-
Predicting what could happen if Hurricane hits

A Sandia National Laboratories team is gearing up for hurricane season, readying analyses to help people in the eye of a storm. The team has two jobs: conducting annual “hurricane swath” analyses of probable impacts on the Gulf Coast and East Coast, and providing quick analyses of crisis response in the face of an imminent hurricane threat to the United States. A swath analysis looks at how a hurricane might interrupt critical services and at impacts to infrastructure specific to an area, such as petroleum and petrochemical industries in Houston or financial services in New York City. It also looks at such things as the economic impact of the storm or how it could upset food deliveries.
-
-
Dealing with man-made earthquakes
Between 1967 and 2000, central and eastern United States experienced on average 20 earthquakes above a magnitude 3.0 a year. Between 2010 and 2012, the number of earthquakes above a magnitude 3.0 in these regions has dramatically increased to an average of 100 a year. This increase in earthquakes prompts two important questions: Are they natural, or man-made? And what should be done in the future as we address the causes and consequences of these events to reduce associated risks?
-
-
Mother Nature offers best protection for coastal communities’ infrastructure
Extreme weather, sea-level rise, and degraded coastal ecosystems are placing people and property at greater risk of damage from coastal hazards. The likelihood and magnitude of losses can be reduced by intact ecosystems near vulnerable coastal communities. Scientists say that natural habitats such as dunes and reefs are critical to protecting millions of U.S. residents and billions of dollars in property from coastal storms.
-
-
Climate change, severe weather threaten U.S. energy sector: Dept. of Energy
The U.S. entire energy system is vulnerable to increasingly severe and costly weather events driven by climate change, according to a U.S. Department of Energy report published last week. These climate and weather trends — increasing temperatures, decreasing water availability, more intense storm events, and sea level rise — each independently, and in some cases in combination, could restrict the supply of secure, sustainable, and affordable energy critical to U.S. economic growth.
-
-
U.S. power plants use more coal, bucking the trend toward natural gas
Power plants in the United States are burning more coal to produce electricity, bucking the trend toward using natural gas, and in the process emitting more greenhouse gasses into the atmosphere, a new government report says. Burning coal to produce electricity was popular just a few years ago, but hydraulic fracturing led to a natural gas boom, driving down gas prices and making natural gas more competitive with coal. The demand for natural gas got so high, however, that its price began to creep up at the same time that the price of coal dropped because of weakening demand for it.
-
-
Japan to restart nuclear power plants

Japan’s fifty nuclear power plants were taken off-line in the wake of the 2011 Fukushima nuclear disaster, but the government Prime Minister Shinzo Abe, which took office in December, said it was planning to restart Japan’s nuclear power generation program.
-
-
Assessing the social, economic effects of Deepwater Horizon spill
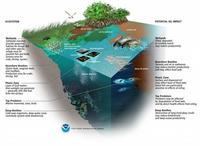
Numerous studies are under way to determine the impacts of the Deepwater Horizon oil spill on the Gulf of Mexico, but the extent and severity of these impacts and the value of the resulting losses cannot fully be measured without considering the goods and services provided by the Gulf, says a new report from the National Research Council (NRC). The report offers an approach that could establish a more comprehensive understanding of the impacts and help inform options for restoration activities.
-
-
Wildfires contribute more to global warming than previously thought
Wildfires produce a witch’s brew of carbon-containing particles. A range of fine carbonaceous particles rising high into the air significantly degrade air quality, damaging human and wildlife health, and interacting with sunlight to affect climate.
-
-
Oil-devouring microbe communities a mile deep in the Gulf
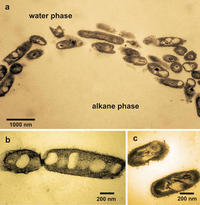
The Deepwater Horizon explosion on 20 April 2010, caused the largest marine oil spill in history, with several million barrels of crude oil released into the Gulf of Mexico over the course of three months. Soon after the spill began, a massive oil slick was visible from orbiting satellites, yet once the underwater gusher was sealed, obvious traces of the crude oil disappeared much sooner than nearly all observers predicted. Some of the oil evaporated; some was skimmed off. Microbes “ate” much of the oil as well.
-
-
Treating oil spills with chemical dispersants may do more damage than good
Treating oil spills at sea with chemical dispersants is detrimental to European fisheries. Post-spill chemical dispersants may reduce problems for surface animals, but the increased contamination under the water reduces the ability for fish and other organisms to cope with subsequent environmental challenges.
-
-
Researchers highlight problem of legacy mercury in the environment
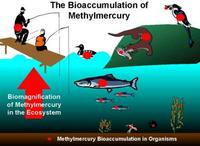
Researchers have published evidence that significant reductions in mercury emissions will be necessary just to stabilize current levels of the toxic element in the environment. So much mercury persists in surface reservoirs (soil, air, and water) from past pollution, going back thousands of years, that it will continue to persist in the ocean and accumulate in fish for decades to centuries, they report.
-
-
U.S. geological carbon dioxide storage potential
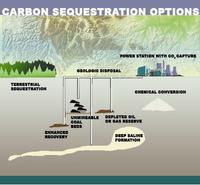
The United States has the potential to store a mean of 3,000 metric gigatons of carbon dioxide (CO2) in geologic basins throughout the country. Technically accessible storage resources are those that can be accessed using today’s technology and pressurization and injection techniques. The most common method of geologic carbon storage involves pressurizing CO2 gas into a liquid, and then injecting it into subsurface rock layers for long-term storage.
-
-
Increasing food production from existing farmland
A policy known as sustainable intensification could help meet the challenges of increasing demands for food from a growing global population. The goal of sustainable intensification is to increase food production from existing farmland. Sustainable intensification would minimize the pressure on the environment in a world in which land, water, and energy are in short supply.
-
-
Research network to search for extraterrestrial intelligence launched in U.K.
A network has been launched to promote academic research in the United Kingdom relating to the search for extraterrestrial intelligence. The network brings together academics from eleven institutions across the country, and it covers a broad spectrum of research topics, including potential methods for detecting signals, the linguistic challenge of deciphering messages, the probability of an extraterrestrial civilization interacting with Earth, and the longevity of civilizations.
-
-
U.S. tax code has minimal effect on CO2, other greenhouse gas emissions
Current federal tax provisions have minimal net effect on greenhouse gas emissions, according to a new report from the National Research Council. The report found that several existing tax subsidies have unexpected effects, and others yield little reduction in greenhouse gas emissions per dollar of revenue loss.
-
- All
- Regional
- Water
- Biometrics
- Borders/Immig
- Business
- Cybersecurity
- Detection
- Disasters
- Government
- Infrastructure
- International
- Public health
- Public Safety
- Communication interoperabillity
- Emergency services
- Emergency medical services
- Fire
- First response
- IEDs
- Law Enforcement
- Law Enforcement Technology
- Military technology
- Nonlethal weapons
- Nuclear weapons
- Personal protection equipment
- Police
- Notification /alert systems
- Situational awareness
- Weapons systems
- Sci-Tech
- Sector Reports
- Surveillance
- Transportation
Advertising & Marketing: advertise@newswirepubs.com
Editorial: editor@newswirepubs.com
General: info@newswirepubs.com
2010-2011 © News Wire Publications, LLC News Wire Publications, LLC
220 Old Country Road | Suite 200 | Mineola | New York | 11501
Permissions and Policies
Editorial: editor@newswirepubs.com
General: info@newswirepubs.com
2010-2011 © News Wire Publications, LLC News Wire Publications, LLC
220 Old Country Road | Suite 200 | Mineola | New York | 11501
Permissions and Policies
