-
Resources used for biofuel reduce resources available for food production
As strategies for energy security, investment opportunities and energy policies prompt ever-growing production and consumption of biofuels like bioethanol and biodiesel, land, and water that could otherwise be used for food production increasingly are used to produce crops for fuel. A new study shows about a third of the world’s malnourished population could be fed by using resources now used for biofuel production.
-
-
World economy unlikely to stop relying on fossil fuels: Study
On the heels of last year’s historic climate agreement in Paris, a new study concludes that fossil fuel consumption is likely to grow without clear and decisive global action to put an adequate price on carbon dioxide emissions and increased clean energy technology.
-
-
Rapid, affordable energy transformation in U.S. possible
The United States could slash greenhouse gas emissions from power production by up to 78 percent below 1990 levels within fifteen years while meeting increased demand, according to a new study. The study used a sophisticated mathematical model to evaluate future cost, demand, generation, and transmission scenarios. It found that with improvements in transmission infrastructure, weather-driven renewable resources could supply most of the nation’s electricity at costs similar to today’s.
-
-
Breakthrough in continuous monitoring of CO2 leaks from carbon storage sites
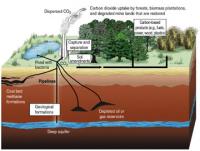
Underground storage of CO2 produced from fossil fuel burning, rather than releasing it into the atmosphere, could play an important role in suppressing climate change. Ensuring that the CO2 does not leak from the storage site is key – but the high number of surveys necessary to make sure there is no CO2 leak makes this a costly endeavor. A team of Japanese researchers may have found a means of achieving easier and lower-cost monitoring for leaks of CO2 stored in underground reservoirs.
-
-
Global learning required to prevent carbon capture, storage from being abandoned
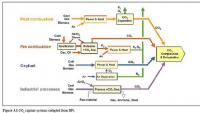
Governments should not be abandoning carbon capture and storage, argues a Cambridge researcher, as it is the only realistic way of dramatically reducing carbon emissions. Instead, they should be investing in global approaches to learn what works – and what doesn’t.
-
-
Toxins found in fracking fluids and wastewater: Study

In an analysis of more than 1,000 chemicals in fluids used in and created by hydraulic fracturing (fracking), researchers found that many of the substances have been linked to reproductive and developmental health problems, and the majority had undetermined toxicity due to insufficient information. The researchers say that further exposure and epidemiological studies are urgently needed to evaluate potential threats to human health from chemicals found in fracking fluids and wastewater created by fracking.
-
-
Gov. Brown declares emergency in wake of massive L.A. natural gas leak
California governor Jerry Brown on Wednesday declared an emergency in a Los Angeles neighborhood where a natural gas well has been spewing record amounts of stinking, global-warming methane gas. Energy experts said the breach at the natural gas storage reservoir, and the subsequent, ongoing release, are the largest known occurrence of its kind.
-
-
Global electricity production vulnerable to climate change, water resource decline
Climate change impacts and associated changes in water resources could lead to reductions in electricity production capacity for more than 60 percent of the power plants worldwide from 2040-2069. A new study calls for a greater focus on adaptation efforts in order to maintain future energy security. Making power plants more efficient and flexible could mitigate much of the decline.
-
-
Making cleaner fuel cells
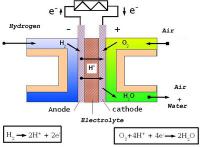
There is a near unanimity in the scientific community that the average temperature on the planet is rising and this is happening because of the increased concentration of carbon dioxide in the atmosphere. Radically redesigning virtually all technological infrastructure is not possible without an acceptable alternative to internal combustion engines: either electric accumulators and electric motors, or fuel cells with electric motors. Fuel cells themselves will not solve the problem of rising temperatures on the planet, but they are part of a possible solution. Researchers have developed ion-exchange synthetic membranes based on amphiphilic compounds that are able to convert the energy of chemical reactions into electrical current.
-
-
Harnessing distributed energy devices to balance the power grid

The electric grid has to balance power supply and demand nearly in real-time, requiring power plants to be adjusted on a second-by-second basis. This instantaneous balance is made significantly more complex by renewable energy such as wind and solar, which add more uncertainty and variability. A new research project is proposing a unique solution to this growing problem: employing the millions of distributed energy resources that already exist, such as solar panels on rooftops and heating and cooling systems in buildings.
-
-
Making the power grid more resilient, flexible
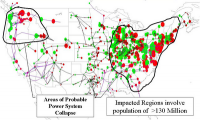
“The biggest and most complex machine ever built by humankind” – this is how one researcher describes the U.S. power grid. A research team has been charged with the formidable task of transforming that big and complex machine from the inside out. Inverters convert DC (direct current) electricity to AC (alternating current) electricity, the kind that forms the basis of today’s power grid. To integrate more inverter-based distributed generation into the grid, the researchers are developing a dynamic distribution system (DDS) that supplements centralized power plants, instead of replacing them.
-
-
Idaho to become U.S. geothermal research hot spot

For all the talk about energy shortages, the fact is the Earth is giant ball of energy that has been producing heat ever since the solar system was formed billions of years ago. The temperature at the core — 6,000 degrees Celsius — is roughly the same as the surface of the sun. All that heat radiates outward through the Earth’s mantle and crust. Less than 1 percent of the electricity in the United States comes from geothermal sources, and energy specialists believe that geothermal power should make a much greater contribution to U.S. electricity. A new consortium plans to pump water into the rock about 8,000 to 12,000 feet deep, fracture the rock and capture heat, then bring heated, pressurized water back to the surface to generate energy.
-
-
“Hydricity”: Using solar energy to produce power round-the-clock

Researchers are proposing a new “hydricity” concept aimed at creating a sustainable economy by not only generating electricity with solar energy, but also producing and storing hydrogen from superheated water for round-the-clock power production.
-
-
Fracking-induced earthquakes increase in magnitude over time
A study by geophysicists shows that earthquakes resulting from fracking-related wastewater injection follow several indicative patterns that are starkly different from natural causes. One of the study’s main conclusions is that the likelihood of large-magnitude manmade, or “induced,” earthquakes in areas where fracking activity takes place, increases over time, independent of the previous seismicity rate. The study’s findings could have implications for both the oil and natural gas industry and for government regulators. Under current practices, extraction activities typically shut down in an area if a high-magnitude earthquake occurs. But according to the researchers, a better approach might be to limit production before a large quake occurs.
-
-
Coal plant plans could make it impossible to hold warming below 2°C

There are 2,440 planned coal plants around the world, totaling 1428GW, which could emit approximately 16-18 percent of the total allowed emissions in 2030 (under a 2°C-compatible scenario, medium range). If all coal plants in the pipeline were to be built, by 2030, emissions from coal power would be 400 percent higher than what is consistent with a 2°C pathway, according to a new analysis.
-
- All
- Regional
- Water
- Biometrics
- Borders/Immig
- Business
- Cybersecurity
- Detection
- Disasters
- Government
- Infrastructure
- International
- Public health
- Public Safety
- Communication interoperabillity
- Emergency services
- Emergency medical services
- Fire
- First response
- IEDs
- Law Enforcement
- Law Enforcement Technology
- Military technology
- Nonlethal weapons
- Nuclear weapons
- Personal protection equipment
- Police
- Notification /alert systems
- Situational awareness
- Weapons systems
- Sci-Tech
- Sector Reports
- Surveillance
- Transportation
Advertising & Marketing: advertise@newswirepubs.com
Editorial: editor@newswirepubs.com
General: info@newswirepubs.com
2010-2011 © News Wire Publications, LLC News Wire Publications, LLC
220 Old Country Road | Suite 200 | Mineola | New York | 11501
Permissions and Policies
Editorial: editor@newswirepubs.com
General: info@newswirepubs.com
2010-2011 © News Wire Publications, LLC News Wire Publications, LLC
220 Old Country Road | Suite 200 | Mineola | New York | 11501
Permissions and Policies
