraser doesn’t explicitly support the lead-crime hypothesis, but in a nimble, haunting narrative, she argues that the connections between an unfettered pollution and violent crime warrant scrutiny.
Bookshelf: Smartphones Shape War in Hyperconnected World
The smartphone is helping to shape the conduct and representation of contemporary war. A new book argues that as an operative device, the smartphone is now “being used as a central weapon of war.”
