-
“Hardened” schools are not safe from gun violence

Hardening of schools seems to be a questionable endeavor, given the dearth of evidence regarding effectiveness, says an expert. A comprehensive review of the literature from 2000 to 2018 regarding school firearm violence prevention, found no programs or practices with evidence that they reduced such gun violence.
-
-
How Columbine became a blueprint for school shooters

When twelve students and one teacher were killed in Littleton, Colorado twenty years ago, it not only became what at the time was the worst high school shooting in U.S. history. It also marked when American society was first handed a script for a new form of violence in schools. Since the 1999 tragedy at Columbine High School, we identified six mass shootings and forty active shooter incidents at elementary, middle or high schools in the United States. In twenty – or nearly half – of those forty-six school shootings, the perpetrator purposely used Columbine as a model.
-
-
Knife-crime assault data to help forecast fatal stabbings

Knife crime data from a 12-month period could be used to help forecast the London neighborhoods most likely to suffer a fatal stabbing the following year, according to latest research.
-
-
Studying Perry Mason to combat “innocence fatigue”
Forensic science historian Professor Ian Burney is studying the influence of Erle Stanley Gardner, creator of renowned TV attorney Perry Mason, in a bid to reveal the roots of the fascination with stories about wrongful criminal conviction. Burney hopes the study will help better understand some of the challenges facing today’s worldwide “innocence projects.”
-
-
It is safer to be a cop today than 50 years ago

There is no doubt that policing is a dangerous profession. But is it safer to be a cop today than it was fifty years ago? Yes, according to a study that analyzed police officer deaths (felonious and non-felonious) in the United States from 1970 to 2016.
-
-
Do armed guards prevent school shootings?
The presence of guns in schools is a fact of life for millions of American children. Forty-three percent of public schools had an armed law enforcement officer during the 2015-2016 school year. Does increasing armed school security could reduce deaths from active shootings or deter the attacks in the first place? Experts say the data is not encouraging. Guns have stopped some mass shootings — but not usually in schools.
-
-
Firearm deaths surges in school-age children
Firearm-related deaths in school-age children are increasing at alarming rates in the United States where homicide rates are about 6- to 9-fold higher than those in comparably developed countries. This epidemic poses increasingly major clinical, public health and policy challenges.
-
-
Recaptured Italian former militant Battisti admits 1970s murders

Former communist militant Cesare Battisti has admitted four murders carried out in the 1970s, during Italy’s so-called “Years of Lead,” weeks after being jailed in Italy for the killings that were part of a failed bid to spark a far-left revolution.
-
-
More mass shooting in states with permissive gun laws
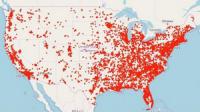
States with more permissive gun laws and greater gun ownership have higher rates of mass shootings, and a growing divide is emerging between states with restrictive versus permissive gun laws. According to a new study, researchers found that in most years permissive states had higher mass shooting rates compared to restrictive states.
-
-
Studying how hate and extremism spread on social media
The ADL and the Network Contagion Research Institute will partner to produce a series of reports that take an in-depth look into how extremism and hate spread on social media – and provide recommendations on how to combat both.
-
-
Combatting human trafficking
Law enforcement organizations across the United States have recently arrested multiple people charged with various crimes that include organizing, operating or paying for services from human trafficking rings. “Human trafficking is not synonymous with human smuggling,” notes one expert.
-
-
White supremacist propaganda and events soared in 2018

White supremacists dramatically stepped up their propaganda efforts targeting neighborhoods and campuses in 2018, far exceeding any previous annual distribution count for the United States and showing how these extremist groups are finding ways to share hateful messages while hiding the identity of individual members.
-
-
European ethno-nationalist and white supremacist movements thrive
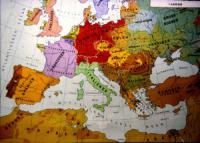
More than seventy years after the defeat of Nazi Germany, ethno-nationalist and white supremacist movements in Europe continue to thrive. They include far-right political parties, neo-Nazi movements, and apolitical protest groups. Some groups openly espouse violent white supremacy, while others have propagated their radical stances under the guise of populism. Though not all of these groups directly link their ideologies to Nazism, their propaganda portrays immigrants and ethnic minorities in a similar manner to how Nazi propaganda portrayed Jews, blaming them for national economic troubles and depicting them as a serious threat to the broader national identity.
-
-
Warrior vs. guardian policing
The pros and cons of policing methods have been heavily debated for decades in the United States. Now, a team of researchers has created a model to measure the differences between two distinct approaches to policing — the warrior approach and the guardian approach.
-
-
Deradicalization and countering violent extremism

Since the early 2000s, more than fifty countries have developed initiatives to counter violent extremism (CVE). Despite this, there still remains a lack of strong evidence on which interventions are effective. Researchers have reviewed the literature on CVE programs to give examples of what good CVE practice should look like.
-
More headlines
The long view
Why Was Pacific Northwest Home to So Many Serial Killers?
Ted Bundy, Gary Ridgway, George Russell, Israel Keyes, and Robert Lee Yates were serial killers who grew up in the Pacific Northwest in the shadow of smelters which spewed plumes of lead, arsenic, and cadmium into the air. As a young man, Charles Manson spent ten years at a nearby prison, where lead has seeped into the soil. The idea of a correlation between early exposure to lead and higher crime rates is not new. Fraser doesn’t explicitly support the lead-crime hypothesis, but in a nimble, haunting narrative, she argues that the connections between an unfettered pollution and violent crime warrant scrutiny.
