-
U.K. to develop laser directed energy weapons
The U.K. Ministry of Defense (MOD) has awarded £30 million contract to produce Laser Directed Energy Weapon (LDEW) Capability Demonstrator to U.K. Dragonfire consortium, led by MBDA. The project will assess innovative LDEW technologies and approaches, culminating in a demonstration of the system in 2019. The contract will assess how the system can pick up and track targets at various ranges and in varied weather conditions over land and water, to allow precision use.
-
-
Israel’s coming chemical weapons crisis
One of the more iconic and sobering elements of Israeli reality were the gas masks distributed on the street or at post offices to every citizen after Saddam Hussein fired SCUD missiles at Israel during the 1991 Gulf War. They continued to be distributed until early 2014, when the Israeli government decided to end the practice in the wake of an international deal to disarm Syria of its chemical weapons stockpiles. Now, nearly three years later, the issue has resurfaced as a direct result of the Syrian civil war—in particular, the threat from both Hezbollah and the Islamic State.
-
-
With proliferation of small arms, absence of war does not equal peace

The proliferation of small arms across many regions of Africa affected by conflict – or adjacent to chronic conflicts – have brought misery, but it has also provided a means for lawless groups to supplement the meagre rewards of nomadic pastoralism through raiding or other forms of violence. Governments in conflict or former conflict zones often have vested interests in maintaining informal armed groups beyond the army and other state security forces — for the entrenchment of political elites, the garnering of rents through armed extortion, or as potential weapons against hostile neighbors. The over-arching problem, according to one researcher, is that “Ending the war is not enough. The issue is to escape the inter-war situation maintained and reproduced by the state.”
-
-
Syrian opposition: Israeli airstrike hit chemical weapons intended for Hezbollah

An Israeli air raid on a depot controlled by the Syrian regime two weeks ago hit a supply of chemical weapons being transferred to the Iran-backed terror group Hezbollah, a spokesperson for a Syrian opposition group said Sunday. Israeli Defense Minister Avigdor Liberman obliquely suggested last week that Israel was responsible for the strike and that the target had been Hezbollah-bound chemical weapons; other Israeli leaders have made it clear in public statements and conversations with foreign leaders that they will act to prevent Hezbollah from acquiring “game-changing” weapons or strengthening its positions on Israel’s borders.
-
-
Israeli defense minister suggests Hezbollah was smuggling chemical weapons
Israel is working hard to keep chemical weapons out of the hands of the Iran-backed terror group Hezbollah, Israeli Defense Minister Avigdor Liberman told a Knesset committee Thursday. His comments to the Knesset seemed to suggest that at least one of the strikes Israel carried out the same day at the Mazzeh military airport near Damascus was in order to stop Hezbollah from acquiring chemical weapons.
-
-
$19 million to develop drugs to treat victims of chemical weapons attacks
First used by the German military against Allied troops in the First World War and in subsequent wars including the Iran-Iraq conflict during the 1980s, chemical weapons were more recently used by the Assad regime in Syria and by ISIS in Iraq and Syria. The National Institutes of Health (NIH) has awarded Rutgers University a five-year grant for more than $19 million for research that would lead to the development of drugs to treat toxicity from chemical agents used in a terrorist attack.
-
-
Swarming robots to help small urban ground units
Urban canyons — with their high vertical structures, tight spaces, and limited lines of sight — constrain military communications, mobility, and tactics in the best of times. These challenges become even more daunting when U.S. forces are in areas they do not control — where they can’t rely on supply chains, infrastructure, and previous knowledge of local conditions and potential threats. to help overcome these challenges and increase the effectiveness of small-unit combat forces operating in urban environments, DARPA has launched its new OFFensive Swarm-Enabled Tactics (OFFSET) program. OFFSET seeks to develop and demonstrate 100+ operationally relevant swarm tactics that could be used by groups of unmanned air and/or ground systems numbering more than 100 robots.
-
-
Purdue launches Institute for Global Security and Defense Innovation
Purdue University president Mitch Daniels announced last Thursday that the university is opening a new Institute for Global Security and Defense Innovation in Discovery Park. In the 2016 fiscal year, the university was awarded more than $50 million for advanced defense-related research projects. The new institute will centralize defense and security research efforts across campus, and, it is hoped, will make Purdue the pre-eminent university in national defense and security. “We can no longer rely on decades of military superiority via so-called technology ‘off-sets,’” said Tomás Díaz de la Rubia, chief scientist and executive director of Purdue’s Discovery Park. “In the future we must out-invent, out-discover, and out-innovate our adversaries every day.”
-
-
Expert: Don’t ignore Iran’s chemical, biological weapons threat while enforcing nuclear deal
While President-elect Donald Trump will likely be stricter in enforcing the terms of the nuclear deal with Iran, the incoming administration should not ignore the threat that Iran’s chemical and biological weapons programs pose, says an expert.
-
-
Israel: Iran is smuggling missile technology to Hezbollah inside commercial flights
Iran is smuggling weapons to the terrorist group Hezbollah inside commercial flights to Lebanon, the Israeli Ambassador to the United Nations has charged in a letter to the UN Security Council. Such actions would violate several Security Council resolutions. The arms were either shipped directly to Hezbollah on commercial flights to Lebanon, or flown to Damascus, Syria, and then shipped to the terror group over land.
-
-
Army issues “Hack the Army” challenge

Army Secretary Eric Fanning announced plans to launch the federal government’s most ambitious “bug bounty” challenge, known as “Hack the Army.” Building off the Army’s previous “Hack the Pentagon” program earlier this year and similar initiatives advanced by private sector companies, the Army will offer cash rewards to hackers who find vulnerabilities in select, public-facing Army Web sites. unlike the Hack the Pentagon program, which offered hackers static Web sites that were not operationally significant as targets, Hack the Army will offer dynamic exchanges of personal identifiable information, sites considered critical to the Army’s recruiting mission.
-
-
Advanced anti-drone protection and neutralization system unveiled
Elbit Systems will use the Israel HLS & Cyber Conference, taking place this week in Tel Aviv, to unveil its ReDrone system, a solution for protection of closed air spaces, national infrastructures, and other critical areas against hostile drones penetrating the protected perimeter. The new system addresses growing global demand for effective – and affordable — airspace protection against hostile drones.
-
-
UN chief alarmed at “weakening taboo” after Syrian chemical weapons attacks
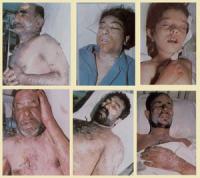
United Nations Secretary-General Ban Ki-Moon expressed his concerned Monday about “the weakening taboo” against chemical weapons attacks, after numerous reports that more such attacks have taken place in Syria in recent weeks. In a letter to the UN Security Council, Ban expressed fears that the use of chemical weapons could become “normalized in this or any conflict, present or future.”
-
-
Shark antibodies for chemical, biological threat detection, treatment
New research shows that shark antibodies offer new alternatives to chemical and biological threat detection and treatment tools. In an era of Department of Defense belt-tightening, the goal is to find more innovative, cost-effective approaches to protecting our warfighters.
-
-
ISIL uses toxic chemicals in its defense of Mosul
In the run up to the U.S.-led coalition campaign to liberate Mosul, U.S. officials warned that ISIS would likely use chemical weapons to slow down the progress of coalition forces and terrorize the residents. Last Thursday ISIS took the first step in its chemical strategy by setting ablaze the Mishraq Chemical plant and sulphur mine, located thirty km south of Mosul. The toxic cloud includes lethal sulphur dioxide and hydrogen sulphide. When combined with residue from burning oil wells, it is deadly for people caught in the open or without gas masks. Military experts say health effects from the toxic fumes from oil and sulphur will likely subside in about eighteen months, but the toxic clouds could harm much of the plant and animal life in the area and make it difficult for local farmers to return to their fields until then.
-
More headlines
The long view
Bookshelf: Smartphones Shape War in Hyperconnected World
The smartphone is helping to shape the conduct and representation of contemporary war. A new book argues that as an operative device, the smartphone is now “being used as a central weapon of war.”
