-
U.K. sets to add Hezbollah to terrorist groups list

The United Kingdom will join the United States, Canada, France, and the Arab League in banning all wings of Hezbollah because of its destabilizing influence in the Middle East. Since 2008 there has been a ban on U.K citizens joining the military wing of Hezbollah. The new ban will apply to the organization’s political wing as well.
-
-
Britain’s MI6 chief visited Israel to discuss Iran’s nuclear threat

The chief of Britain’s MI6 intelligence service recently visited Israel to discuss the threat posed by Iran’s nuclear program. Israeli intelligence believes that Iran is “making preparations” to develop nuclear weapons without blatantly violating the 2015 deal. However, the Islamic Republic has not yet made the political decision to break out, according to the Israeli assessment.
-
-
58 former national security officials challenge national emergency declaration
A group of 58 former senior U.S. national security officials will today (Monday) release a statement criticizing President Donald Trump’s for using, without factual justification, a national emergency declaration to fund a wall along the U.S.-Mexico border. “Under no plausible assessment of the evidence is there a national emergency today that entitles the president to tap into funds appropriated for other purposes to build a wall at the southern border,” the group of former senior officials said.
-
-
Deradicalization and countering violent extremism

Since the early 2000s, more than fifty countries have developed initiatives to counter violent extremism (CVE). Despite this, there still remains a lack of strong evidence on which interventions are effective. Researchers have reviewed the literature on CVE programs to give examples of what good CVE practice should look like.
-
-
It’s spy vs. spy vs. spy

“I think what we’re seeing unfolding on the news every day right now is, potentially, the greatest intelligence or espionage scandal in modern history, maybe in history, full stop. The Kremlin has managed to get a candidate who’s very favorable to itself in the White House. It is still slightly hypothetical, because we don’t know the results of the investigation, but the fact that [the FBI] started an investigation at all, and this question had to be asked at all, shows how weird and unprecedented this situation is. If the music stops right now and actually there’s nothing to it, still the fact that we had to ask this question, and it was investigated, is extraordinary,” says Calder Walton, Ernest May Fellow in History and Policy at Harvard Kennedy School (HKS) and editor of the forthcoming 3-volume The Cambridge History of Espionage and Intelligence.
-
-
Doctor-affiliated PACs fund candidates opposing gun safety policies
Researchers found that physician-affiliated political action committees provided more financial support to candidates who opposed increased background checks, contrary to many societies’ recommendations for evidence-based policies to reduce firearm injuries.
-
-
Israel fighting Iran’s efforts to upgrade Hezbollah’s rockets

Israel has been countering Iranian efforts to use suitcases to smuggle GPS components into Syria to upgrade Hezbollah’s rocket arsenal. In 2017, once it appeared that Syrian dictator Bashar al-Assad would survive the civil war that was tearing his country apart, “Iran embarked on a grandiose plan for increasing its influence in the shattered country,” says an expert. Iran’s goal was to “build a force of up to 100,000 Shiite fighters from Pakistan, Afghanistan and Iraq. They built intelligence bases and an air force base within each Syrian airbase. And they brought civilians in order to indoctrinate them,” said Israel Defense Force’s former chief of staff, Gen. Gadi Eisenkot.
-
-
There is no national emergency on the border, Mr. President
President Trump [last week] declared a national emergency on the border to construct some portion of his promised border fence. “We’re talking about an invasion of our country with drugs, with human traffickers, with all types of criminals and gangs,” President Trump said during his remarks. Lawyers will spill much ink arguing about the legalities surrounding the law and whether President Trump can declare a national emergency. Regardless of what the law ultimately means, no reasonable person can look at the southern border and agree that it rises to the level of a national emergency.
-
-
Reducing Illinois gun violence
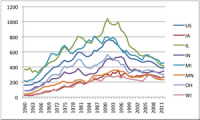
Illinois could reduce the number of people killed each year by gun violence by implementing ten policies supported by available research, according to a new report. The Johns Hopkins report identifies weaknesses or gaps in current Illinois law and offers recommendations to reduce gun violence.
-
-
After Aurora shooting, lawmakers revive proposal to disarm unlawful gun owners
Illinois revokes thousands of gun licenses every year. But it’s rare for law enforcement to remove firearms from owners barred from having them. Legislators in Illinois are scrambling to address a gap in state law that many have blamed for allowing the gunman who killed five people in Aurora last week to keep his handgun even after he was banned from possessing firearms.
-
-
U.S. Coast Guard officer to be charged with mass terrorism plot
Christopher Paul Hasson, a U.S. Coast Guard officer will appear in court today (Thursday), charged with plotting a massive, 2-prong attack modeled after the 2011 Anders Behring Breivik’s terrorist attack in Norway. Breivik killed eight people in Oslo as a diversion, before killing 69 teenagers in a summer camp organized by the Norwegian Social Democratic Party. Hasson compiled a hit list of liberal politicians, Supreme Court judges, and journalists – but his violent plans extended to trying to “establish a white homeland,” and using biological weapons to “kill almost every last person on Earth.”
-
-
U.S. hate groups hit record number last year amid increased violence
American hate groups had a bumper year in 2018 as a surge in black and white nationalist groups lifted their number to a new record high, the Southern Poverty Law Center said in a report issued Wednesday. The increase was driven by growth in both black and white nationalist groups, the SPLC said. The number of white nationalist groups jumped from 100 to 148, while the number of black nationalist groups — typically anti-Semitic, anti-LGBTQ and anti-white — rose from 233 to 264. Some conservative groups have accused the SPLC of unfairly labeling them as “hate groups,” and last month, the Center for Immigration Studies sued the SPLC for “falsely designating” it as a hate group in 2016, saying the SPLC has produced no evidence that the group maligns immigrants as a class.
-
-
Putting data privacy in the hands of users
In today’s world of cloud computing, users of mobile apps and web services store personal data on remote data center servers. Services often aggregate multiple users’ data across servers to gain insights on, say, consumer shopping patterns to help recommend new items to specific users, or may share data with advertisers. Traditionally, however, users haven’t had the power to restrict how their data are processed and shared. New platform acts as a gatekeeper to ensure web services adhere to a user’s custom data restrictions.
-
-
U.S. will not take back Alabama woman who joined Islamic State
The United States claims Hoda Muthana does not have a U.S. passport, and has no right to obtain one. A lawyer for her family argued Muthana does have that right because she was born in New Jersey.
-
-
Seven MPs quit Labour over party’s failure to address anti-Semitism
Seven Labour politicians have quit Britain’s main opposition party over leader Jeremy Corbyn’s failure to tackle anti-Semitism and his approach to Brexit. They will sit as a new, independent group of MPs while planning their next steps in the worst Labour split for nearly 40 years.
-
More headlines
The long view
What Does Netflix’s Drama “Adolescence” Tell Us About Incels and the Manosphere?
While Netflix’s psychological crime drama ‘Adolescence’ is a work of fiction, its themes offer insight into the very real and troubling rise of the incel and manosphere culture online.
A Shining Star in a Contentious Legacy: Could Marty Makary Be the Saving Grace of a Divisive Presidency?
While much of the Trump administration has sparked controversy, the FDA’s consumer-first reforms may be remembered as its brightest legacy. From AI-driven drug reviews to bans on artificial dyes, the FDA’s agenda resonates with the public in ways few Trump-era policies have.
The Center Can Hold — States’ Rights and Local Privilege in a Climate of Federal Overreach
As American institutions weather the storms of executive disruption, legal ambiguity, and polarized governance, we must reexamine what it means for “the center” to hold.
How to Reverse Nation’s Declining Birth Rate
Health experts urge policies that buoy families: lower living costs, affordable childcare, help for older parents who want more kids
Foundation for U.S. Breakthroughs Feels Shakier to Researchers
With each dollar of its grants, the National Institutes of Health —the world’s largest funder of biomedical research —generates, on average, $2.56 worth of economic activity across all 50 states. NIH grants also support more than 400,000 U.S. jobs, and have been a central force in establishing the country’s dominance in medical research. Waves of funding cuts and grant terminations under the second Trump administration are a threat to the U.S. status as driver of scientific progress, and to the nation’s economy.
The True Cost of Abandoning Science
“We now face a choice: to remain at the vanguard of scientific inquiry through sound investment, or to cede our leadership and watch others answer the big questions that have confounded humanity for millennia —and reap the rewards.”
