-
Saltwater intrusion threatens South Florida’s water supplies
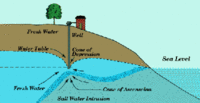
South Florida’s water supply is becoming increasingly endangered by saltwater that is steadily seeping in from the ocean and contaminating supplies; despite the best efforts of local communities to stop the problem, saltwater intrusion is spreading
-
-
Industrial stent-like repairs for failing pipelines
There are thousands of miles of pipe underground in the United States, some more than 100 years old; gas, oil, water, and sewage seep, and sometimes gush, through corroded joints and defective welds every day; new technology uses carbon and glass laminates to repair and replace failing pipelines
-
-
Sea level rise to take economic toll on California coast
California beach towns could face hefty economic losses caused by sea level rise, according to a new state-commissioned study; the study estimates the cost of coastal storm damage and erosion, both of which are expected to increase as sea levels rise
-
-
Safeguarding the Internet of tomorrow
The recommendations of a high-level cybersecurity summit held Belfast include developing self-learning, self aware cyber security technologies, protecting smart utility grids, and enhancing the security of mobile networks. The summit concluded that these are among the top research priorities needed to safeguard the Internet of tomorrow
-
-
Carbon abatement technologies compete for prizes
The U.K. Technology Strategy Board is investing up to £4.5 million in carbon abatement technologies (CATs), centered mainly on innovative projects with strong elements of technology demonstration; to select the technologies, the TSB is holding a competition
-
-
9/11 legacy: more resilient skyscrapers

Following the 9/11 attacks on the Twin Towers in New York, many predicted that the age of the skyscraper was over; there has been no slowdown in skyscraper orders, however — but the skyscrapers being built today are much stronger than the Twin Towers were; new materials, innovative designs, and attention to safety make today’s skyscraper much more resilient to man-made and natural disasters
-
-
Decade after 9/11, infrastructure interdependence a major problem for U.S.
After years of study of the impact on infrastructure of the 9/11 attacks, a groups of experts paints a disconcerting picture of major infrastructure systems that were highly dependent upon one another; even today, these experts see this deep interdependency as a liability and threat to national security and the quality of life for its citizens
-
-
Earthquake prediction, a holy grail of science
Predicting earthquakes has proven to be an elusive pursuit for scientist and the mainstream consensus is that it will never happen, but one group remains hopeful; unlike the majority of geologists, who now believe it is nearly impossible to accurately predict earthquakes, those still searching for solutions tend to work in physics and atmospheric science
-
-
AI helps identify leaky pipes, prevent flooding
Engineers have pioneered new methods for detecting leaky pipes and identifying flood risks with technologies normally used for computer game graphics and Artificial Intelligence; these techniques could help to identify water supply and flooding problems more quickly than ever before
-
-
Microbes clean up nuclear waste -- and generate electricity
Researchers have discovered how microbes generate electricity while cleaning up nuclear waste and other toxic metals; the microbes effectively immobilize the radioactive material and prevent it from leaching into groundwater; the discovery could benefit sites changed forever by nuclear contamination
-
-
Swiss nuclear energy phase-out possible

In the wake of Germany’s decision to abandon nuclear power generation, other countries have also been examining that option; a respected Swiss research center looked into the mater, finding that restructuring the Swiss energy system without nuclear power by 2050 is in principle technologically possible and economically manageable
-
-
Studying the effects of fire on steel structures, nuclear plants
Building fires may reach temperatures of 1,000 degrees Celsius, or more than 1,800 degrees Fahrenheit, and the strength of steel structures drops by about 40 percent when exposed to temperatures exceeding 500 degrees Celsius; scientists study precisely what happens to the connections between a floor’s steel beams and the building columns when these connections are exposed to intense heat
-
-
Cutting soot emissions fastest, cheapest way to slow warming
Reducing soot emissions from diesel engines and other sources could slow melting of sea ice in the Arctic faster and more economically than any other quick fix; the good news is that decreasing soot could have a rapid effect — unlike carbon dioxide, which remains in the atmosphere for years, soot disappears within a few weeks, so that there is no long-term reservoir with a continuing warming effect
-
-
The Geophysicist's Guide to Striking It Rich
Prospecting — the search for valuable reserves such as gold, diamonds, and natural gas — is not just a matter of luck; it is about knowing where to look; now researchers at Tel Aviv University have modernized the hit-or-miss search with advanced technology that scans the earth for signs of lucrative resources that could lurk beneath the surface
-
-
Simple solution for removing arsenic from water

Almost 100 million people in developing countries are exposed to dangerously high levels of arsenic in their drinking water, unable to afford complex purification technology; scientists developed a simple, inexpensive method for removing arsenic based on chopped up pieces of ordinary plastic beverage bottles coated with a nutrient found in many foods and dietary supplements
-
- All
- Regional
- Water
- Biometrics
- Borders/Immig
- Business
- Cybersecurity
- Detection
- Disasters
- Government
- Infrastructure
- International
- Public health
- Public Safety
- Communication interoperabillity
- Emergency services
- Emergency medical services
- Fire
- First response
- IEDs
- Law Enforcement
- Law Enforcement Technology
- Military technology
- Nonlethal weapons
- Nuclear weapons
- Personal protection equipment
- Police
- Notification /alert systems
- Situational awareness
- Weapons systems
- Sci-Tech
- Sector Reports
- Surveillance
- Transportation
Advertising & Marketing: advertise@newswirepubs.com
Editorial: editor@newswirepubs.com
General: info@newswirepubs.com
2010-2011 © News Wire Publications, LLC News Wire Publications, LLC
220 Old Country Road | Suite 200 | Mineola | New York | 11501
Permissions and Policies
Editorial: editor@newswirepubs.com
General: info@newswirepubs.com
2010-2011 © News Wire Publications, LLC News Wire Publications, LLC
220 Old Country Road | Suite 200 | Mineola | New York | 11501
Permissions and Policies
