-
Critics say $265 billion transportation bill insufficient
Transportation advocates criticize the lack of an increase in funding in the Senate’s $265 billion surface transportation bill recently unveiled. Senate leaders said the bill would replace the current transportation funding measure and maintain current funding levels, adjusted for inflation, for the next six years. The proposed bill includes $44 billion annually for road and transit projects, based on a Congressional Budget Office(CBO) estimate of how much funding will be needed to maintain current federal transit programs. The CBC has projected that Department of Transportation’s Highway Trust Fund will run out of money by August 2014 without congressional action.
-
-
Coral reefs offer valuable protection for coastal infrastructure
Growing natural hazards from coastal storms, flooding, and rising sea levels are leading to major investments worldwide in coastal defense structures such as seawalls and breakwaters. A new study shows that coral reefs can provide risk reduction benefits comparable to artificial defenses, and reef restoration and enhancement is a cost-effective alternative to manmade structures. Restoring coral reefs as a way to protect coastal infrastructure is also cheaper: the typical price for a tropical breakwater project is $197 million, compared with $129 million for restoring a reef.
-
-
Cybersecurity bill not likely before a crisis proves its necessity
A recent simulation, with 350 participants from congressional staffs, the cybersecurity sector, and the U.S. military, examined whether or not Congress was capable of passing a comprehensive cybersecurity legislation to protect the country’s critical infrastructure from debilitating cyberattacks. The simulation participants concluded that Congress is not likely to act unless there is a major cyber crisis, and that until such crisis occurs, smaller measures, such as the president’s voluntary cybersecurity framework, are the best that can be hoped for.
-
-
24 U.S. nuclear plants vulnerable to earthquakes
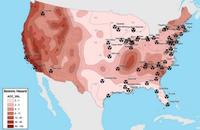
The U.S Nuclear Regulatory Commission (NRC) has concluded that the designs of twenty-four U.S. nuclear plants do not meet contemporary standards to withstand an earthquake in the vicinity of the facility. This analysis has revealed that these facilities could face significant, even disastrous, damage from earthquakes which are larger than what they were designed to encounter.
-
-
Loss of West Antarctic glacier unstoppable, contributing significantly to sea level rise
A rapidly melting section of the West Antarctic Ice Sheet appears to be in irreversible decline, with nothing to stop the entire glacial basin from disappearing into the sea, according to researchers at UC Irvine and NASA. The new study presents multiple lines of evidence — incorporating forty years of observations — that six massive glaciers in the Amundsen Sea sector “have passed the point of no return.” The volume of melted ice would be enough to raise global sea level by four feet.
-
-
Large areas of Plains states now drier than during Dust Bowl

As a result of the drought conditions that have largely remained a constant since 2011, parts of the Texas and Oklahoma panhandles, as well as northeastern New Mexico and southeaster Colorado, are now drier than they were during the infamous Dust Bowl of the 1930s. While experts explain that the possibility of another Dust Bowl is not likely due to modern farming and irrigation techniques which have been enacted as a response in the 1930s, greater erosion due to drought and wind has resulted in a number of vicious dust storms.
-
-
States lack expertise, staff to deal with cyberthreats to utilities
The vulnerability of national electric grids to cyberattacks has caught the attention of federal utility regulators and industry safety groups, but state commissions tasked with regulating local distribution utilities are slow to respond to emerging cybersecurity risks. The annual membership directory of state utility regulators lists hundreds of key staff members of state commissions throughout the country, but not a single staff position had “cybersecurity” in the title.
-
-
Miami “Ground Zero” for risks associated with sea level rise
During a special Senate hearing last month in Miami Beach, Senator Bill Nelson (D-Florida) described Florida as “Ground Zero” for climate change and the threat it poses to coastal communities. Sea level rise is especially worrisome to Floridians because Miami has the most property assets at risk in the world, according to the World Resources Institute(WRI). Miami has $14.7 billion in beach front property. Also, fifteen million out of the state’s twenty million residents live in coastal communities vulnerable to sea level rise.
-
-
Researchers map 198,000 glaciers to improve sea-level rise estimates
An international team of researchers has completed the first mapping of virtually all of the world’s glaciers — including their locations and sizes — allowing for calculations of their volumes and ongoing contributions to global sea rise as the world warms. The team mapped and catalogued some 198,000 glaciers around the world as part of the massive Randolph Glacier Inventory, or RGI, better to understand rising seas over the coming decades as a result of melting glaciers.
-
-
As fracking activity grows in Mexico, so does the number of fracking-induced tremors

Mexico has the fourth largest amount of recoverable shale gas in the world, with 681 trillion cubic feet. As fracking activity has increased in the state of Nuevo Leon, so have the number of tremors. Between January and mid-April, forty-eight tremors, some reaching a magnitude of roughly 4.3, were recorded across the state of Nuevo Leon, compared to two tremors in the same period last year.
-
-
Ice melting in East Antarctica may lead to unstoppable sea-level rise
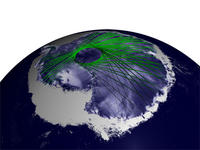
The melting of a rather small ice volume on East Antarctica’s shore could trigger a persistent ice discharge into the ocean, resulting in unstoppable sea-level rise for thousands of years to come, a new study finds. East Antarctica’s Wilkes Basin is like a bottle on a slant, say the study’s authors. Once uncorked, it empties out. The basin is the largest region of marine ice on rocky ground in East Antarctica.
-
-
Switching from cattle fields to “carbon farms” to tackle climate change

Changing cattle fields to forests is a cheap way of tackling climate change and saving species threatened with extinction, a new study has found. The main use of land in communities the western Andes of Colombia is cattle farming, but a new study found farmers could make the same or more money by allowing their land naturally to regenerate. Researchers report that under carbon markets designed to stop global warming, these farmers could get paid to change the use of their land from growing cows to “growing carbon” — receiving around $1.99 per ton of carbon dioxide the trees remove from the atmosphere.
-
-
Russia may launch crippling cyberattacks on U.S. in retaliation for Ukraine sanctions
U.S. officials and security experts are warning that Russian hackers may attack the computer networks of U.S. banks and critical infrastructure firms in retaliation for new sanctions by the Obama administration, imposed in response to Russia’s actions in Ukraine. Cybersecurity specialists consider Russian hackers among the best at infiltrating networks and some say that they have already inserted malicious software on computer systems in the United States.
-
-
Innovative U.S. cybersecurity initiative to address cyberthreats
Cyberattacks on computer networks around the world reached 1.7 billion in 2013, up from 1.6 billion in 2012. The administration’s 2012 Enhanced Cybersecurity Services(ECS) program, launched to protect the private sector from hackers by letting approved companies access classified information on cyber threats and sell cybersecurity services to critical infrastructure targets, is still in its early stages fourteen months after its launch.
-
-
Wetland preservation is good business

A recently published study is making the case for wetland preservation by highlighting the economic incentives that such preservation could provide to urban centers.Infrastructure investment in urban waterfronts could soon be seen as one of the best economic decisions a city could make. The National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration says that “$1 million invested in coastal restoration creates 17.1 jobs, compared to just 8.9 jobs for every $1 million invested in oil and gas development.”
-
- All
- Regional
- Water
- Biometrics
- Borders/Immig
- Business
- Cybersecurity
- Detection
- Disasters
- Government
- Infrastructure
- International
- Public health
- Public Safety
- Communication interoperabillity
- Emergency services
- Emergency medical services
- Fire
- First response
- IEDs
- Law Enforcement
- Law Enforcement Technology
- Military technology
- Nonlethal weapons
- Nuclear weapons
- Personal protection equipment
- Police
- Notification /alert systems
- Situational awareness
- Weapons systems
- Sci-Tech
- Sector Reports
- Surveillance
- Transportation
Advertising & Marketing: advertise@newswirepubs.com
Editorial: editor@newswirepubs.com
General: info@newswirepubs.com
2010-2011 © News Wire Publications, LLC News Wire Publications, LLC
220 Old Country Road | Suite 200 | Mineola | New York | 11501
Permissions and Policies
Editorial: editor@newswirepubs.com
General: info@newswirepubs.com
2010-2011 © News Wire Publications, LLC News Wire Publications, LLC
220 Old Country Road | Suite 200 | Mineola | New York | 11501
Permissions and Policies
