-
2012-14 California drought the worst in 1,200 years
New research shows that the California drought of 2012-14 has been the worst in 1,200 years. California is the world’s eighth largest economy and the source of a substantial amount of U.S. produce. Surface water supply shortages there have impacts well beyond the state’s borders. The research indicates that natural climate system variability is compounded by human-caused climate change and that “hot” droughts such as the current one are likely to occur again in the future.
-
-
Predicting future droughts in California
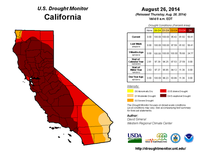
According to a new NOAA-sponsored study, natural oceanic and atmospheric patterns are the primary drivers behind California’s ongoing drought. A high pressure ridge off the West Coast (typical of historic droughts) prevailed for three winters, blocking important wet season storms, with ocean surface temperature patterns making such a ridge much more likely. The study found no conclusive evidence linking human-caused climate change and the California drought.
-
-
CO2 warming effects already felt a decade after being emitted
It takes just ten years for a single emission of carbon dioxide (CO2) to have its maximum warming effects on the Earth. This is according to researchers who have dispelled a common misconception that the main warming effects from a CO2 emission will not be felt for several decades. This means that the benefits from emission reductions — the avoidance of extreme weather events such as droughts, heatwaves, and flooding — will be felt by those who have worked to curb the emissions and not just future generations. Some of the bigger climate impacts from warming, however, such as sea-level rise, melting ice sheets, and long-lasting damage to ecosystems, will have a much bigger time lag.
-
-
Research shows how global warming links to carbon emissions
A team of researchers from the Universities of Liverpool, Southampton, and Bristol have derived the first theoretical equation to demonstrate that global warming is a direct result of the build-up of carbon emissions since the late 1800s, when man-made carbon emissions began. The results are in accord with previous data from climate models. The results show every million-million tons of carbon emitted will generate one degree Celsius of global warming. They also show that the build-up of carbon emitted over the last 200 years will then last for many centuries to millennia even if carbon emissions are subsequently phased out.
-
-
Southeastern Louisiana has a problem: "The sea is rising and the land is sinking"
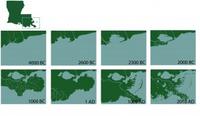
Southeastern Louisiana is drowning at the rate of one football field per hour, totaling up to sixteen square miles annually. In just eighty years, sea level rise, fossil fuel extraction, and having too few wetlands separating the Gulf from the flood protection levee systems have caused some 2,000 square miles of Louisiana’s coastal landscape to sink into the Gulf of Mexico. The issues facing Louisiana’s southeastern coast pose a threat to American energy and economic stability. A $50 billion, 50-year coastal restoration plan, formulated in 2007, is yet to be accepted and funded, but experts note that if sea-level rise is as bad as the worst case scenario, several projects at the heart of the restoration plan would become infective.
-
-
Debate over California’s Salton Sea rescue plan coming to a head
The California State Water Resources Control Board (SWRCB) is currently reviewing a plan to arrest the deterioration of the Salton Sea, a shallow, saline lake which runs along the state’s Imperial and Coachella valleys above the San Andreas Fault. The Salton Sea was inadvertently created by engineers with the California Development Company when they cut off a series of canals in an effort to manage river flooding between 1904 to 1906. It has since been a popular vacation destination.
-
-
A solution to the U.S. water problem: People who use more water, pay more
Approximately one-third of the United States is in at least a moderate state of drought. Exacerbating the drought is a rapidly increasing population. The U.S. Census Bureau estimates the country’s population will balloon from nearly 310 million in 2010 to more than 420 million in 2060. Experts say that current levels of water consumption cannot continue. One expert says that seasonally adjusted increasing block rates could be the answer. In short, people who use more water, pay more.
-
-
Reducing the impact of extreme weather
How do we reduce the impact of extreme weather today while preparing ourselves for future changes? What can we do to build our resilience? A new report from the Royal Society investigates these, and other, key questions to help inform important decisions about adaptation and risk reduction that are being made at global, national and local levels.
-
-
New report highlights “significant and increasing” risks from extreme weather

A comprehensive new report, published by the Royal Society, indicates that exposure of human populations to extreme weather is set to increase as global climate and population size, location, and age continue to change. The report focuses on the risks to people from floods, droughts, and heatwaves. These are some of the most frequent and damaging extreme events that currently occur and their impacts will change with the changing climate. The report also calls for changes to global financial accounting and regulation to ensure that extreme weather risk is made explicit. At present, these risks are not systematically factored into investors’ valuations or assessed by creditors.
-
-
San Francisco to add local groundwater to reservoir supply
The San Francisco Public Utilities Commission has begun digging in the area around Golden Gate Park with the intention of adding local underground water flows to the traditionally sourced water from the Hetch Hetchy Reservoir in Yosemite. The change is expected to take place over the next two years and will replace between 10 to 15 percent of the water supply. Despite the fact that the water is less pure, city officials expect that difference will be negligible.
-
-
Global warming skeptics unmoved by extreme weather
What will it take to convince skeptics of global warming that the phenomenon is real? Surely, many scientists believe, enough droughts, floods, and heat waves will begin to change minds. A new study throws cold water on that theory. Winter 2012 was the fourth warmest winter in the United States dating back to at least 1895. Researchers found, however, that when it came to attributing the abnormally warm weather to global warming, respondents largely held fast to their existing beliefs and were not influenced by actual temperatures. This study and past research shows that political party identification plays a significant role in determining global warming beliefs. People who identify as Republican tend to doubt the existence of global warming, while Democrats generally believe in it.
-
-
Water sector ready for investment, technological innovation

Investors looking for promising growth markets would do well to consider their water bill. Water’s artificially low price in most of the United States is one factor holding back innovative new water technologies, according to the report – but the time is right for change. Across the West, drought has left wide swaths of agricultural land brown, with massive wildfires raging through tinder-dry forests, residential wells tapped out and unemployed farm workers crowding food pantries. The drought is projected to cost the agricultural sector about $2.2 billion in 2014. The social and ecological damage is also profound. Technological innovation in the water sector could bring a raft of benefits ranging from the conservation of scarce water supplies to the expansion of water supplies through technologies that recycle or desalinate, for example.
-
-
Porous molecules bind greenhouse gases
While carbon dioxide presents the biggest greenhouse problem, several other compounds are hundreds or thousands of times more potent in their greenhouse effect per unit of mass. These compounds include Freons, used as common refrigerants, and fluorocarbons, highly stable organic compounds in which one or more hydrogen atoms have been replaced with fluorine. Chemistry researchers have developed a molecule that assembles spontaneously into a lightweight structure with microscopic pores capable of binding large quantities of several potent greenhouse gases.
-
-
Gas can be a “bridge fuel” to a low-carbon future

Major new suggests that gas could play an important role as a “bridging fuel” to a low-carbon economy, but warns that it will not be long before gas becomes part of the problem rather than the solution. The research combines the latest energy system modelling techniques with analysis of U.K. gas security to assess future demand.
-
-
Study ties conflict risk in sub-Saharan Africa to climate change, socioeconomics, geography
A massive new study indicates there is a statistical link between hotter temperatures generated by climate change and the risk of armed conflicts in sub-Saharan Africa. A research team assessed more than 78,000 armed conflicts between 1980 and 2012 in the Sahel region of Africa — a semi-arid belt just south of the Saharan Desert that spans about 3,000 miles and more than a dozen countries from the Atlantic to the Indian oceans. The team was looking for links between armed conflicts and temperature and rainfall anomalies, as well as assessing other causes of violence in the Sahel.
-
- All
- Regional
- Water
- Biometrics
- Borders/Immig
- Business
- Cybersecurity
- Detection
- Disasters
- Government
- Infrastructure
- International
- Public health
- Public Safety
- Communication interoperabillity
- Emergency services
- Emergency medical services
- Fire
- First response
- IEDs
- Law Enforcement
- Law Enforcement Technology
- Military technology
- Nonlethal weapons
- Nuclear weapons
- Personal protection equipment
- Police
- Notification /alert systems
- Situational awareness
- Weapons systems
- Sci-Tech
- Sector Reports
- Surveillance
- Transportation
Advertising & Marketing: advertise@newswirepubs.com
Editorial: editor@newswirepubs.com
General: info@newswirepubs.com
2010-2011 © News Wire Publications, LLC News Wire Publications, LLC
220 Old Country Road | Suite 200 | Mineola | New York | 11501
Permissions and Policies
Editorial: editor@newswirepubs.com
General: info@newswirepubs.com
2010-2011 © News Wire Publications, LLC News Wire Publications, LLC
220 Old Country Road | Suite 200 | Mineola | New York | 11501
Permissions and Policies
