-
Invasion at “Fort Knox of Uranium” raises security concerns

The Y-12 National Security Complex in Oak Ridge, Tennessee, is regarded asthe Fort Knox of Uranium, so the fact that three anti-nuclear activists, one of them an 82-year old nun, were able to breach the high-security complex’s protective fences is not reassuring; that they did so using nothing more than bolt cutters, after announcing their arrival from half-a-mile away, and that they could stay, undetected, in a highly secure area on the nuclear complex’s ground for two hours, is even more worrisome
-
-
Y-12 and operator error
Three anti-nuclear activists, led by an 82-year old nun, breached the perimeter security system of the supposedly highly secure Y-2 nuclear facility at Oak Ridge, Tennessee, where nuclear weapons components are manufactured (note that the Oak Ridge National Laboratory [ONRL] is not affiliated with the Y-12 National Security Complex); they then spent several hours in a secure area of the facility, leisurely spray-painting slogans on the facility’s walls – without the facility’s security staff, or the sophisticated $500 million security cameras and sensors, detecting them; to understand what happened at Y-2, we must accept that operator error is an essential problem in national security, and that the problem is pervasive and normal; the only way to deal with the operator error phenomenon is to build redundancies into the system
-
-
Long Beach Police Department purchases underwater inspection system for port
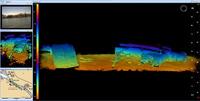
The Port of Long Beach is the second busiest seaport in the United States and is a major gateway for trade with Asia, handling more than six million containers annually; to enhance port security, the City of Long Beach Police Department has purchased an Underwater Inspection System (UIS) from Cod Octopus
-
-
New device dismantles pipe bombs safely, preserving forensic evidence
Thousands of pipe bombs are made each year, and thousands of pipe bomb threats are called into local police and FBI authorities across the country; many are false alarms, but those that are not can be deadly; dismantling a pipe bomb is tricky and serious business, and missteps during the dismantling process can produce catastrophic results
-
-
Drone use spreads to more areas and missions

As security challenges in the United State and around the globe change, many countries have one thing in common: unmanned drones will be a significant part of the future of security; advancements in technology are driving the use of UAVs into newareas
-
-
Geoengineering clouds to slow global warming

Researchers are taking a second look at the possibility of using futuristic ships to shoot salt water high into the sky over the oceans, creating clouds that reflect sunlight and thus counter global warming; The theory behind idea, called “marine cloud brightening,” is that adding particles, in this case sea salt, to the sky over the ocean would form large, long-living clouds
-
-
Greenland melting breaks record four weeks early – with two weeks more to go
Melting over the Greenland ice sheet shattered the seasonal record on 8 August — a full four weeks before the close of the melting season; with more melting yet to come in August, this year’s overall melting will fall way above the old records; researchers devise a “cumulative melting index,” which measures the type of melting which adds to the runoff of melt-water that makes sea levels rise
-
-
Unmanned civilian drones vulnerable to hijacking
Unmanned drones have become the eyes and ears of the military in recent years, giving them an advantage in intelligence gathering and in operations without risking soldiers’ lives; the drones’ versatility and low price have made them an attractive tool for domestic law enforcement and first response missions; there is one glitch, though: drones can be hijacked; if that happens, these swift, unmanned aircrafts could become weapons for terrorists
-
-
New earthquake assessment finds increased risk for Washington Dams
Central Washington state has always been considered low risk for earthquakes back when big hydropower dams went up on the Columbia River many decades ago; a recently completed seismic hazard assessment, however, shows that there is a much greater earthquake potential for the area than previously thought; now, dam owners have to figure out whether their dams can hold up to an earthquake; if retrofits are needed, they could cost hundreds of millions of dollars
-
-
New system could predict solar flares, give advance warning to help protect power grids

Researchers may have discovered a new method to predict solar flares more than a day before they occur, providing advance warning to help protect satellites, power grids, and astronauts from potentially dangerous radiation
-
-
Close to 1,000 earthquakes shook Arizona in 3-year period: study
Historically, most of Arizona has experienced low levels of recorded seismicity, with infrequent moderate and large earthquakes in the state; comprehensive analyses of seismicity within Arizona have not been previously possible due to a lack of seismic stations in most regions, contributing to the perception that widespread earthquakes in Arizona are rare; a new study debunks this myth
-
-
Hurricanes which pass over fresh water can be stronger

About 60 percent of the world’s population resides in areas that are prone to hurricanes or cyclones; researchers find that if a hurricane’s path carries it over large areas of fresh water, it will potentially intensify 50 percent faster than those that do not pass over such regions, meaning it has greater potential to become a stronger storm and be more devastating
-
-
Earthquake risks in Europe

How strong can earthquakes in Germany be? Where in Europe are the earthquake activities concentrated? These questions are the basis for risk assessments and become relevant when it comes to the safety of buildings or the generation of tsunami; a new Earthquake Catalogue for Europe and the Mediterranean, which offers details of 45,000 earthquakes during the last millennium, suggests answers to these questions
-
-
Obama considering executive order for infrastructure protection
President Barack Obama is exploring whether to issue an executive order to protect the U.S. critical computer infrastructure from cyber attacks; White House sources say an executive order is being considered after a 2 August procedural vote in the Senate that all but doomed a scyberecurity bill endorsed by Obama as well as current and former national security officials from both Republican and Democratic administrations
-
-
Climatic impacts of megapolitan expansion
Arizona’s Sun Corridor is the most rapidly-growing megapolitan area in the United States. Nestled in a semi-arid environment, it is composed of four metropolitan areas: Phoenix, Tucson, Prescott, and Nogales. With a population projection expected to exceed 9 million people by 2040; a first study of its kind, attempting to quantify the impact of rapidly expanding megapolitan areas on regional climate, showed that local maximum summertime warming resulting from projected expansion of the urban Sun Corridor could approach 4 degrees Celsius
-
More headlines
The long view
Falling Space Debris: How High Is the Risk I'll Get Hit?
An International Space Station battery fell back to Earth and, luckily, splashed down harmlessly in the Atlantic. Should we have worried? Space debris reenters our atmosphere every week.
Using Drone Swarms to Fight Forest Fires
Forest fires are becoming increasingly catastrophic across the world, accelerated by climate change. Researchers are using multiple swarms of drones to tackle natural disasters like forest fires.
